ปกป้อง Vert.x Web API ของคุณด้วยการควบคุมการเข้าถึงตามบทบาท (RBAC) และการตรวจสอบ JWT
คู่มือนี้จะช่วยให้คุณนำการอนุญาต (Authorization) ไปใช้เพื่อรักษาความปลอดภัยให้กับ Vert.x Web API ของคุณ โดยใช้ การควบคุมการเข้าถึงตามบทบาท (RBAC) และ JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) ที่ออกโดย Logto
ก่อนเริ่มต้น
แอปพลิเคชันไคลเอนต์ของคุณจำเป็นต้องขอรับโทเค็นการเข้าถึง (Access tokens) จาก Logto หากคุณยังไม่ได้ตั้งค่าการเชื่อมต่อกับไคลเอนต์ โปรดดู เริ่มต้นอย่างรวดเร็ว สำหรับ React, Vue, Angular หรือเฟรมเวิร์กฝั่งไคลเอนต์อื่น ๆ หรือดู คู่มือเครื่องต่อเครื่อง สำหรับการเข้าถึงแบบเซิร์ฟเวอร์ต่อเซิร์ฟเวอร์
คู่มือนี้เน้นที่ การตรวจสอบโทเค็นฝั่งเซิร์ฟเวอร์ ในแอป Vert.x Web ของคุณ
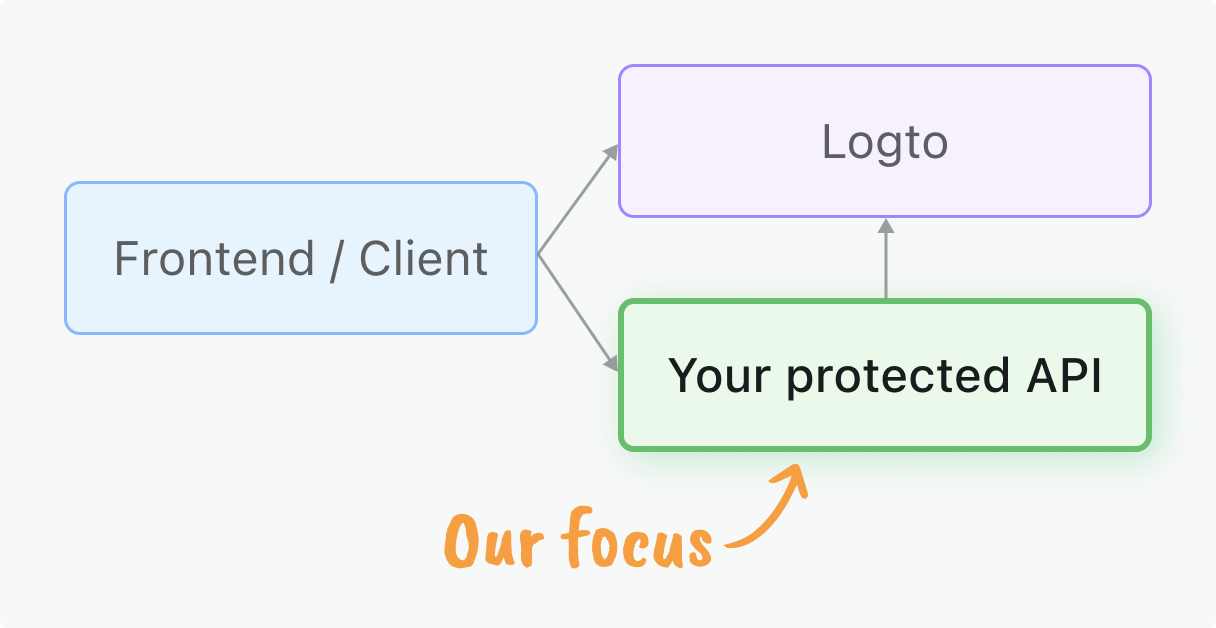
สิ่งที่คุณจะได้เรียนรู้
- การตรวจสอบ JWT: เรียนรู้วิธีตรวจสอบโทเค็นการเข้าถึง (Access tokens) และดึงข้อมูลการยืนยันตัวตน (Authentication)
- การสร้าง Middleware: สร้าง middleware ที่นำกลับมาใช้ซ้ำได้สำหรับการปกป้อง API
- โมเดลสิทธิ์ (Permission models): เข้าใจและนำรูปแบบการอนุญาต (Authorization) ที่แตกต่างกันไปใช้:
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอลสำหรับ endpoint ทั่วทั้งแอปพลิเคชัน
- สิทธิ์ขององค์กรสำหรับควบคุมฟีเจอร์เฉพาะผู้เช่า (tenant)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กรสำหรับการเข้าถึงข้อมูลแบบหลายผู้เช่า (multi-tenant)
- การผสาน RBAC: บังคับใช้สิทธิ์และขอบเขต (Scopes) ตามบทบาท (RBAC) ใน endpoint ของ API ของคุณ
ข้อกำหนดเบื้องต้น
- ติดตั้ง Java เวอร์ชันเสถียรล่าสุด
- มีความเข้าใจพื้นฐานเกี่ยวกับ Vert.x Web และการพัฒนาเว็บ API
- ตั้งค่าแอป Logto เรียบร้อยแล้ว (ดู เริ่มต้นอย่างรวดเร็ว หากยังไม่ได้ตั้งค่า)
ภาพรวมของโมเดลสิทธิ์ (Permission models overview)
ก่อนดำเนินการปกป้องทรัพยากร ให้เลือกโมเดลสิทธิ์ที่เหมาะสมกับสถาปัตยกรรมแอปพลิเคชันของคุณ ซึ่งสอดคล้องกับ สถานการณ์การอนุญาต (authorization scenarios) หลักสามแบบของ Logto:
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล (Global API resources)
- สิทธิ์ขององค์กร (ไม่ใช่ API) (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร (Organization-level API resources)
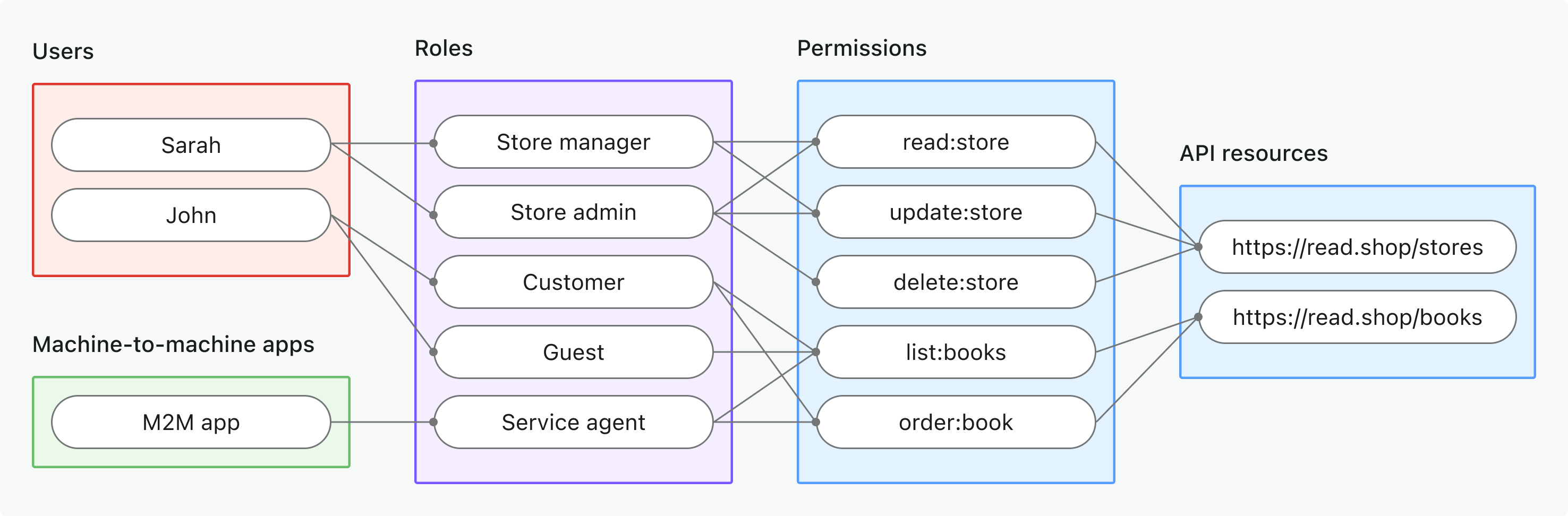
- กรณีการใช้งาน: ปกป้องทรัพยากร API ที่ใช้ร่วมกันทั่วทั้งแอปพลิเคชัน (ไม่เฉพาะองค์กร)
- ประเภทโทเค็น: โทเค็นการเข้าถึง (Access token) ที่มีผู้รับ (audience) ระดับโกลบอล
- ตัวอย่าง: Public APIs, บริการหลักของผลิตภัณฑ์, จุดเชื่อมต่อสำหรับผู้ดูแลระบบ
- เหมาะสำหรับ: ผลิตภัณฑ์ SaaS ที่มี API ใช้ร่วมกันโดยลูกค้าทุกคน, microservices ที่ไม่มีการแยก tenant
- เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม: ปกป้องทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล
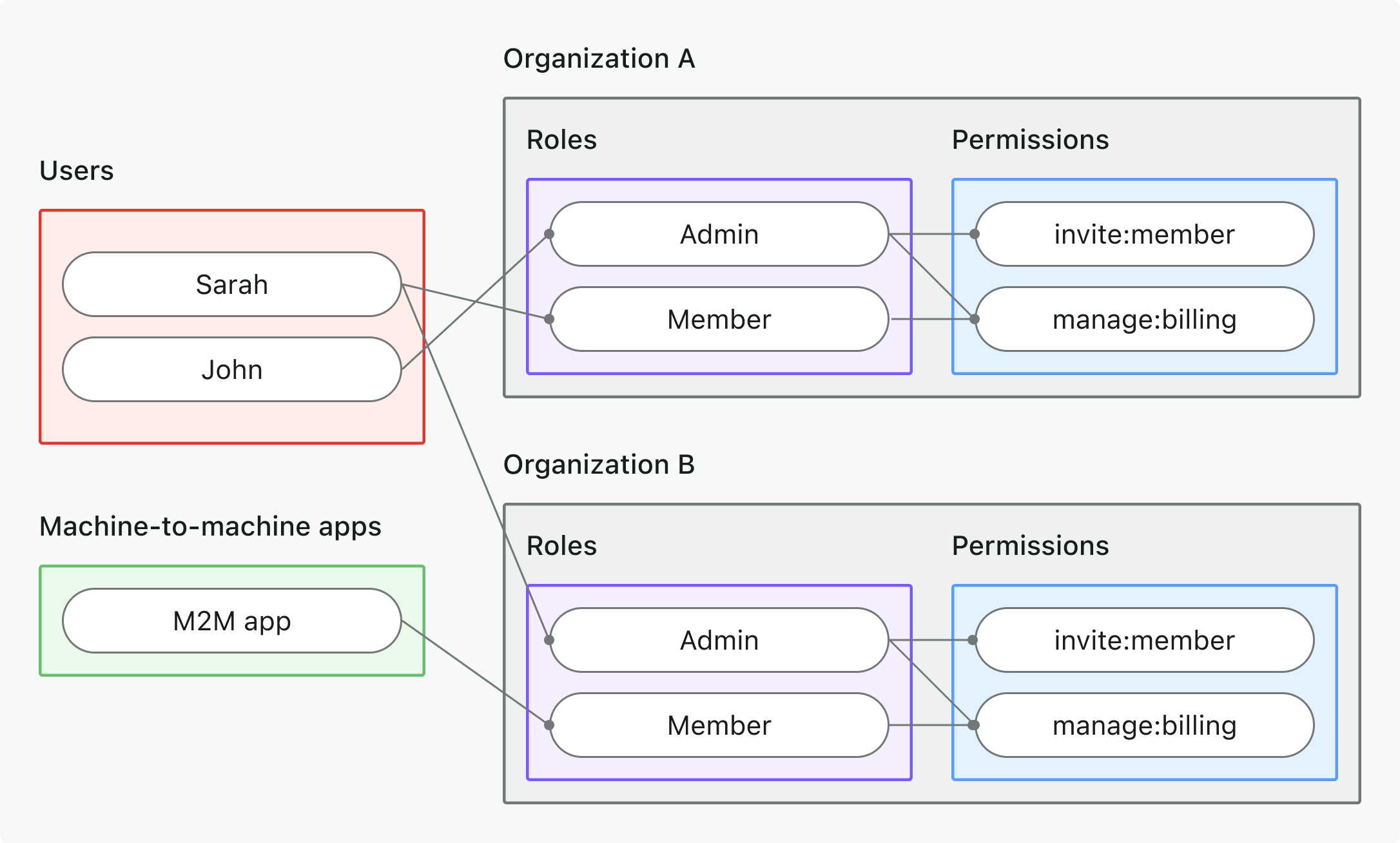
- กรณีการใช้งาน: ควบคุมการกระทำเฉพาะองค์กร, ฟีเจอร์ UI, หรือ business logic (ไม่ใช่ API)
- ประเภทโทเค็น: โทเค็นองค์กร (Organization token) ที่มีผู้รับ (audience) เฉพาะองค์กร
- ตัวอย่าง: การจำกัดฟีเจอร์, สิทธิ์แดชบอร์ด, การควบคุมการเชิญสมาชิก
- เหมาะสำหรับ: SaaS หลายผู้เช่า (multi-tenant) ที่มีฟีเจอร์และเวิร์กโฟลว์เฉพาะองค์กร
- เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม: ปกป้องสิทธิ์ขององค์กร (ไม่ใช่ API)
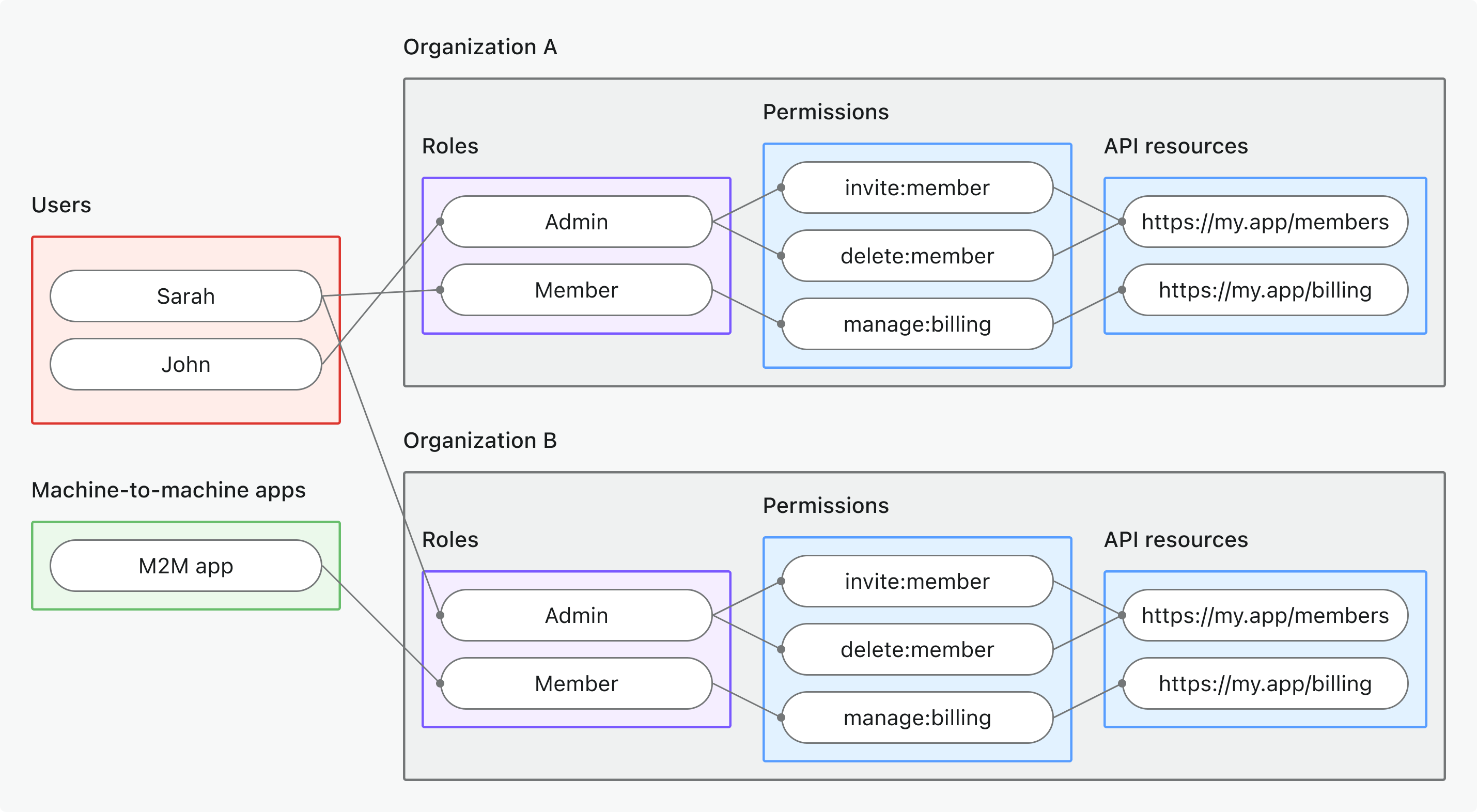
- กรณีการใช้งาน: ปกป้องทรัพยากร API ที่เข้าถึงได้ในบริบทขององค์กรเฉพาะ
- ประเภทโทเค็น: โทเค็นองค์กร (Organization token) ที่มีผู้รับเป็นทรัพยากร API + บริบทองค์กร
- ตัวอย่าง: API หลายผู้เช่า, จุดเชื่อมต่อข้อมูลที่จำกัดขอบเขตองค์กร, microservices เฉพาะ tenant
- เหมาะสำหรับ: SaaS หลายผู้เช่าที่ข้อมูล API ถูกจำกัดขอบเขตองค์กร
- เรียนรู้เพิ่มเติม: ปกป้องทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร
💡 เลือกโมเดลของคุณก่อนดำเนินการต่อ - การนำไปใช้จะอ้างอิงแนวทางที่คุณเลือกตลอดคู่มือนี้
ขั้นตอนเตรียมความพร้อมอย่างรวดเร็ว
กำหนดค่าทรัพยากรและสิทธิ์ของ Logto
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล
- สิทธิ์ขององค์กร (ไม่ใช่ API)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร
- สร้างทรัพยากร API: ไปที่ Console → ทรัพยากร API และลงทะเบียน API ของคุณ (เช่น
https://api.yourapp.com) - กำหนดสิทธิ์: เพิ่มขอบเขต (scopes) เช่น
read:products,write:orders– ดู กำหนดทรัพยากร API พร้อมสิทธิ์ - สร้างบทบาทระดับโกลบอล: ไปที่ Console → บทบาท และสร้างบทบาทที่รวมสิทธิ์ API ของคุณ – ดู กำหนดค่าบทบาทระดับโกลบอล
- กำหนดบทบาท: กำหนดบทบาทให้กับผู้ใช้หรือแอป M2M ที่ต้องการเข้าถึง API
- กำหนดสิทธิ์ขององค์กร: สร้างสิทธิ์ขององค์กรที่ไม่ใช่ API เช่น
invite:member,manage:billingในเทมเพลตขององค์กร - ตั้งค่าบทบาทขององค์กร: กำหนดค่าเทมเพลตขององค์กรด้วยบทบาทเฉพาะองค์กรและกำหนดสิทธิ์ให้กับบทบาทเหล่านั้น
- กำหนดบทบาทขององค์กร: กำหนดผู้ใช้ให้กับบทบาทขององค์กรในแต่ละบริบทขององค์กร
- สร้างทรัพยากร API: ลงทะเบียนทรัพยากร API ของคุณเช่นเดียวกับข้างต้น แต่จะใช้ในบริบทขององค์กร
- กำหนดสิทธิ์: เพิ่มขอบเขต (scopes) เช่น
read:data,write:settingsที่จำกัดในบริบทขององค์กร - กำหนดค่าเทมเพลตขององค์กร: ตั้งค่าบทบาทขององค์กรที่รวมสิทธิ์ของทรัพยากร API ของคุณ
- กำหนดบทบาทขององค์กร: กำหนดผู้ใช้หรือแอป M2M ให้กับบทบาทขององค์กรที่รวมสิทธิ์ API
- ตั้งค่าหลายผู้เช่า: ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่า API ของคุณสามารถจัดการข้อมูลและการตรวจสอบที่จำกัดในแต่ละองค์กรได้
เริ่มต้นด้วย คู่มือการควบคุมการเข้าถึงตามบทบาท (RBAC) ของเรา สำหรับคำแนะนำการตั้งค่าแบบทีละขั้นตอน
อัปเดตแอปพลิเคชันฝั่งไคลเอนต์ของคุณ
ร้องขอขอบเขต (scopes) ที่เหมาะสมในไคลเอนต์ของคุณ:
- การยืนยันตัวตนผู้ใช้: อัปเดตแอปของคุณ → เพื่อร้องขอขอบเขต API และ/หรือบริบทขององค์กร
- เครื่องต่อเครื่อง: กำหนดค่า M2M scopes → สำหรับการเข้าถึงระหว่างเซิร์ฟเวอร์
กระบวนการนี้มักเกี่ยวข้องกับการอัปเดตการกำหนดค่าไคลเอนต์ของคุณเพื่อรวมหนึ่งหรือมากกว่ารายการต่อไปนี้:
- พารามิเตอร์
scopeในกระบวนการ OAuth - พารามิเตอร์
resourceสำหรับการเข้าถึงทรัพยากร API organization_idสำหรับบริบทขององค์กร
ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าผู้ใช้หรือแอป M2M ที่คุณทดสอบได้รับการกำหนดบทบาทหรือบทบาทขององค์กรที่มีสิทธิ์ที่จำเป็นสำหรับ API ของคุณแล้ว
เริ่มต้นโปรเจกต์ API ของคุณ
ในการเริ่มต้นโปรเจกต์ Vert.x Web ใหม่ คุณสามารถสร้างโปรเจกต์ Maven ด้วยตนเองได้ดังนี้:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>your-api-name</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<vertx.version>4.5.0</vertx.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-auth-jwt</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web-client</artifactId>
<version>${vertx.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
สร้างเซิร์ฟเวอร์ Vert.x Web พื้นฐาน:
package com.example;
import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle;
import io.vertx.core.Promise;
import io.vertx.ext.web.Router;
import io.vertx.ext.web.handler.BodyHandler;
public class MainVerticle extends AbstractVerticle {
@Override
public void start(Promise<Void> startPromise) throws Exception {
Router router = Router.router(vertx);
router.route().handler(BodyHandler.create());
router.get("/hello").handler(ctx -> {
ctx.response()
.putHeader("content-type", "text/plain")
.end("Hello from Vert.x Web!");
});
vertx.createHttpServer()
.requestHandler(router)
.listen(3000, http -> {
if (http.succeeded()) {
startPromise.complete();
System.out.println("HTTP server started on port 3000");
} else {
startPromise.fail(http.cause());
}
});
}
}
package com.example;
import io.vertx.core.Vertx;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Vertx vertx = Vertx.vertx();
vertx.deployVerticle(new MainVerticle());
}
}
ดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการตั้งค่าเส้นทาง (routes), ตัวจัดการ (handlers) และฟีเจอร์อื่น ๆ ได้ที่เอกสาร Vert.x Web
กำหนดค่าคงที่และยูทิลิตี้
กำหนดค่าคงที่และยูทิลิตี้ที่จำเป็นในโค้ดของคุณเพื่อจัดการการดึงและตรวจสอบโทเค็น คำขอที่ถูกต้องต้องมี header Authorization ในรูปแบบ Bearer <access_token>
public class AuthorizationException extends RuntimeException {
private final int statusCode;
public AuthorizationException(String message) {
this(message, 403); // ค่าเริ่มต้นเป็น 403 Forbidden
}
public AuthorizationException(String message, int statusCode) {
super(message);
this.statusCode = statusCode;
}
public int getStatusCode() {
return statusCode;
}
}
ดึงข้อมูลเกี่ยวกับ Logto tenant ของคุณ
คุณจะต้องใช้ค่าต่อไปนี้เพื่อยืนยันโทเค็นที่ออกโดย Logto:
- URI ของ JSON Web Key Set (JWKS): URL ไปยัง public keys ของ Logto ใช้สำหรับตรวจสอบลายเซ็นของ JWT
- ผู้ออก (Issuer): ค่าผู้ออกที่คาดหวัง (OIDC URL ของ Logto)
ขั้นแรก ให้ค้นหา endpoint ของ Logto tenant ของคุณ คุณสามารถหาได้จากหลายที่:
- ใน Logto Console ที่ Settings → Domains
- ในการตั้งค่าแอปพลิเคชันใด ๆ ที่คุณตั้งค่าใน Logto, Settings → Endpoints & Credentials
ดึงค่าจาก OpenID Connect discovery endpoint
ค่าทั้งหมดนี้สามารถดึงได้จาก OpenID Connect discovery endpoint ของ Logto:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/.well-known/openid-configuration
ตัวอย่างการตอบกลับ (ละเว้นฟิลด์อื่นเพื่อความกระชับ):
{
"jwks_uri": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/jwks",
"issuer": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc"
}
เขียนค่าคงที่ในโค้ดของคุณ (ไม่แนะนำ)
เนื่องจาก Logto ไม่อนุญาตให้ปรับแต่ง JWKS URI หรือผู้ออก (issuer) คุณสามารถเขียนค่าคงที่เหล่านี้ไว้ในโค้ดของคุณได้ อย่างไรก็ตาม ไม่แนะนำให้ใช้วิธีนี้ในแอปพลิเคชัน production เพราะอาจเพิ่มภาระในการดูแลรักษาหากมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงค่าคอนฟิกในอนาคต
- JWKS URI:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/jwks - ผู้ออก (Issuer):
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc
ตรวจสอบโทเค็นและสิทธิ์ (permissions)
หลังจากดึงโทเค็นและดึงข้อมูล OIDC config แล้ว ให้ตรวจสอบสิ่งต่อไปนี้:
- ลายเซ็น (Signature): JWT ต้องถูกต้องและลงนามโดย Logto (ผ่าน JWKS)
- ผู้ออก (Issuer): ต้องตรงกับผู้ออกของ Logto tenant ของคุณ
- ผู้รับ (Audience): ต้องตรงกับตัวบ่งชี้ทรัพยากร API ที่ลงทะเบียนใน Logto หรือบริบทขององค์กรหากเกี่ยวข้อง
- วันหมดอายุ (Expiration): โทเค็นต้องไม่หมดอายุ
- สิทธิ์ (ขอบเขต) (Permissions (scopes)): โทเค็นต้องมีขอบเขตที่จำเป็นสำหรับ API / การกระทำของคุณ ขอบเขตจะเป็นสตริงที่คั่นด้วยช่องว่างใน
scopeการอ้างสิทธิ์ (claim) - บริบทองค์กร (Organization context): หากปกป้องทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร ให้ตรวจสอบการอ้างสิทธิ์
organization_id
ดู JSON Web Token เพื่อเรียนรู้เพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับโครงสร้างและการอ้างสิทธิ์ของ JWT
สิ่งที่ต้องตรวจสอบสำหรับแต่ละโมเดลสิทธิ์ (What to check for each permission model)
การอ้างสิทธิ์ (claims) และกฎการตรวจสอบจะแตกต่างกันไปตามโมเดลสิทธิ์:
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล (Global API resources)
- สิทธิ์ขององค์กร (ไม่ใช่ API) (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร (Organization-level API resources)
- การอ้างสิทธิ์ผู้รับ (
aud): ตัวบ่งชี้ทรัพยากร API - การอ้างสิทธิ์องค์กร (
organization_id): ไม่มี - ขอบเขต (สิทธิ์) ที่ต้องตรวจสอบ (
scope): สิทธิ์ของทรัพยากร API
- การอ้างสิทธิ์ผู้รับ (
aud):urn:logto:organization:<id>(บริบทองค์กรอยู่ในการอ้างสิทธิ์aud) - การอ้างสิทธิ์องค์กร (
organization_id): ไม่มี - ขอบเขต (สิทธิ์) ที่ต้องตรวจสอบ (
scope): สิทธิ์ขององค์กร
- การอ้างสิทธิ์ผู้รับ (
aud): ตัวบ่งชี้ทรัพยากร API - การอ้างสิทธิ์องค์กร (
organization_id): รหัสองค์กร (ต้องตรงกับคำขอ) - ขอบเขต (สิทธิ์) ที่ต้องตรวจสอบ (
scope): สิทธิ์ของทรัพยากร API
สำหรับสิทธิ์ขององค์กรที่ไม่ใช่ API บริบทขององค์กรจะแสดงโดยการอ้างสิทธิ์ aud (เช่น
urn:logto:organization:abc123) การอ้างสิทธิ์ organization_id จะมีเฉพาะในโทเค็นทรัพยากร API
ระดับองค์กรเท่านั้น
ควรตรวจสอบทั้งสิทธิ์ (ขอบเขต) และบริบท (ผู้รับ, องค์กร) เสมอ เพื่อความปลอดภัยของ API แบบหลายผู้เช่า
เพิ่มตรรกะการตรวจสอบ
เราใช้ไลบรารี JWT ที่แตกต่างกันขึ้นอยู่กับเฟรมเวิร์ก กรุณาติดตั้ง dependencies ที่จำเป็น:
เพิ่มลงใน pom.xml ของคุณ:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-auth-jwt</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.vertx</groupId>
<artifactId>vertx-web-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
import io.vertx.core.Future;
import io.vertx.core.Handler;
import io.vertx.core.Vertx;
import io.vertx.core.json.JsonArray;
import io.vertx.core.json.JsonObject;
import io.vertx.ext.auth.jwt.JWTAuth;
import io.vertx.ext.auth.jwt.JWTAuthOptions;
import io.vertx.ext.web.RoutingContext;
import io.vertx.ext.web.client.WebClient;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class JwtAuthHandler implements Handler<RoutingContext> {
private final JWTAuth jwtAuth;
private final WebClient webClient;
private final String expectedIssuer;
private final String jwksUri;
public JwtAuthHandler(Vertx vertx) {
this.webClient = WebClient.create(vertx);
this.jwtAuth = JWTAuth.create(vertx, new JWTAuthOptions());
// อย่าลืมตั้งค่าตัวแปรสภาพแวดล้อมเหล่านี้ในระบบที่นำไปใช้งานของคุณ
this.expectedIssuer = System.getenv("JWT_ISSUER");
this.jwksUri = System.getenv("JWKS_URI");
// ดึง JWKS และกำหนดค่า JWT auth
fetchJWKS().onSuccess(jwks -> {
// กำหนดค่า JWKS (ตัวอย่างนี้เรียบง่าย - คุณอาจต้องใช้ parser JWKS ที่เหมาะสม)
});
}
@Override
public void handle(RoutingContext context) {
String authHeader = context.request().getHeader("Authorization");
if (authHeader == null || !authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(401)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"Authorization header missing or invalid\"}"); // ไม่มีหรือ header การอนุญาตไม่ถูกต้อง
return;
}
String token = authHeader.substring(7);
jwtAuth.authenticate(new JsonObject().put("jwt", token))
.onSuccess(user -> {
try {
JsonObject principal = user.principal();
verifyPayload(principal);
context.put("auth", principal);
context.next();
} catch (AuthorizationException e) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(e.getStatusCode()) // ใช้รหัสสถานะจาก exception
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"" + e.getMessage() + "\"}");
} catch (Exception e) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(401)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"Invalid token\"}"); // โทเค็นไม่ถูกต้อง
}
})
.onFailure(err -> {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(401)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"Invalid token: " + err.getMessage() + "\"}"); // โทเค็นไม่ถูกต้อง
});
}
private Future<JsonObject> fetchJWKS() {
return webClient.getAbs(this.jwksUri)
.send()
.map(response -> response.bodyAsJsonObject());
}
private void verifyPayload(JsonObject principal) {
// ตรวจสอบผู้ออก (issuer) ด้วยตนเองสำหรับ Vert.x
String issuer = principal.getString("iss");
if (issuer == null || !expectedIssuer.equals(issuer)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Invalid issuer: " + issuer); // ผู้ออกไม่ถูกต้อง
}
// เพิ่มตรรกะการตรวจสอบเพิ่มเติมของคุณที่นี่ตามโมเดลสิทธิ์ (permission model)
// ใช้เมธอดช่วยเหลือด้านล่างสำหรับการดึง claim
}
// เมธอดช่วยเหลือสำหรับ Vert.x JWT
private List<String> extractAudiences(JsonObject principal) {
JsonArray audiences = principal.getJsonArray("aud");
if (audiences != null) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (Object aud : audiences) {
result.add(aud.toString());
}
return result;
}
return List.of();
}
private String extractScopes(JsonObject principal) {
return principal.getString("scope");
}
private String extractOrganizationId(JsonObject principal) {
return principal.getString("organization_id");
}
}
ตามโมเดลสิทธิ์ (permission model) ของคุณ ให้ดำเนินการตรรกะการตรวจสอบที่เหมาะสม:
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล (Global API resources)
- สิทธิ์ขององค์กร (ไม่ใช่ API) (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร (Organization-level API resources)
// ตรวจสอบว่า audience claim ตรงกับตัวบ่งชี้ทรัพยากร API ของคุณ
List<String> audiences = extractAudiences(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
if (!audiences.contains("https://your-api-resource-indicator")) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Audience ไม่ถูกต้อง");
}
// ตรวจสอบ scope ที่จำเป็นสำหรับทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล
List<String> requiredScopes = Arrays.asList("api:read", "api:write"); // แทนที่ด้วย scope ที่ต้องการจริง
String scopes = extractScopes(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
List<String> tokenScopes = scopes != null ? Arrays.asList(scopes.split(" ")) : List.of();
if (!tokenScopes.containsAll(requiredScopes)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("ขอบเขตไม่เพียงพอ");
}
// ตรวจสอบว่า audience claim ตรงกับรูปแบบขององค์กร
List<String> audiences = extractAudiences(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
boolean hasOrgAudience = audiences.stream()
.anyMatch(aud -> aud.startsWith("urn:logto:organization:"));
if (!hasOrgAudience) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Audience สำหรับสิทธิ์องค์กรไม่ถูกต้อง");
}
// ตรวจสอบว่า organization ID ตรงกับ context (คุณอาจต้องดึงจาก request context)
String expectedOrgId = "your-organization-id"; // ดึงจาก request context
String expectedAud = "urn:logto:organization:" + expectedOrgId;
if (!audiences.contains(expectedAud)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Organization ID ไม่ตรงกัน");
}
// ตรวจสอบ scope ขององค์กรที่จำเป็น
List<String> requiredScopes = Arrays.asList("invite:users", "manage:settings"); // แทนที่ด้วย scope ที่ต้องการจริง
String scopes = extractScopes(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
List<String> tokenScopes = scopes != null ? Arrays.asList(scopes.split(" ")) : List.of();
if (!tokenScopes.containsAll(requiredScopes)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("ขอบเขตขององค์กรไม่เพียงพอ");
}
// ตรวจสอบว่า audience claim ตรงกับตัวบ่งชี้ทรัพยากร API ของคุณ
List<String> audiences = extractAudiences(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
if (!audiences.contains("https://your-api-resource-indicator")) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Audience ไม่ถูกต้องสำหรับทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร");
}
// ตรวจสอบว่า organization ID ตรงกับ context (คุณอาจต้องดึงจาก request context)
String expectedOrgId = "your-organization-id"; // ดึงจาก request context
String orgId = extractOrganizationId(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
if (!expectedOrgId.equals(orgId)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("Organization ID ไม่ตรงกัน");
}
// ตรวจสอบ scope ที่จำเป็นสำหรับทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร
List<String> requiredScopes = Arrays.asList("api:read", "api:write"); // แทนที่ด้วย scope ที่ต้องการจริง
String scopes = extractScopes(token); // การดึงข้อมูลเฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก
List<String> tokenScopes = scopes != null ? Arrays.asList(scopes.split(" ")) : List.of();
if (!tokenScopes.containsAll(requiredScopes)) {
throw new AuthorizationException("ขอบเขตของ API ระดับองค์กรไม่เพียงพอ");
}
เมธอดช่วยเหลือสำหรับการดึง claim ต่าง ๆ จะขึ้นอยู่กับแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์ก ดูรายละเอียดการใช้งานในไฟล์ validation เฉพาะแต่ละเฟรมเวิร์กด้านบน
นำ middleware ไปใช้กับ API ของคุณ
ตอนนี้ ให้นำ middleware ไปใช้กับเส้นทาง API ที่ต้องการป้องกันของคุณ
import io.vertx.core.AbstractVerticle;
import io.vertx.core.Promise;
import io.vertx.core.json.JsonObject;
import io.vertx.ext.web.Router;
import io.vertx.ext.web.RoutingContext;
public class MainVerticle extends AbstractVerticle {
@Override
public void start(Promise<Void> startPromise) throws Exception {
Router router = Router.router(vertx);
// ใช้งาน middleware กับเส้นทางที่ต้องการป้องกัน
router.route("/api/protected*").handler(new JwtAuthHandler(vertx));
router.get("/api/protected").handler(this::protectedEndpoint);
vertx.createHttpServer()
.requestHandler(router)
.listen(8080, result -> {
if (result.succeeded()) {
startPromise.complete();
} else {
startPromise.fail(result.cause());
}
});
}
private void protectedEndpoint(RoutingContext context) {
// เข้าถึง JWT principal ได้โดยตรงจาก context
JsonObject principal = context.get("auth");
if (principal == null) {
context.response()
.setStatusCode(500)
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end("{\"error\": \"ไม่พบ JWT principal\"}");
return;
}
String scopes = principal.getString("scope");
JsonObject response = new JsonObject()
.put("sub", principal.getString("sub"))
.put("client_id", principal.getString("client_id"))
.put("organization_id", principal.getString("organization_id"))
.put("scopes", scopes != null ? scopes.split(" ") : new String[0])
.put("audience", principal.getJsonArray("aud"));
context.response()
.putHeader("Content-Type", "application/json")
.end(response.encode());
}
}
ทดสอบ API ที่ได้รับการป้องกันของคุณ
รับโทเค็นการเข้าถึง (Access tokens)
จากแอปพลิเคชันไคลเอนต์ของคุณ: หากคุณได้ตั้งค่าการเชื่อมต่อไคลเอนต์แล้ว แอปของคุณจะสามารถรับโทเค็นได้โดยอัตโนมัติ ดึงโทเค็นการเข้าถึงและนำไปใช้ในคำขอ API
สำหรับการทดสอบด้วย curl / Postman:
-
โทเค็นผู้ใช้: ใช้เครื่องมือสำหรับนักพัฒนาของแอปไคลเอนต์ของคุณเพื่อคัดลอกโทเค็นการเข้าถึงจาก localStorage หรือแท็บ network
-
โทเค็นเครื่องต่อเครื่อง: ใช้ client credentials flow ตัวอย่างที่ไม่เป็นทางการโดยใช้ curl:
curl -X POST https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/token \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "grant_type=client_credentials" \
-d "client_id=your-m2m-client-id" \
-d "client_secret=your-m2m-client-secret" \
-d "resource=https://your-api-resource-indicator" \
-d "scope=api:read api:write"คุณอาจต้องปรับพารามิเตอร์
resourceและscopeให้ตรงกับทรัพยากร API และสิทธิ์ของคุณ; อาจต้องใช้พารามิเตอร์organization_idหาก API ของคุณอยู่ในขอบเขตองค์กร
ต้องการตรวจสอบเนื้อหาโทเค็นใช่ไหม? ใช้ JWT decoder ของเราเพื่อถอดรหัสและตรวจสอบ JWT ของคุณ
ทดสอบ endpoint ที่ได้รับการป้องกัน
คำขอที่มีโทเค็นถูกต้อง
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
ผลลัพธ์ที่คาดหวัง:
{
"auth": {
"sub": "user123",
"clientId": "app456",
"organizationId": "org789",
"scopes": ["api:read", "api:write"],
"audience": ["https://your-api-resource-indicator"]
}
}
ไม่มีโทเค็น
curl http://localhost:3000/api/protected
ผลลัพธ์ที่คาดหวัง (401):
{
"error": "Authorization header is missing"
}
โทเค็นไม่ถูกต้อง
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer invalid-token" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
ผลลัพธ์ที่คาดหวัง (401):
{
"error": "Invalid token"
}
การทดสอบเฉพาะโมเดลสิทธิ์ (Permission model-specific testing)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับโกลบอล (Global API resources)
- สิทธิ์ขององค์กร (ไม่ใช่ API) (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- ทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร (Organization-level API resources)
กรณีทดสอบสำหรับ API ที่ได้รับการป้องกันด้วย global scopes:
- ขอบเขตถูกต้อง: ทดสอบด้วยโทเค็นที่มีขอบเขต API ที่ต้องการ (เช่น
api:read,api:write) - ขาดขอบเขต: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อโทเค็นไม่มีขอบเขตที่จำเป็น
- audience ไม่ถูกต้อง: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อ audience ไม่ตรงกับทรัพยากร API
# โทเค็นที่ขาดขอบเขต - คาดหวัง 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-without-required-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
กรณีทดสอบสำหรับการควบคุมการเข้าถึงเฉพาะองค์กร:
- โทเค็นองค์กรถูกต้อง: ทดสอบด้วยโทเค็นที่มี context ขององค์กรที่ถูกต้อง (organization ID และ scopes)
- ขาดขอบเขต: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อผู้ใช้ไม่มีสิทธิ์สำหรับการกระทำที่ร้องขอ
- องค์กรไม่ถูกต้อง: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อ audience ไม่ตรงกับ context ขององค์กร (
urn:logto:organization:<organization_id>)
# โทเค็นสำหรับองค์กรผิด - คาดหวัง 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-for-different-organization" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
กรณีทดสอบที่ผสมผสานการตรวจสอบทรัพยากร API กับ context ขององค์กร:
- องค์กร + ขอบเขต API ถูกต้อง: ทดสอบด้วยโทเค็นที่มีทั้ง context ขององค์กรและขอบเขต API ที่ต้องการ
- ขาดขอบเขต API: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อโทเค็นองค์กรไม่มีสิทธิ์ API ที่จำเป็น
- องค์กรไม่ถูกต้อง: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อเข้าถึง API ด้วยโทเค็นจากองค์กรอื่น
- audience ไม่ถูกต้อง: คาดหวัง 403 Forbidden เมื่อ audience ไม่ตรงกับทรัพยากร API ระดับองค์กร
# โทเค็นองค์กรที่ไม่มีขอบเขต API - คาดหวัง 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer organization-token-without-api-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
อ่านเพิ่มเติม
RBAC ในทางปฏิบัติ: การนำการอนุญาต (Authorization) ที่ปลอดภัยมาใช้กับแอปพลิเคชันของคุณ
สร้างแอปพลิเคชัน SaaS แบบหลายผู้เช่า: คู่มือฉบับสมบูรณ์ตั้งแต่การออกแบบจนถึงการนำไปใช้