使用角色型存取控制 (RBAC, Role-based Access Control) 與 JWT 驗證 (JWT validation) 保護你的 Chi API
本指南將協助你透過 角色型存取控制 (RBAC, Role-based Access Control) 以及由 Logto 簽發的 JSON Web Token (JWT),為你的 Chi API 實作授權 (Authorization) 機制,提升安全性。
開始前
你的用戶端應用程式需要從 Logto 取得存取權杖 (Access tokens)。如果你尚未完成用戶端整合,請參考我們針對 React、Vue、Angular 或其他前端框架的 快速入門,或伺服器對伺服器存取請參閱 機器對機器指南。
本指南聚焦於在你的 Chi 應用程式中,對這些權杖進行伺服器端驗證。
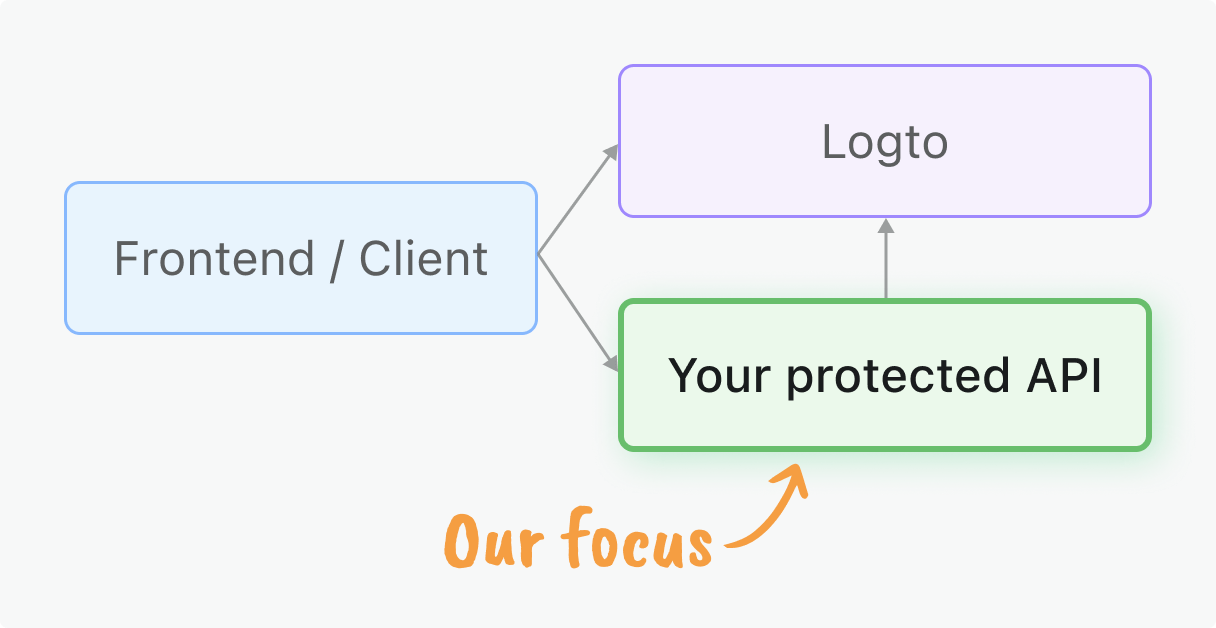
你將學到
- JWT 驗證: 學習如何驗證存取權杖 (Access tokens) 並擷取驗證 (Authentication) 資訊
- 中介軟體實作: 建立可重複使用的中介軟體以保護 API
- 權限模型: 理解並實作不同的授權 (Authorization) 模式:
- 全域 API 資源 (Global API resources) 用於應用程式層級端點
- 組織權限 (Organization permissions) 控制租戶專屬功能
- 組織層級 API 資源 (Organization-level API resources) 用於多租戶資料存取
- RBAC 整合: 在 API 端點強制執行角色型權限 (Role-based permissions) 與權限範圍 (Scopes)
先決條件
- 已安裝最新版穩定版 Go
- 基本了解 Chi 與 Web API 開發
- 已設定 Logto 應用程式(如有需要請參閱 快速入門)
權限 (Permission) 模型總覽
在實作保護機制前,請先選擇最適合你應用程式架構的權限模型。這與 Logto 的三大授權 (Authorization) 情境相符:
- 全域 API 資源 (Global API resources)
- 組織(非 API)權限 (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- 組織層級 API 資源 (Organization-level API resources)
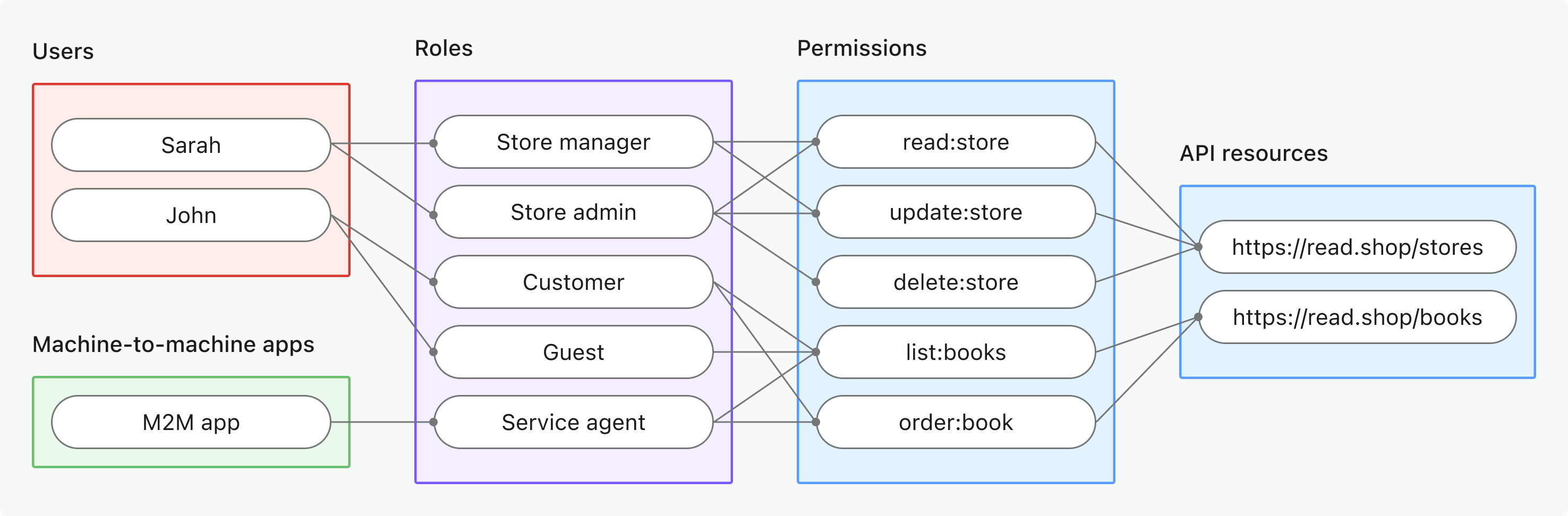
- 適用情境: 保護整個應用程式共用的 API 資源(非組織專屬)
- 權杖類型: 具有全域受眾 (global audience) 的存取權杖 (Access token)
- 範例: 公開 API、核心產品服務、管理端點
- 最適用於: 所有客戶共用 API 的 SaaS 產品、無租戶隔離的微服務架構
- 深入瞭解: 保護全域 API 資源
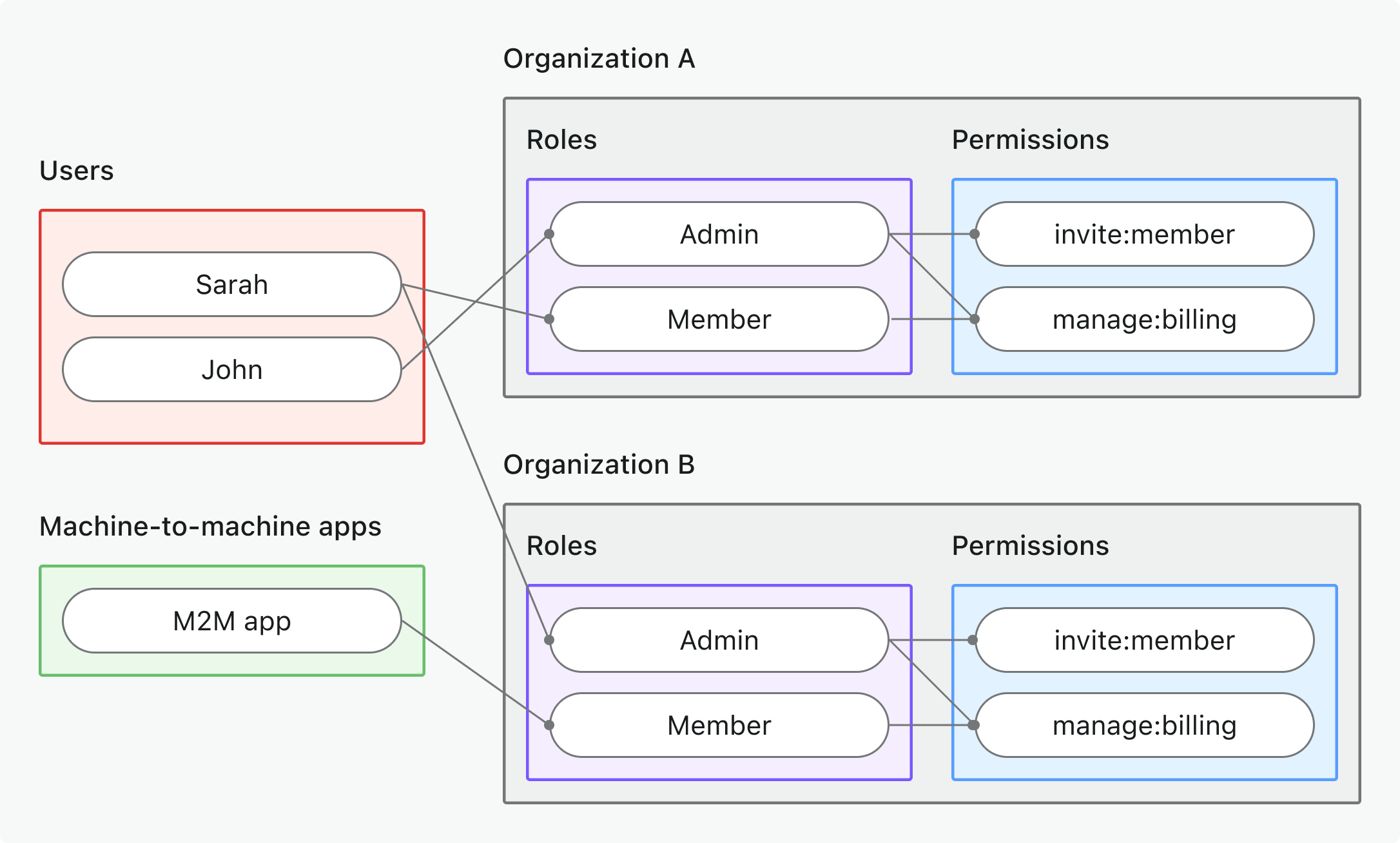
- 適用情境: 控制組織專屬的操作、UI 功能或商業邏輯(非 API)
- 權杖類型: 具有組織專屬受眾 (organization-specific audience) 的組織權杖 (Organization token)
- 範例: 功能開關、儀表板權限、成員邀請控制
- 最適用於: 具有組織專屬功能與流程的多租戶 SaaS
- 深入瞭解: 保護組織(非 API)權限
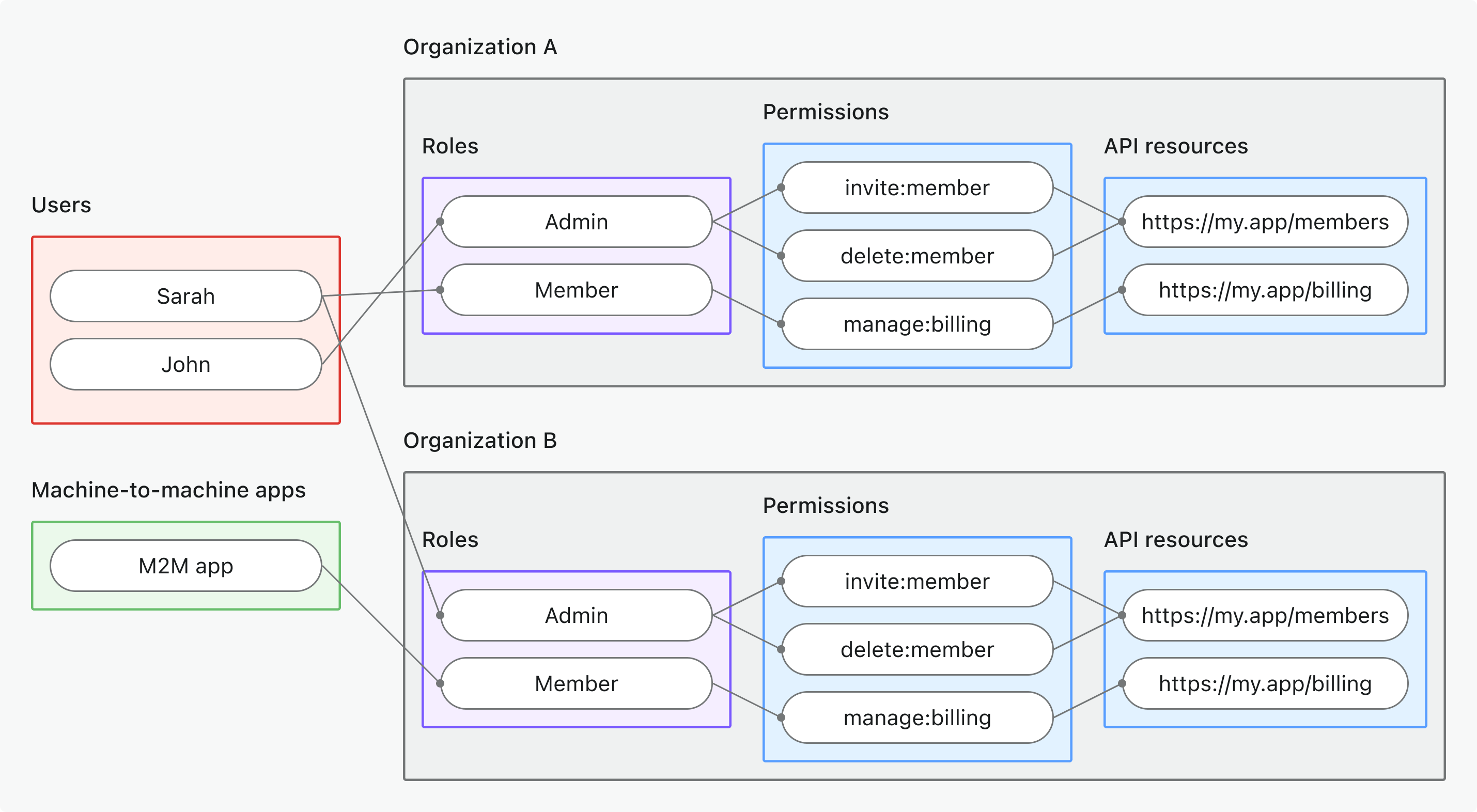
- 適用情境: 保護僅在特定組織情境下可存取的 API 資源
- 權杖類型: 具有 API 資源受眾 (API resource audience) + 組織情境 (organization context) 的組織權杖 (Organization token)
- 範例: 多租戶 API、組織範圍資料端點、租戶專屬微服務
- 最適用於: API 資料以組織為範圍的多租戶 SaaS
- 深入瞭解: 保護組織層級 API 資源
💡 請在繼續前選擇你的模型 —— 本指南後續內容將以你選擇的方式為參考。
快速準備步驟
設定 Logto 資源與權限 (Permissions)
- 全域 API 資源 (Global API resources)
- 組織(非 API)權限 (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- 組織層級 API 資源 (Organization-level API resources)
- 建立 API 資源 (API resource): 前往 Console → API 資源 (API resources) 並註冊你的 API(例如:
https://api.yourapp.com) - 定義權限 (Permissions): 新增如
read:products、write:orders等權限範圍 (Scopes) —— 參考 定義帶有權限的 API 資源 - 建立全域角色 (Global roles): 前往 Console → 角色 (Roles) 並建立包含 API 權限的角色 —— 參考 設定全域角色
- 指派角色 (Assign roles): 將角色指派給需要 API 存取權的使用者或 M2M 應用程式
- 定義組織權限 (Organization permissions): 在組織範本中建立如
invite:member、manage:billing等非 API 組織權限 - 設定組織角色 (Organization roles): 在組織範本中配置組織專屬角色並指派權限給這些角色
- 指派組織角色 (Assign organization roles): 在每個組織情境下將使用者指派到組織角色
- 建立 API 資源 (API resource): 如上註冊你的 API 資源,但將用於組織情境
- 定義權限 (Permissions): 新增如
read:data、write:settings等限定於組織情境的權限範圍 (Scopes) - 設定組織範本 (Configure organization template): 設定包含 API 資源權限的組織角色
- 指派組織角色 (Assign organization roles): 將使用者或 M2M 應用程式指派到包含 API 權限的組織角色
- 多租戶設定 (Multi-tenant setup): 確保你的 API 能處理組織範圍的資料與驗證
建議從我們的 角色型存取控制 (RBAC) 指南 開始,獲得逐步設定說明。
更新你的用戶端應用程式
在用戶端請求適當的權限範圍 (Scopes):
- 使用者驗證 (Authentication):更新你的應用程式 → 以請求你的 API 權限範圍和/或組織情境
- 機器對機器 (M2M):設定 M2M 權限範圍 → 以進行伺服器對伺服器存取
通常需要在用戶端設定中新增以下一項或多項:
- OAuth 流程中的
scope參數 - 用於 API 資源存取的
resource參數 - 組織情境下的
organization_id
請確保你測試的使用者或 M2M 應用程式已被指派包含所需 API 權限的正確角色或組織角色。
初始化你的 API 專案
要用 Chi 初始化一個新的 Go 專案,你可以按照以下步驟操作:
go mod init your-api-name
go get github.com/go-chi/chi/v5
接著,建立一個基本的 Chi 伺服器設定:
package main
import (
"net/http"
"github.com/go-chi/chi/v5"
)
func main() {
r := chi.NewRouter()
http.ListenAndServe(":3000", r)
}
如需更多關於路由、middleware 及其他功能的設定細節,請參考 Chi 官方文件。
初始化常數與工具函式
在你的程式碼中定義必要的常數與工具函式,以處理權杖(token)的擷取與驗證。一個有效的請求必須包含 Authorization 標頭,格式為 Bearer <存取權杖 (Access token)>。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
"strings"
)
const (
JWKS_URI = "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/jwks"
ISSUER = "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc"
)
type AuthorizationError struct {
Message string
Status int
}
func (e *AuthorizationError) Error() string {
return e.Message
}
func NewAuthorizationError(message string, status ...int) *AuthorizationError {
statusCode := http.StatusForbidden // 預設為 403 Forbidden
if len(status) > 0 {
statusCode = status[0]
}
return &AuthorizationError{
Message: message,
Status: statusCode,
}
}
func extractBearerTokenFromHeaders(r *http.Request) (string, error) {
const bearerPrefix = "Bearer "
authorization := r.Header.Get("Authorization")
if authorization == "" {
return "", NewAuthorizationError("Authorization 標頭遺失", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
if !strings.HasPrefix(authorization, bearerPrefix) {
return "", NewAuthorizationError(fmt.Sprintf("Authorization 標頭必須以 \"%s\" 開頭", bearerPrefix), http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
return strings.TrimPrefix(authorization, bearerPrefix), nil
}
取得你的 Logto 租戶資訊
你需要以下數值來驗證 Logto 發行的權杖:
- JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) URI:Logto 公鑰的網址,用於驗證 JWT 簽章。
- 簽發者 (Issuer):預期的簽發者值(Logto 的 OIDC URL)。
首先,找到你的 Logto 租戶端點。你可以在多個地方找到:
- 在 Logto Console,設定 → 網域。
- 在你於 Logto 配置過的任何應用程式設定中,設定 → 端點與憑證。
從 OpenID Connect 探索端點取得
這些數值可以從 Logto 的 OpenID Connect 探索端點取得:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/.well-known/openid-configuration
以下為範例回應(為簡潔省略其他欄位):
{
"jwks_uri": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/jwks",
"issuer": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc"
}
在程式碼中硬編碼(不建議)
由於 Logto 不允許自訂 JWKS URI 或簽發者 (Issuer),你可以將這些數值硬編碼在程式碼中。但這不建議用於正式環境,因為若未來有設定變更,可能會增加維護負擔。
- JWKS URI:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/jwks - 簽發者 (Issuer):
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc
驗證權杖與權限
在擷取權杖並取得 OIDC 設定後,請驗證以下項目:
- 簽章 (Signature): JWT 必須有效且由 Logto(透過 JWKS)簽署。
- 簽發者 (Issuer): 必須符合你的 Logto 租戶簽發者。
- 受眾 (Audience): 必須符合在 Logto 註冊的 API 資源標示符 (resource indicator),或在適用時符合組織 (Organization) 上下文。
- 過期時間 (Expiration): 權杖不得過期。
- 權限範圍 (Permissions, scopes): 權杖必須包含 API/操作所需的權限範圍 (scopes)。scopes 會以空格分隔字串出現在
scope宣告 (claim) 中。 - 組織 (Organization) 上下文: 若保護的是組織層級 API 資源,需驗證
organization_id宣告 (claim)。
詳情請參閱 JSON Web Token 以瞭解 JWT 結構與宣告 (claims)。
各權限模型需檢查的項目
不同權限模型下,宣告 (claims) 與驗證規則有所不同:
- 全域 API 資源
- 組織(非 API)權限
- 組織層級 API 資源
- 受眾宣告 (
aud): API 資源標示符 (API resource indicator) - 組織宣告 (
organization_id): 不存在 - 權限範圍需檢查 (
scope): API 資源權限 (API resource permissions)
- 受眾宣告 (
aud):urn:logto:organization:<id>(組織上下文於aud宣告中) - 組織宣告 (
organization_id): 不存在 - 權限範圍需檢查 (
scope): 組織權限 (Organization permissions)
- 受眾宣告 (
aud): API 資源標示符 (API resource indicator) - 組織宣告 (
organization_id): 組織 ID(必須與請求相符) - 權限範圍需檢查 (
scope): API 資源權限 (API resource permissions)
對於非 API 組織權限,組織上下文由 aud 宣告表示 (例如
urn:logto:organization:abc123)。organization_id 宣告僅存在於組織層級 API 資源權杖中。
對於多租戶 API,務必同時驗證權限範圍 (scopes) 及上下文(受眾 (audience)、組織 (organization)),以確保安全。
新增驗證邏輯
我們使用 github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx 來驗證 JWT。如尚未安裝,請先安裝:
go mod init your-project
go get github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx/v3
首先,將這些共用元件加入你的 auth_middleware.go:
import (
"context"
"strings"
"time"
"github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx/v3/jwk"
"github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx/v3/jwt"
)
var jwkSet jwk.Set
func init() {
// 初始化 JWKS 快取
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 10*time.Second)
defer cancel()
var err error
jwkSet, err = jwk.Fetch(ctx, JWKS_URI)
if err != nil {
panic("Failed to fetch JWKS: " + err.Error())
}
}
// validateJWT 驗證 JWT 並回傳解析後的權杖
func validateJWT(tokenString string) (jwt.Token, error) {
token, err := jwt.Parse([]byte(tokenString), jwt.WithKeySet(jwkSet))
if err != nil {
return nil, NewAuthorizationError("Invalid token: "+err.Error(), http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
// 驗證簽發者 (Issuer)
if token.Issuer() != ISSUER {
return nil, NewAuthorizationError("Invalid issuer", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
if err := verifyPayload(token); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return token, nil
}
// 輔助函式:取得權杖中的字串宣告 (Claim)
func getStringClaim(token jwt.Token, key string) string {
if val, ok := token.Get(key); ok {
if str, ok := val.(string); ok {
return str
}
}
return ""
}
func getScopesFromToken(token jwt.Token) []string {
if val, ok := token.Get("scope"); ok {
if scope, ok := val.(string); ok && scope != "" {
return strings.Split(scope, " ")
}
}
return []string{}
}
func getAudienceFromToken(token jwt.Token) []string {
return token.Audience()
}
接著,實作中介軟體來驗證存取權杖 (Access token):
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
)
type contextKey string
const AuthContextKey contextKey = "auth"
func VerifyAccessToken(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
tokenString, err := extractBearerTokenFromHeaders(r)
if err != nil {
authErr := err.(*AuthorizationError)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.WriteHeader(authErr.Status)
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(map[string]string{"error": authErr.Message})
return
}
token, err := validateJWT(tokenString)
if err != nil {
authErr := err.(*AuthorizationError)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.WriteHeader(authErr.Status)
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(map[string]string{"error": authErr.Message})
return
}
// 將權杖 (token) 儲存在 context 以便通用使用
ctx := context.WithValue(r.Context(), AuthContextKey, token)
next.ServeHTTP(w, r.WithContext(ctx))
})
}
根據你的權限模型,你可能需要採用不同的 verifyPayload 邏輯:
- 全域 API 資源 (Global API resources)
- 組織(非 API)權限 (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- 組織層級 API 資源 (Organization-level API resources)
func verifyPayload(token jwt.Token) error {
// 檢查 audience 宣告是否符合你的 API 資源標示符 (Resource indicator)
if !hasAudience(token, "https://your-api-resource-indicator") {
return NewAuthorizationError("Invalid audience")
}
// 檢查全域 API 資源所需的權限範圍 (Scopes)
requiredScopes := []string{"api:read", "api:write"} // 請替換為實際所需的權限範圍
if !hasRequiredScopes(token, requiredScopes) {
return NewAuthorizationError("Insufficient scope")
}
return nil
}
func verifyPayload(token jwt.Token) error {
// 檢查 audience 宣告是否為組織格式
if !hasOrganizationAudience(token) {
return NewAuthorizationError("Invalid audience for organization permissions")
}
// 檢查組織 ID 是否與上下文一致(你可能需要從請求上下文中取得)
expectedOrgID := "your-organization-id" // 從請求上下文取得
if !hasMatchingOrganization(token, expectedOrgID) {
return NewAuthorizationError("Organization ID mismatch")
}
// 檢查所需的組織權限範圍
requiredScopes := []string{"invite:users", "manage:settings"} // 請替換為實際所需的權限範圍
if !hasRequiredScopes(token, requiredScopes) {
return NewAuthorizationError("Insufficient organization scope")
}
return nil
}
func verifyPayload(token jwt.Token) error {
// 檢查 audience 宣告是否符合你的 API 資源標示符
if !hasAudience(token, "https://your-api-resource-indicator") {
return NewAuthorizationError("Invalid audience for organization-level API resources")
}
// 檢查組織 ID 是否與上下文一致(你可能需要從請求上下文中取得)
expectedOrgID := "your-organization-id" // 從請求上下文取得
if !hasMatchingOrganizationID(token, expectedOrgID) {
return NewAuthorizationError("Organization ID mismatch")
}
// 檢查組織層級 API 資源所需的權限範圍
requiredScopes := []string{"api:read", "api:write"} // 請替換為實際所需的權限範圍
if !hasRequiredScopes(token, requiredScopes) {
return NewAuthorizationError("Insufficient organization-level API scopes")
}
return nil
}
新增這些輔助函式以驗證 payload:
// hasAudience 檢查權杖是否包含指定的受眾 (Audience)
func hasAudience(token jwt.Token, expectedAud string) bool {
audiences := token.Audience()
for _, aud := range audiences {
if aud == expectedAud {
return true
}
}
return false
}
// hasOrganizationAudience 檢查權杖是否為組織受眾格式
func hasOrganizationAudience(token jwt.Token) bool {
audiences := token.Audience()
for _, aud := range audiences {
if strings.HasPrefix(aud, "urn:logto:organization:") {
return true
}
}
return false
}
// hasRequiredScopes 檢查權杖是否包含所有必要的權限範圍 (Scopes)
func hasRequiredScopes(token jwt.Token, requiredScopes []string) bool {
scopes := getScopesFromToken(token)
for _, required := range requiredScopes {
found := false
for _, scope := range scopes {
if scope == required {
found = true
break
}
}
if !found {
return false
}
}
return true
}
// hasMatchingOrganization 檢查權杖受眾是否與預期組織一致
func hasMatchingOrganization(token jwt.Token, expectedOrgID string) bool {
expectedAud := fmt.Sprintf("urn:logto:organization:%s", expectedOrgID)
return hasAudience(token, expectedAud)
}
// hasMatchingOrganizationID 檢查權杖中的 organization_id 是否與預期一致
func hasMatchingOrganizationID(token jwt.Token, expectedOrgID string) bool {
orgID := getStringClaim(token, "organization_id")
return orgID == expectedOrgID
}
套用中介軟體至你的 API
現在,將中介軟體套用到你受保護的 API 路由。
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"github.com/go-chi/chi/v5"
"github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx/v3/jwt"
)
func main() {
r := chi.NewRouter()
// 對受保護路由套用中介軟體
r.With(VerifyAccessToken).Get("/api/protected", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 直接從 context 取得存取權杖 (Access token) 資訊
tokenInterface := r.Context().Value(AuthContextKey)
if tokenInterface == nil {
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(map[string]string{"error": "Token not found"})
return
}
token := tokenInterface.(jwt.Token)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(map[string]interface{}{
"sub": token.Subject(),
"client_id": getStringClaim(token, "client_id"),
"organization_id": getStringClaim(token, "organization_id"),
"scopes": getScopesFromToken(token),
"audience": getAudienceFromToken(token),
})
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", r)
}
或使用路由群組:
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"net/http"
"github.com/go-chi/chi/v5"
"github.com/lestrrat-go/jwx/v3/jwt"
)
func main() {
r := chi.NewRouter()
// 建立受保護的路由群組
r.Route("/api", func(r chi.Router) {
r.Use(VerifyAccessToken)
r.Get("/protected", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
// 直接從 context 取得存取權杖 (Access token) 資訊
token := r.Context().Value(AuthContextKey).(jwt.Token)
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
json.NewEncoder(w).Encode(map[string]interface{}{
"sub": token.Subject(),
"client_id": getStringClaim(token, "client_id"),
"organization_id": getStringClaim(token, "organization_id"),
"scopes": getScopesFromToken(token),
"audience": getAudienceFromToken(token),
"message": "成功存取受保護資料 (Protected data accessed successfully)",
})
})
})
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", r)
}
測試你的受保護 API
取得存取權杖 (Access tokens)
從你的用戶端應用程式取得: 如果你已完成用戶端整合,你的應用程式可以自動取得權杖。擷取存取權杖 (Access token) 並在 API 請求中使用。
使用 curl / Postman 測試:
-
使用者權杖 (User tokens): 使用你的用戶端應用程式的開發者工具,從 localStorage 或網路分頁複製存取權杖 (Access token)
-
機器對機器權杖 (Machine-to-machine tokens): 使用 client credentials flow。以下是使用 curl 的非標準範例:
curl -X POST https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/token \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "grant_type=client_credentials" \
-d "client_id=your-m2m-client-id" \
-d "client_secret=your-m2m-client-secret" \
-d "resource=https://your-api-resource-indicator" \
-d "scope=api:read api:write"你可能需要根據你的 API 資源 (API resource) 和權限 (Permissions) 調整
resource和scope參數;如果你的 API 以組織 (Organization) 為範圍,也可能需要organization_id參數。
需要檢查權杖內容嗎?請使用我們的 JWT 解碼工具 來解碼並驗證你的 JWT。
測試受保護端點
有效權杖請求
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
預期回應:
{
"auth": {
"sub": "user123",
"clientId": "app456",
"organizationId": "org789",
"scopes": ["api:read", "api:write"],
"audience": ["https://your-api-resource-indicator"]
}
}
缺少權杖
curl http://localhost:3000/api/protected
預期回應 (401):
{
"error": "Authorization header is missing"
}
無效權杖
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer invalid-token" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
預期回應 (401):
{
"error": "Invalid token"
}
權限模型專屬測試
- 全域 API 資源 (Global API resources)
- 組織(非 API)權限 (Organization (non-API) permissions)
- 組織層級 API 資源 (Organization-level API resources)
針對以全域權限範圍 (Scopes) 保護的 API 測試情境:
- 有效權限範圍 (Valid scopes): 使用包含所需 API 權限範圍(如
api:read、api:write)的權杖測試 - 缺少權限範圍 (Missing scopes): 權杖缺少必要權限範圍時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
- 錯誤受眾 (Wrong audience): 權杖受眾 (Audience) 不符合 API 資源時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
# 權杖缺少必要權限範圍 - 預期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-without-required-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
針對組織專屬存取控制的測試情境:
- 有效組織權杖 (Valid organization token): 使用包含正確組織 (Organization) 資訊(組織 ID 與權限範圍)的權杖測試
- 缺少權限範圍 (Missing scopes): 使用者沒有執行請求操作的權限時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
- 錯誤組織 (Wrong organization): 權杖受眾 (Audience) 不符合組織上下文(
urn:logto:organization:<organization_id>)時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
# 錯誤組織的權杖 - 預期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-for-different-organization" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
結合 API 資源驗證與組織上下文的測試情境:
- 有效組織 + API 權限範圍 (Valid organization + API scopes): 權杖同時具備組織上下文與所需 API 權限範圍時測試
- 缺少 API 權限範圍 (Missing API scopes): 組織權杖缺少必要 API 權限時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
- 錯誤組織 (Wrong organization): 使用不同組織的權杖存取 API 時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
- 錯誤受眾 (Wrong audience): 權杖受眾 (Audience) 不符合組織層級 API 資源時,預期回傳 403 Forbidden
# 組織權杖缺少 API 權限範圍 - 預期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer organization-token-without-api-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
延伸閱讀
RBAC 實務應用:為你的應用程式實現安全授權 (Authorization)
建立多租戶 SaaS 應用程式:從設計到實作的完整指南