Basic SAML integration setup
This guide will help you configure your SAML application in Logto. Follow these steps to set up the basic SAML integration.
Application settings
Basic information
- Application name (Required): Enter a name for your SAML application. This name will help you identify the application in Logto.
- Description: Add an optional description to provide more details about your application.
SAML service provider configuration
-
Assertion consumer service URL (Reply URL) (Required): Enter the URL where Logto should send the SAML assertion after successful authentication. This URL should match the ACS URL provided in your Service Provider (SP) application.
-
Service Provider (SP) Entity ID (Required): Enter the unique identifier for your Service Provider. This value should match the Entity ID found in your SP application. The SP Entity ID is a string input that typically follows a URI format (but not necessary).
- Common formats include:
urn:your-domain.com:sp:saml:{serviceProviderId}https://your-domain/saml/{serviceProviderId}
- Common formats include:
SAML IdP metadata
After configuring the basic settings, Logto will provide you with important SAML Identity Provider (IdP) metadata that you'll need to configure in your Service Provider:
IdP metadata URL
Use this URL to configure your SP with the IdP metadata. The metadata contains all necessary information for SAML integration.
Single sign-on service URL
This is the URL where your SP should send SAML authentication requests.
IdP entity ID
The unique identifier for the Identity Provider.
"Single sign-on service URL" and "IdP entity ID" have already been included in IdP metadata, so you don't need to configure it separately if your SP can handle metadata URL.
SAML signing certificate
Logto uses this certificate to sign SAML assertions. You'll need to configure this in your SP to verify the signatures:
- Expires at: The certificate's expiration date
- Fingerprint: The certificate's unique fingerprint for verification
- Status: The current status of the certificate (Active or Inactive)
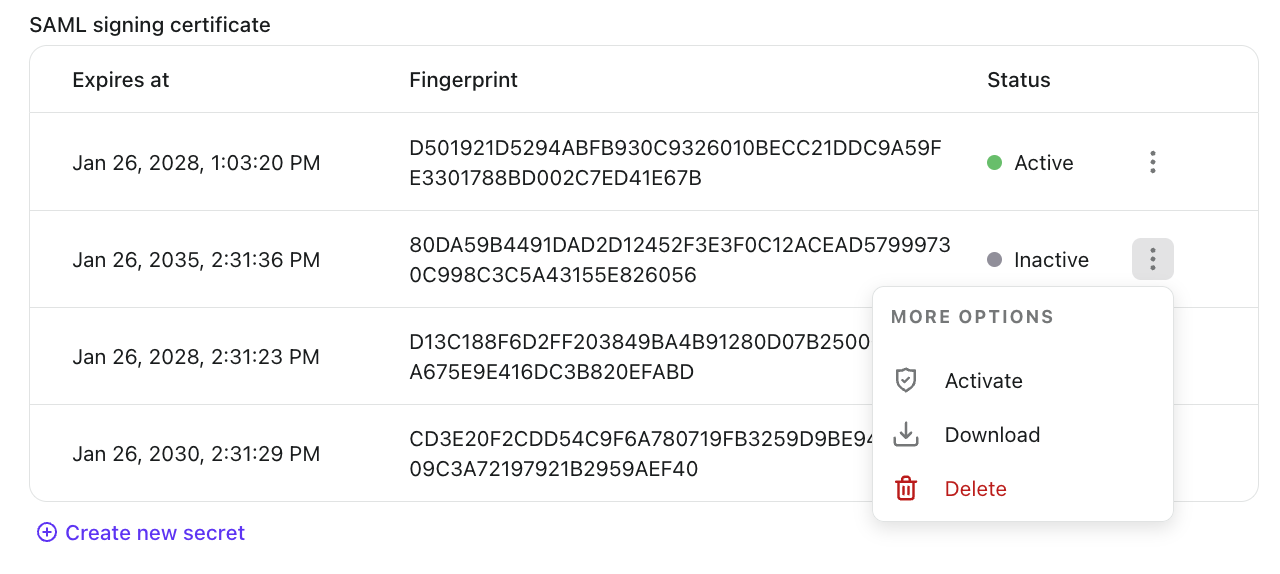
- Only one certificate can be active at a time. The active certificate will be used in the IdP metadata URL.
- The IdP metadata URL will not be available if there is no active certificate.
- You cannot delete an active certificate. To delete a certificate, you must first deactivate it.
- When you activate an inactive certificate, the currently active certificate will be automatically deactivated.
Additional settings
Name ID format
Select how you want the user identifier to be formatted in the SAML assertion. The default is "Persistent" which uses the Logto user ID as the Name ID.
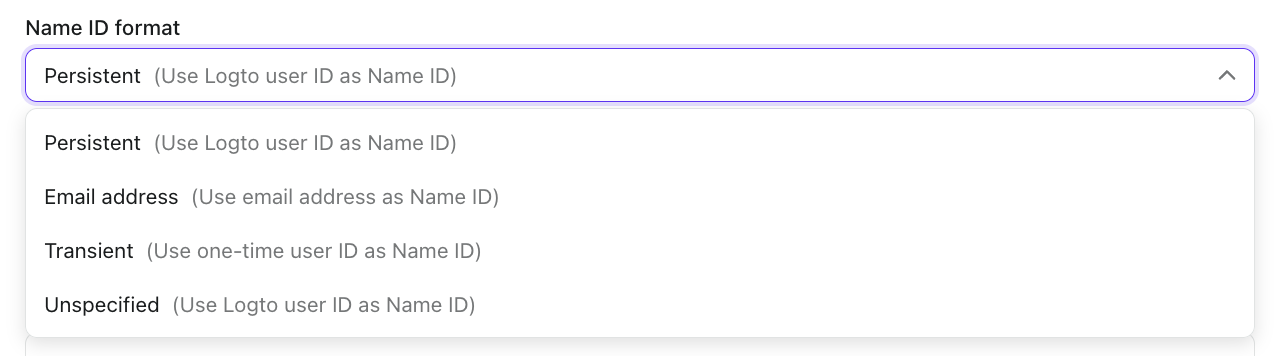
You can find there are four available formats provided by Logto:
-
Persistent (Use Logto user ID as Name ID): Creates a permanent, non-reusable identifier that remains consistent across sessions. This is ideal for maintaining a stable user identity across multiple sign-ins and is recommended for most enterprise applications.
-
Email address (Use email address as Name ID): Uses the user's email address as the identifier. This is useful when your Service Provider relies on email addresses for user identification or when you need human-readable identifiers.
-
Transient (Use one-time user ID as Name ID): Generates a temporary, one-time identifier that changes with each authentication request. This provides enhanced privacy and is suitable for applications where persistent user tracking is not desired.
-
Unspecified (Use Logto user ID as Name ID for now): Similar to Persistent format but indicates that no specific format is required. This offers flexibility while still using the stable Logto user ID as the identifier.
Encrypt SAML assertion
Toggle this option if you want to encrypt the SAML assertion for enhanced security. When enabled, the SAML assertion will be encrypted before being sent to your SP.

When you enable SAML assertion encryption, you must provide your Service Provider's signing certificate. This certificate will be used to encrypt the SAML assertion, ensuring that only your SP can decrypt and read the assertion content.