使用基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 和 JWT 验证保护你的 Vert.x Web API
本指南将帮助你通过 基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 和 Logto 签发的 JSON Web Token (JWT) 实现授权 (Authorization),以保护你的 Vert.x Web API。
开始之前
你的客户端应用需要从 Logto 获取访问令牌 (Access tokens)。如果你还没有完成客户端集成,请查看我们的 快速开始,适用于 React、Vue、Angular 或其他客户端框架,或者参考我们的 机器对机器指南 以实现服务器到服务器的访问。
本指南聚焦于在你的 Vert.x Web 应用中对这些令牌进行服务端验证。
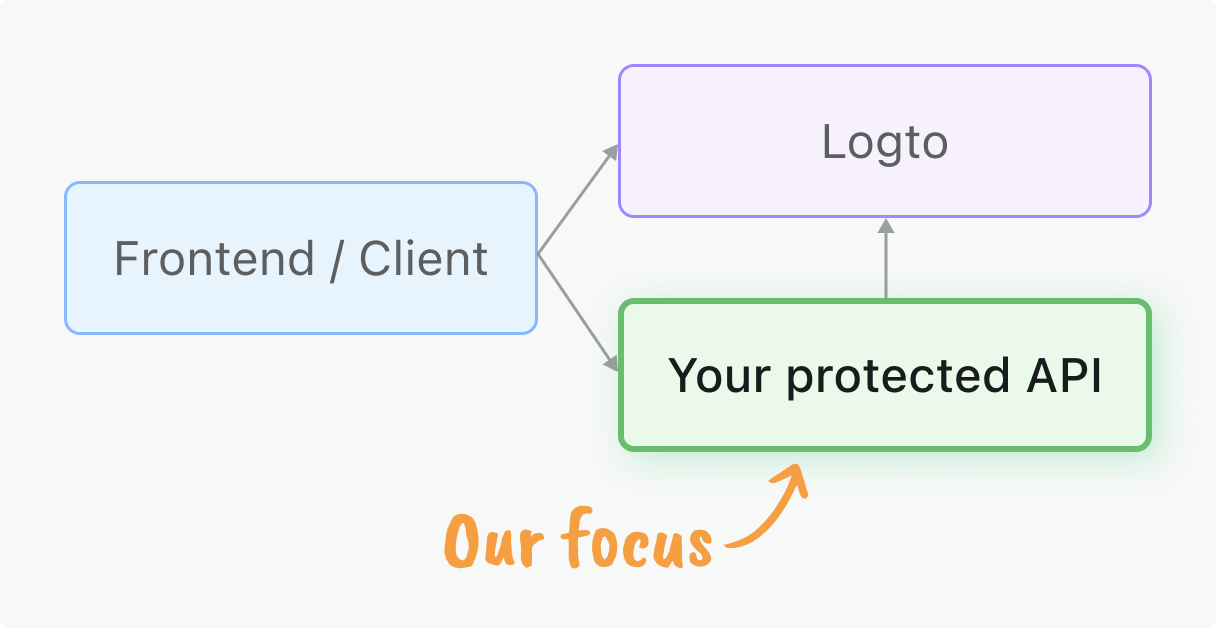
你将学到什么
- JWT 验证:学习如何验证访问令牌 (Access tokens) 并提取认证 (Authentication) 信息
- 中间件实现:创建可复用的中间件以保护 API
- 权限模型:理解并实现不同的授权 (Authorization) 模式:
- 应用级端点的全局 API 资源
- 用于租户特定功能控制的组织权限
- 多租户数据访问的组织级 API 资源
- RBAC 集成:在你的 API 端点中强制执行基于角色的权限 (Permissions) 和权限范围 (Scopes)
前置条件
- 已安装 Java 的最新稳定版本
- 基本了解 Vert.x Web 及 Web API 开发
- 已配置 Logto 应用(如有需要请参见 快速开始)
权限 (Permission) 模型概览
在实施保护之前,请选择适合你应用架构的权限 (Permission) 模型。这与 Logto 的三大授权 (Authorization) 场景保持一致:
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (Organization)(非 API)权限 (Permissions)
- 组织级 API 资源
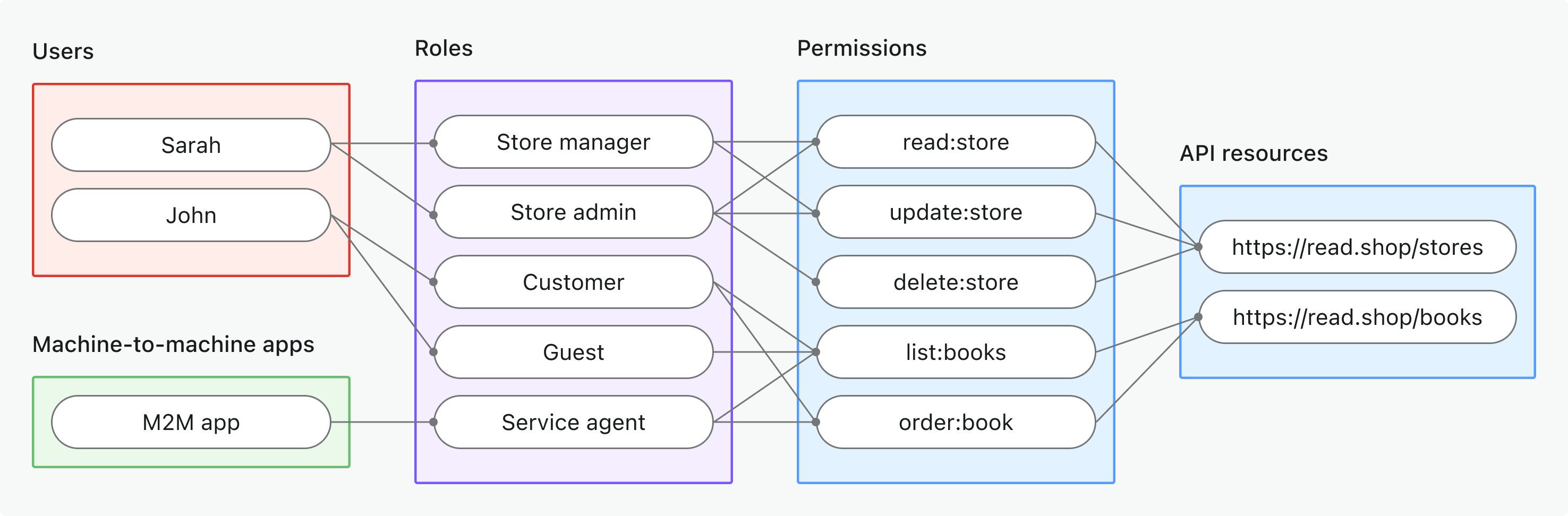
- 使用场景: 保护整个应用共享的 API 资源(非组织 (Organization) 专属)
- 令牌类型: 具有全局受众 (Audience) 的访问令牌 (Access token)
- 示例: 公共 API、核心产品服务、管理端点
- 最适合: 所有客户都使用 API 的 SaaS 产品、无租户隔离的微服务
- 了解更多: 保护全局 API 资源
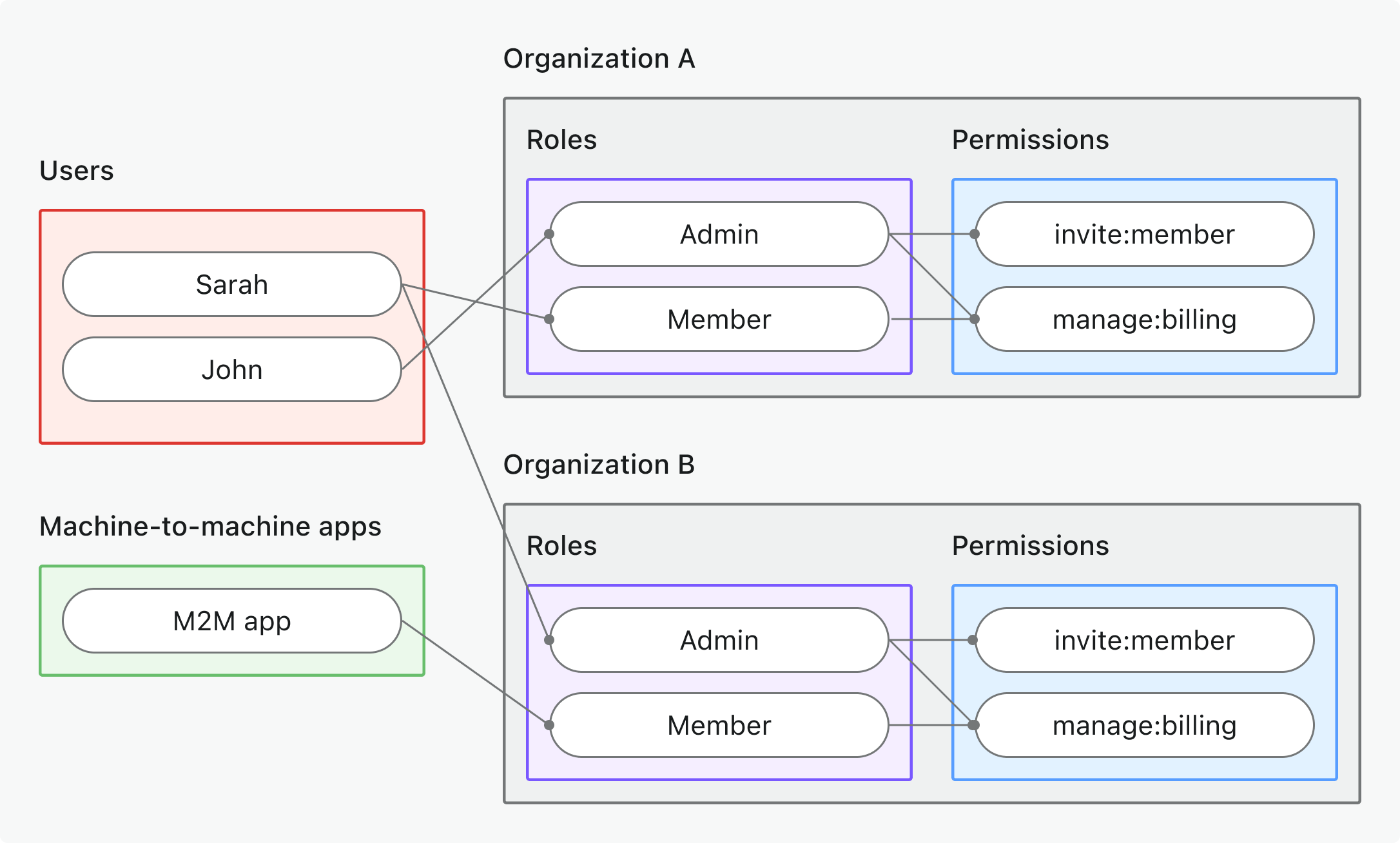
- 使用场景: 控制组织 (Organization) 专属的操作、UI 功能或业务逻辑(非 API)
- 令牌类型: 具有组织 (Organization) 专属受众 (Audience) 的组织令牌 (Organization token)
- 示例: 功能开关、仪表盘权限 (Permissions)、成员邀请控制
- 最适合: 拥有组织 (Organization) 专属功能和工作流的多租户 SaaS
- 了解更多: 保护组织 (Organization)(非 API)权限 (Permissions)
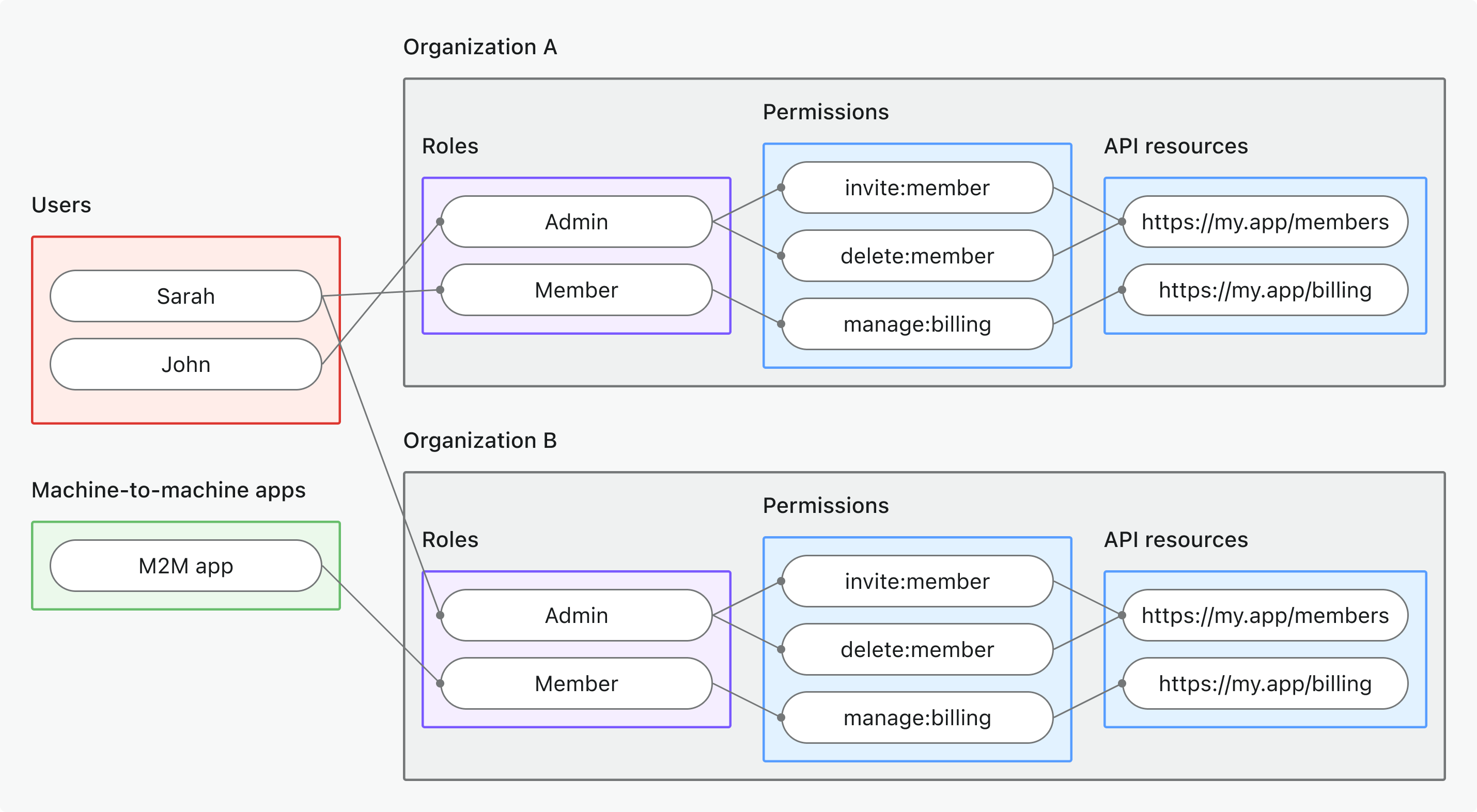
- 使用场景: 保护在特定组织 (Organization) 上下文中可访问的 API 资源
- 令牌类型: 具有 API 资源受众 (Audience) + 组织 (Organization) 上下文的组织令牌 (Organization token)
- 示例: 多租户 API、组织 (Organization) 范围的数据端点、租户专属微服务
- 最适合: API 数据以组织 (Organization) 为范围的多租户 SaaS
- 了解更多: 保护组织级 API 资源
💡 在继续之前选择你的模型 —— 本指南后续内容将以你选择的方式为参考。
快速准备步骤
配置 Logto 资源和权限
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织(非 API)权限
- 组织级 API 资源
- 创建 API 资源:前往 控制台 → API 资源 并注册你的 API(例如,
https://api.yourapp.com) - 定义权限:添加如
read:products、write:orders等权限(Scopes)——参见 定义带权限的 API 资源 - 创建全局角色:前往 控制台 → 角色 并创建包含你的 API 权限的角色——参见 配置全局角色
- 分配角色:将角色分配给需要访问 API 的用户或 M2M 应用程序
- 定义组织权限:在组织模板中创建如
invite:member、manage:billing等非 API 组织权限 - 设置组织角色:在组织模板中配置组织专属角色,并为其分配权限
- 分配组织角色:在每个组织上下文中将用户分配到组织角色
- 创建 API 资源:如上注册你的 API 资源,但它将在组织上下文中使用
- 定义权限:添加如
read:data、write:settings等限定于组织上下文的权限(Scopes) - 配置组织模板:设置包含你的 API 资源权限的组织角色
- 分配组织角色:将用户或 M2M 应用程序分配到包含 API 权限的组织角色
- 多租户设置:确保你的 API 能处理组织范围的数据和校验
从我们的 基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 指南 开始,获取分步设置说明。
更新你的客户端应用
在客户端请求合适的权限(Scopes):
- 用户认证 (Authentication):更新你的应用 → 以请求你的 API 权限和 / 或组织上下文
- 机器对机器:为服务器间访问 配置 M2M 权限(Scopes)→
通常需要在客户端配置中更新以下一项或多项:
- OAuth 流程中的
scope参数 - 用于 API 资源访问的
resource参数 - 用于组织上下文的
organization_id
请确保你测试的用户或 M2M 应用已被分配包含所需 API 权限的合适角色或组织角色。
初始化你的 API 项目
要初始化一个新的 Vert.x Web 项目,你可以手动创建一个 Maven 项目:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>your-api-name</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<vertx.version>4.5.0</vertx.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-auth-jwt</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web-client</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
创建一个基础的 Vert.x Web 服务器:
package com.example;
import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle;
import io.vertx.core.Promise;
import io.vertx.ext.web.Router;
import io.vertx.ext.web.handler.BodyHandler;
public class MainVerticle extends AbstractVerticle {
@Override
public void start(Promise<Void> startPromise) throws Exception {
Router router = Router.router(vertx);
router.route().handler(BodyHandler.create());
router.get("/hello").handler(ctx -> {
ctx.response()
.putHeader("content-type", "text/plain")
.end("Hello from Vert.x Web!");
});
vertx.createHttpServer()
.requestHandler(router)
.listen(3000, http -> {
if (http.succeeded()) {
startPromise.complete();
System.out.println("HTTP server started on port 3000");
} else {
startPromise.fail(http.cause());
}
});
}
}
package com.example;
import io.vertx.core.Vertx;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx();
vertx.deployVerticle(new MainVerticle());
}
}
更多关于如何设置路由、处理器以及其他功能的详细信息,请参考 Vert.x Web 官方文档。
初始化常量和工具方法
在你的代码中定义必要的常量和工具函数,用于处理令牌的提取和校验。一个有效的请求必须包含 Authorization 请求头,格式为 Bearer <访问令牌 (Access token)>。
public class AuthorizationException extends RuntimeException {
private final int statusCode;
public AuthorizationException(String message) {
this(message, 403); // 默认使用 403 Forbidden
}
public AuthorizationException(String message, int statusCode) {
super(message);
this.statusCode = statusCode;
}
public int getStatusCode() {
return statusCode;
}
}
获取你的 Logto 租户信息
你需要以下数值来验证 Logto 签发的令牌:
- JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) URI:Logto 公钥的 URL,用于验证 JWT 签名。
- 发行者 (Issuer):期望的发行者 (Issuer) 值(Logto 的 OIDC URL)。
首先,找到你的 Logto 租户的端点。你可以在多个地方找到它:
- 在 Logto 控制台的 设置 → 域名 下。
- 在你在 Logto 配置的任何应用程序设置中,设置 → 端点与凭证。
从 OpenID Connect 发现端点获取
这些数值可以从 Logto 的 OpenID Connect 发现端点获取:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/.well-known/openid-configuration
以下是一个示例响应(为简洁省略了其他字段):
{
"jwks_uri": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/jwks",
"issuer": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc"
}
在代码中硬编码(不推荐)
由于 Logto 不允许自定义 JWKS URI 或发行者 (Issuer),你可以在代码中硬编码这些数值。但对于生产环境的应用程序,这并不推荐,因为如果将来某些配置发生变化,可能会增加维护成本。
- JWKS URI:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/jwks - 发行者 (Issuer):
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc
校验令牌和权限
在提取令牌并获取 OIDC 配置后,请验证以下内容:
- 签名: JWT 必须有效且由 Logto(通过 JWKS)签名。
- 发行者 (Issuer): 必须与你的 Logto 租户的发行者 (Issuer) 匹配。
- 受众 (Audience): 必须与你在 Logto 中注册的 API 的资源指示器 (resource indicator) 匹配,或在适用时匹配组织 (organization) 上下文。
- 过期时间: 令牌必须未过期。
- 权限 (Scopes): 令牌必须包含你的 API / 操作所需的权限 (scopes)。权限 (scopes) 是
scope声明中的以空格分隔的字符串。 - 组织 (Organization) 上下文: 如果保护的是组织级 API 资源,请验证
organization_id声明。
参见 JSON Web Token 以了解更多关于 JWT 结构和声明 (Claims) 的信息。
针对每种权限 (Permission) 模型需要检查什么
不同的权限 (Permission) 模型,其声明 (Claims) 和验证规则也不同:
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (非 API) 权限
- 组织级 API 资源
- 受众 (Audience) 声明 (
aud): API 资源指示器 (resource indicator) - 组织 (Organization) 声明 (
organization_id): 不存在 - 需要检查的权限 (Scopes) (
scope): API 资源权限 (permissions)
- 受众 (Audience) 声明 (
aud):urn:logto:organization:<id>(组织上下文在aud声明中) - 组织 (Organization) 声明 (
organization_id): 不存在 - 需要检查的权限 (Scopes) (
scope): 组织权限 (permissions)
- 受众 (Audience) 声明 (
aud): API 资源指示器 (resource indicator) - 组织 (Organization) 声明 (
organization_id): 组织 ID(必须与请求匹配) - 需要检查的权限 (Scopes) (
scope): API 资源权限 (permissions)
对于非 API 的组织 (Organization) 权限 (Permissions),组织上下文由 aud 声明表示
(例如,urn:logto:organization:abc123)。organization_id 声明仅在组织级 API 资源令牌中存在。
对于安全的多租户 API,请始终同时验证权限 (scopes) 和上下文(受众 (audience)、组织 (organization))。
添加校验逻辑
我们会根据不同的框架使用不同的 JWT 库。请安装所需的依赖:
在你的 pom.xml 中添加:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-auth-jwt</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
import io.vertx.core.Future;
import io.vertx.core.Handler;
import io.vertx.core.Vertx;
import io.vertx.core.json.JsonArray;
import io.vertx.core.json.JsonObject;
import io.vertx.ext.auth.jwt.JWTAuth;
import io.vertx.ext.auth.jwt.JWTAuthOptions;
import io.vertx.ext.web.RoutingContext;
import io.vertx.ext.web.client.WebClient;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JwtAuthHandler implements Handler<RoutingContext> {
private final JWTAuth jwtAuth;
private final WebClient webClient;
private final String expectedIssuer;
private final String jwksUri;
public JwtAuthHandler(Vertx vertx) {
this.webClient = WebClient.create(vertx);
this.jwtAuth = JWTAuth.create(vertx, new JWTAuthOptions());
// 记得在你的部署环境中设置这些环境变量
this.expectedIssuer = System.getenv("JWT_ISSUER");
this.jwksUri = System.getenv("JWKS_URI");
// 获取 JWKS 并配置 JWT 认证 (Authentication)
fetchJWKS().onSuccess(jwks -> {
// 配置 JWKS(简化版——你可能需要一个更完善的 JWKS 解析器)
});
}
@Override
public void handle(RoutingContext context) {
String authHeader = context.request().getHeader("Authorization");
if (authHeader == null || !authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(401)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"Authorization header missing or invalid\"}");
return;
}
String token = authHeader.substring(7);
jwtAuth.authenticate(new JsonObject().put("jwt", token))
.onSuccess(user -> {
try {
JsonObject principal = user.principal();
verifyPayload(principal);
context.put("auth", principal);
context.next();
} catch (AuthorizationException e) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(e.getStatusCode()) // 使用异常的状态码
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"" + e.getMessage() + "\"}");
} catch (Exception e) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(401)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"Invalid token\"}");
}
})
.onFailure(err -> {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(401)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"Invalid token: " + err.getMessage() + "\"}");
});
}
private Future<JsonObject> fetchJWKS() {
return webClient.getAbs(this.jwksUri)
.send()
.map(response -> response.bodyAsJsonObject());
}
private void verifyPayload(JsonObject principal) {
// 在 Vert.x 中手动验证发行者 (Issuer)
String issuer = principal.getString("iss");
if (issuer == null || !expectedIssuer.equals(issuer)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Invalid issuer: " + issuer);
}
// 在这里根据权限 (Permission) 模型实现你的额外验证逻辑
// 可使用下面的辅助方法提取声明 (Claim)
}
// Vert.x JWT 的辅助方法
private List<String> extractAudiences(JsonObject principal) {
JsonArray audiences = principal.getJsonArray("aud");
if (audiences != null) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Object aud : audiences) {
result.add(aud.toString());
}
return result;
}
return List.of();
}
private String extractScopes(JsonObject principal) {
return principal.getString("scope");
}
private String extractOrganizationId(JsonObject principal) {
return principal.getString("organization_id");
}
}
根据你的权限 (Permission) 模型,实现相应的验证逻辑:
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (Organization)(非 API)权限 (Permissions)
- 组织级 API 资源
// 检查 audience (受众) 声明是否与你的 API 资源指示器匹配
List<String> audiences = extractAudiences(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
if (!audiences.contains("https://your-api-resource-indicator")) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Invalid audience");
}
// 检查全局 API 资源所需的权限 (Scopes)
List<String> requiredScopes = Arrays.asList("api:read", "api:write"); // 替换为你实际需要的权限 (Scopes)
String scopes = extractScopes(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
List<String> tokenScopes = scopes != null ? Arrays.asList(scopes.split(" ")) : List.of();
if (!tokenScopes.containsAll(requiredScopes)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Insufficient scope");
}
// 检查 audience (受众) 声明是否为组织 (Organization) 格式
List<String> audiences = extractAudiences(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
boolean hasOrgAudience = audiences.stream()
.anyMatch(aud -> aud.startsWith("urn:logto:organization:"));
if (!hasOrgAudience) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Invalid audience for organization permissions");
}
// 检查组织 (Organization) ID 是否与上下文匹配(你可能需要从请求上下文中提取)
String expectedOrgId = "your-organization-id"; // 从请求上下文中提取
String expectedAud = "urn:logto:organization:" + expectedOrgId;
if (!audiences.contains(expectedAud)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Organization ID mismatch");
}
// 检查所需的组织 (Organization) 权限 (Scopes)
List<String> requiredScopes = Arrays.asList("invite:users", "manage:settings"); // 替换为你实际需要的权限 (Scopes)
String scopes = extractScopes(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
List<String> tokenScopes = scopes != null ? Arrays.asList(scopes.split(" ")) : List.of();
if (!tokenScopes.containsAll(requiredScopes)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Insufficient organization scope");
}
// 检查 audience (受众) 声明是否与你的 API 资源指示器匹配
List<String> audiences = extractAudiences(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
if (!audiences.contains("https://your-api-resource-indicator")) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Invalid audience for organization-level API resources");
}
// 检查组织 (Organization) ID 是否与上下文匹配(你可能需要从请求上下文中提取)
String expectedOrgId = "your-organization-id"; // 从请求上下文中提取
String orgId = extractOrganizationId(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
if (!expectedOrgId.equals(orgId)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Organization ID mismatch");
}
// 检查组织级 API 资源所需的权限 (Scopes)
List<String> requiredScopes = Arrays.asList("api:read", "api:write"); // 替换为你实际需要的权限 (Scopes)
String scopes = extractScopes(token); // 框架相关的提取方式
List<String> tokenScopes = scopes != null ? Arrays.asList(scopes.split(" ")) : List.of();
if (!tokenScopes.containsAll(requiredScopes)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Insufficient organization-level API scopes");
}
用于提取声明 (Claims) 的辅助方法是框架相关的。具体实现细节请参见上方各框架的验证文件。
将中间件应用到你的 API
现在,将中间件应用到你的受保护 API 路由。
import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle;
import io.vertx.core.Promise;
import io.vertx.core.json.JsonObject;
import io.vertx.ext.web.Router;
import io.vertx.ext.web.RoutingContext;
public class MainVerticle extends AbstractVerticle {
@Override
public void start(Promise<Void> startPromise) throws Exception {
Router router = Router.router(vertx);
// 对受保护路由应用中间件
router.route("/api/protected*").handler(new JwtAuthHandler(vertx));
router.get("/api/protected").handler(this::protectedEndpoint);
vertx.createHttpServer()
.requestHandler(router)
.listen(8080, result -> {
if (result.succeeded()) {
startPromise.complete();
} else {
startPromise.fail(result.cause());
}
});
}
private void protectedEndpoint(RoutingContext context) {
// 直接从 context 获取 JWT 主体
JsonObject principal = context.get("auth");
if (principal == null) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(500)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"未找到 JWT 主体 (principal not found)\"}");
return;
}
String scopes = principal.getString("scope");
JsonObject response = new JsonObject()
.put("sub", principal.getString("sub"))
.put("client_id", principal.getString("client_id"))
.put("organization_id", principal.getString("organization_id"))
.put("scopes", scopes != null ? scopes.split(" ") : new String[0])
.put("audience", principal.getJsonArray("aud"));
context.response()
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end(response.encode());
}
}
测试你的受保护 API
获取访问令牌 (Access tokens)
从你的客户端应用程序获取: 如果你已经完成了客户端集成,你的应用可以自动获取令牌。提取访问令牌 (Access token),并在 API 请求中使用它。
使用 curl / Postman 进行测试:
-
用户令牌: 使用你的客户端应用的开发者工具,从 localStorage 或网络面板复制访问令牌 (Access token)
-
机器对机器令牌: 使用客户端凭证流。以下是一个使用 curl 的非规范示例:
curl -X POST https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/token \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "grant_type=client_credentials" \
-d "client_id=your-m2m-client-id" \
-d "client_secret=your-m2m-client-secret" \
-d "resource=https://your-api-resource-indicator" \
-d "scope=api:read api:write"你可能需要根据你的 API 资源和权限调整
resource和scope参数;如果你的 API 是组织范围的,还可能需要organization_id参数。
需要查看令牌内容?使用我们的 JWT 解码器 来解码和验证你的 JWT。
测试受保护的端点
有效令牌请求
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
预期响应:
{
"auth": {
"sub": "user123",
"clientId": "app456",
"organizationId": "org789",
"scopes": ["api:read", "api:write"],
"audience": ["https://your-api-resource-indicator"]
}
}
缺少令牌
curl http://localhost:3000/api/protected
预期响应 (401):
{
"error": "Authorization header is missing"
}
无效令牌
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer invalid-token" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
预期响应 (401):
{
"error": "Invalid token"
}
权限模型相关测试
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (非 API) 权限
- 组织级 API 资源
针对受全局权限保护的 API 的测试场景:
- 有效权限 (Scopes): 使用包含所需 API 权限(如
api:read、api:write)的令牌进行测试 - 缺少权限 (Scopes): 当令牌缺少所需权限时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 受众 (Audience) 错误: 当受众与 API 资源不匹配时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
# 缺少权限的令牌 - 预期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-without-required-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
针对组织特定访问控制的测试场景:
- 有效组织令牌 (Organization token): 使用包含正确组织上下文(组织 ID 和权限)的令牌进行测试
- 缺少权限 (Scopes): 当用户没有请求操作的权限时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 组织错误: 当受众与组织上下文(
urn:logto:organization:<organization_id>)不匹配时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
# 错误组织的令牌 - 预期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-for-different-organization" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
结合 API 资源验证与组织上下文的测试场景:
- 有效组织 + API 权限: 使用同时包含组织上下文和所需 API 权限的令牌进行测试
- 缺少 API 权限: 当组织令牌缺少所需 API 权限时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 组织错误: 使用来自不同组织的令牌访问 API 时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 受众 (Audience) 错误: 当受众与组织级 API 资源不匹配时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
# 组织令牌缺少 API 权限 - 预期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer organization-token-without-api-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
延伸阅读
RBAC 实践:为你的应用实现安全授权 (Authorization)
构建多租户 SaaS 应用:从设计到实现的完整指南