使用基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 和 JWT 验证保护你的 Rocket API
本指南将帮助你通过使用 基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 和 Logto 签发的 JSON Web Token (JWT) 来实现 Rocket API 的授权 (Authorization) 安全防护。
开始之前
你的客户端应用需要从 Logto 获取访问令牌 (Access tokens)。如果你还没有完成客户端集成,请查看我们的 快速开始,适用于 React、Vue、Angular 或其他客户端框架,或者参考我们的 机器对机器指南 以实现服务器到服务器的访问。
本指南聚焦于在你的 Rocket 应用中对这些令牌进行服务端验证。
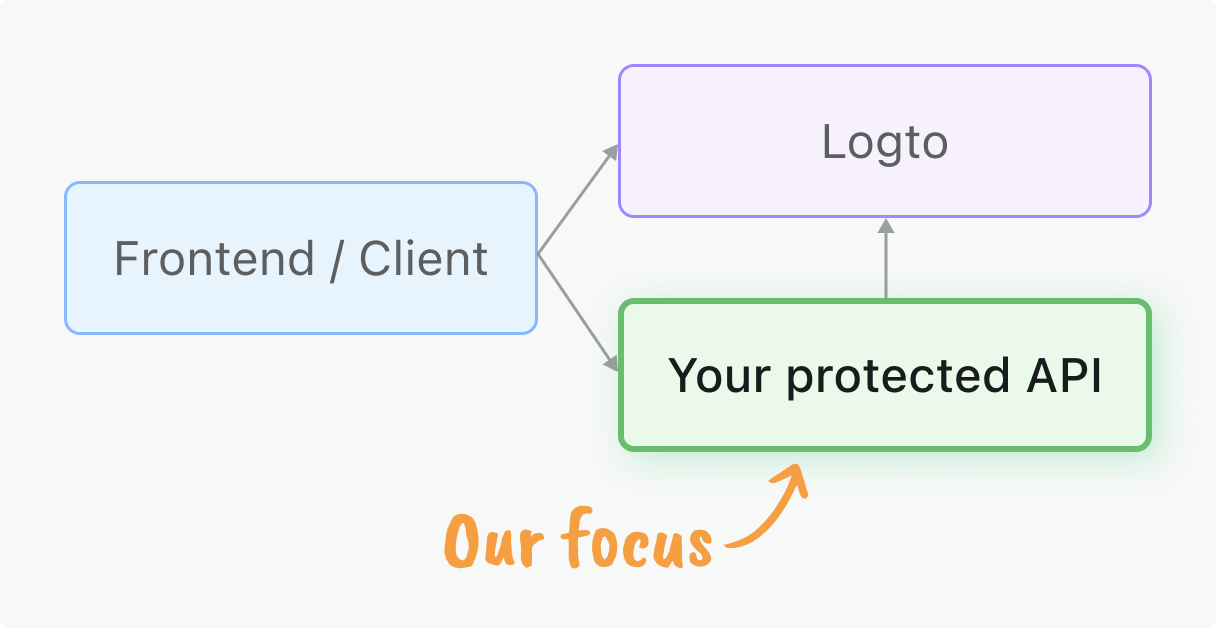
你将学到什么
- JWT 验证:学习如何验证访问令牌 (Access tokens) 并提取认证 (Authentication) 信息
- 中间件实现:创建可复用的中间件以保护 API
- 权限模型:理解并实现不同的授权 (Authorization) 模式:
- 应用级端点的全局 API 资源
- 用于租户特定功能控制的组织权限
- 多租户数据访问的组织级 API 资源
- RBAC 集成:在你的 API 端点中强制执行基于角色的权限 (Permissions) 和权限范围 (Scopes)
前置条件
- 已安装 Rust 的最新稳定版本
- 基本了解 Rocket 及 Web API 开发
- 已配置 Logto 应用(如有需要请参见 快速开始)
权限 (Permission) 模型概览
在实施保护之前,请选择适合你应用架构的权限 (Permission) 模型。这与 Logto 的三大授权 (Authorization) 场景保持一致:
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (Organization)(非 API)权限 (Permissions)
- 组织级 API 资源
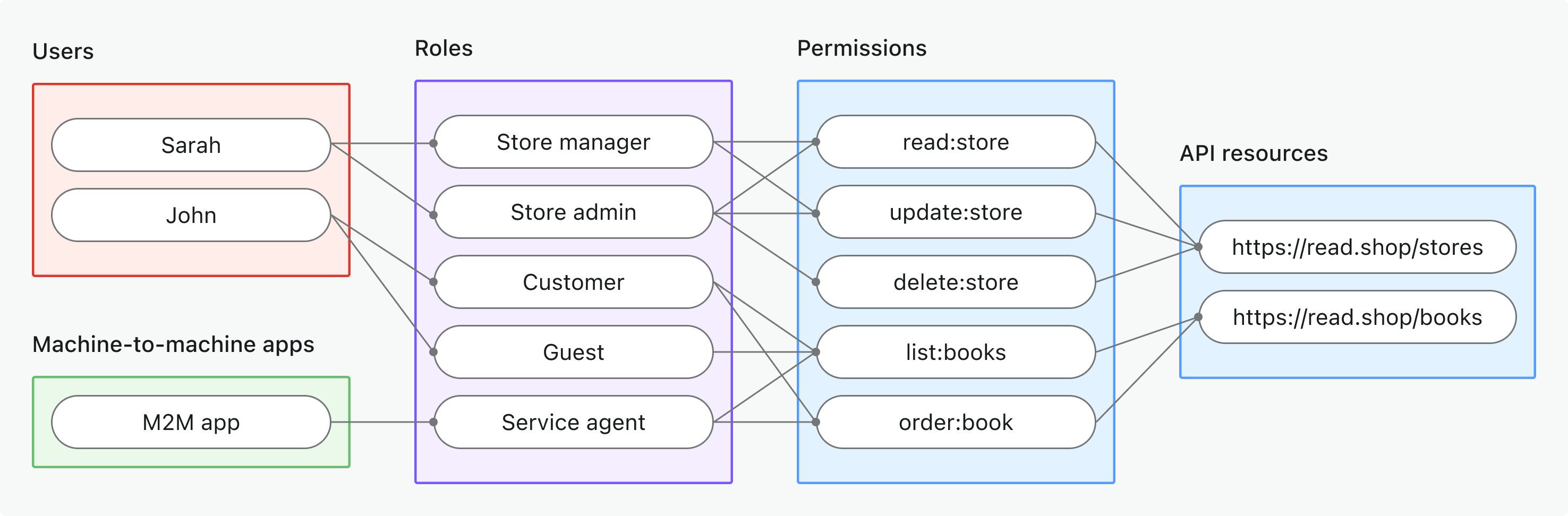
- 使用场景: 保护整个应用共享的 API 资源(非组织 (Organization) 专属)
- 令牌类型: 具有全局受众 (Audience) 的访问令牌 (Access token)
- 示例: 公共 API、核心产品服务、管理端点
- 最适合: 所有客户都使用 API 的 SaaS 产品、无租户隔离的微服务
- 了解更多: 保护全局 API 资源
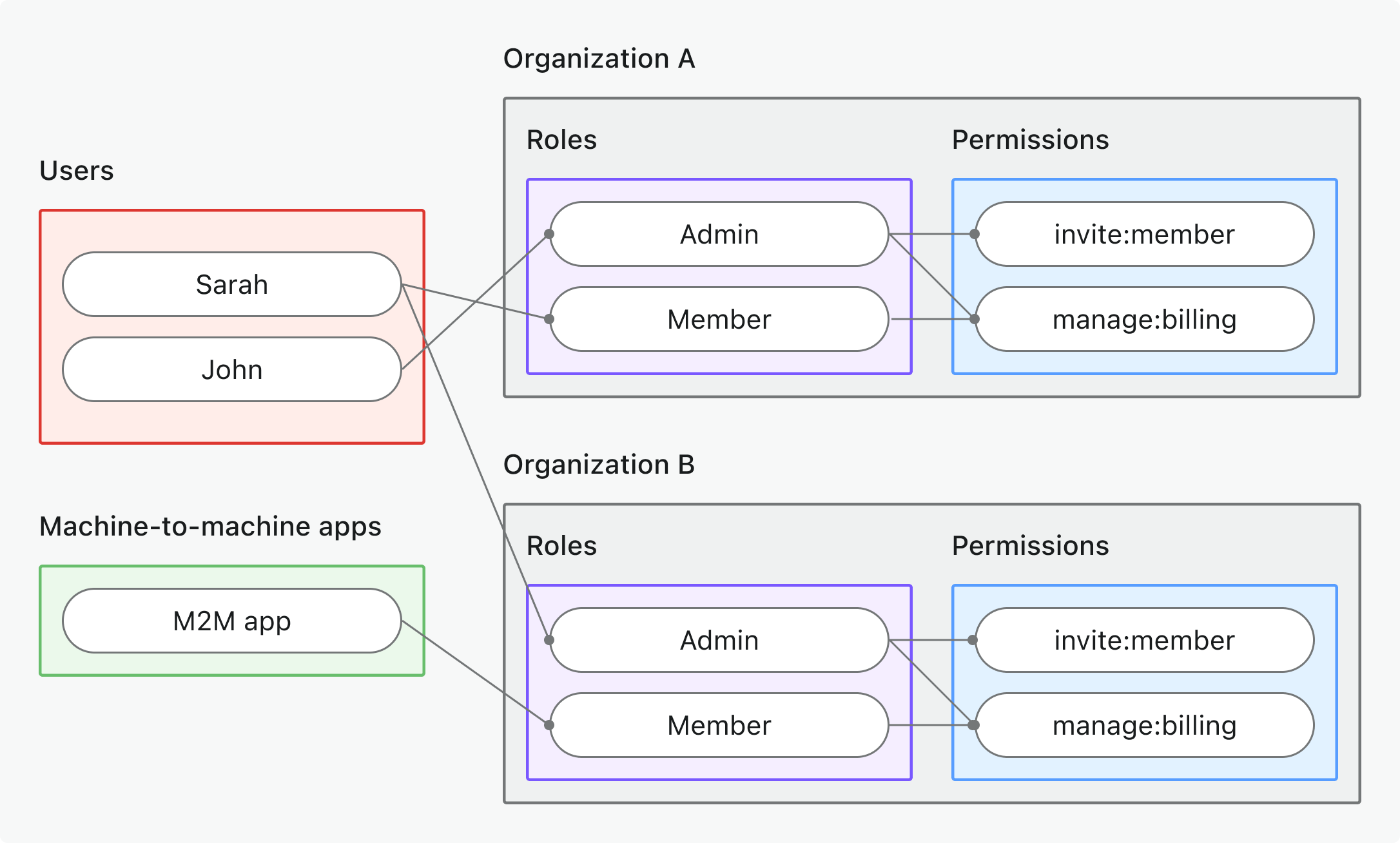
- 使用场景: 控制组织 (Organization) 专属的操作、UI 功能或业务逻辑(非 API)
- 令牌类型: 具有组织 (Organization) 专属受众 (Audience) 的组织令牌 (Organization token)
- 示例: 功能开关、仪表盘权限 (Permissions)、成员邀请控制
- 最适合: 拥有组织 (Organization) 专属功能和工作流的多租户 SaaS
- 了解更多: 保护组织 (Organization)(非 API)权限 (Permissions)
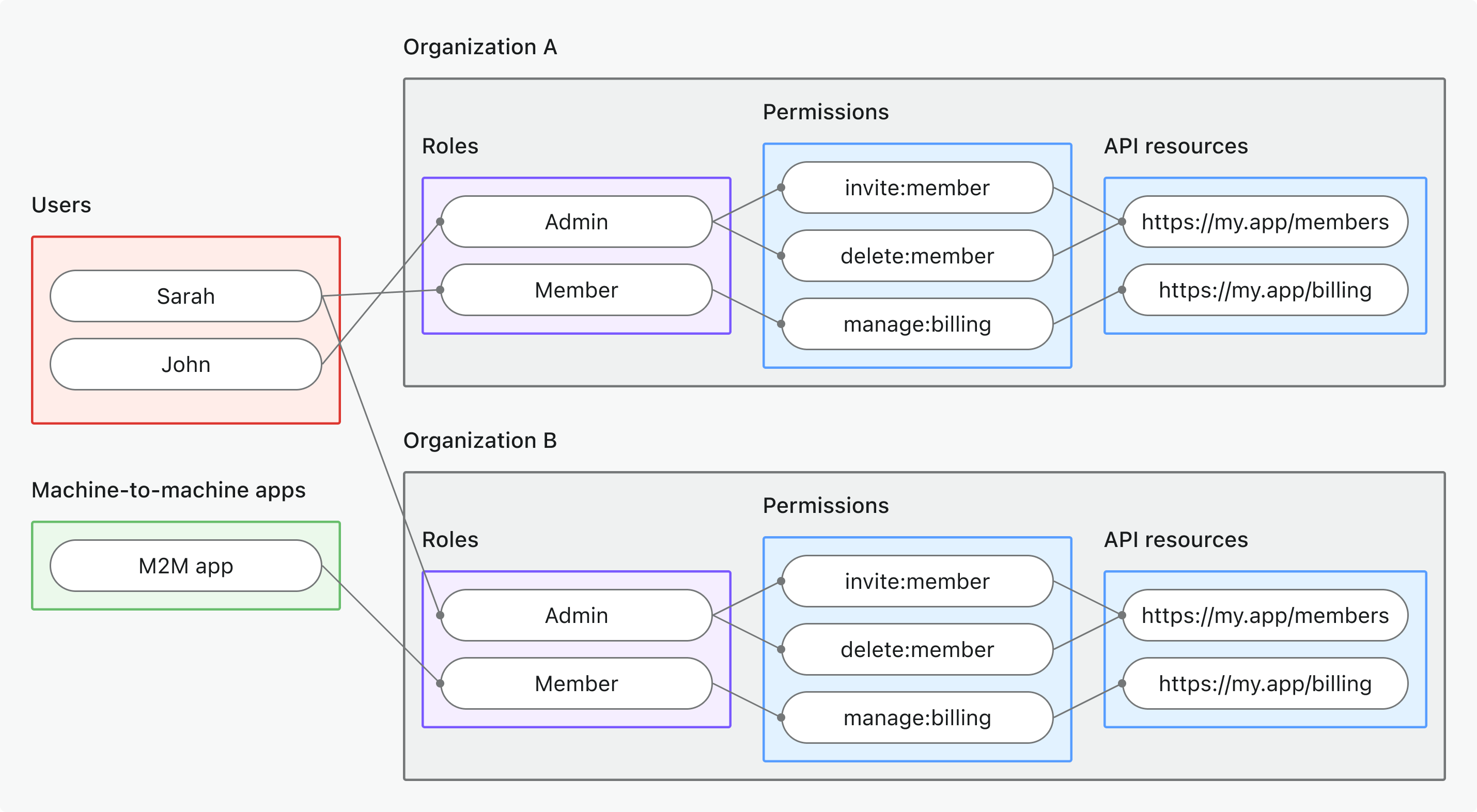
- 使用场景: 保护在特定组织 (Organization) 上下文中可访问的 API 资源
- 令牌类型: 具有 API 资源受众 (Audience) + 组织 (Organization) 上下文的组织令牌 (Organization token)
- 示例: 多租户 API、组织 (Organization) 范围的数据端点、租户专属微服务
- 最适合: API 数据以组织 (Organization) 为范围的多租户 SaaS
- 了解更多: 保护组织级 API 资源
💡 在继续之前选择你的模型 —— 本指南后续内容将以你选择的方式为参考。
快速准备步骤
配置 Logto 资源和权限
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织(非 API)权限
- 组织级 API 资源
- 创建 API 资源:前往 控制台 → API 资源 并注册你的 API(例如,
https://api.yourapp.com) - 定义权限:添加如
read:products、write:orders等权限(Scopes)——参见 定义带权限的 API 资源 - 创建全局角色:前往 控制台 → 角色 并创建包含你的 API 权限的角色——参见 配置全局角色
- 分配角色:将角色分配给需要访问 API 的用户或 M2M 应用程序
- 定义组织权限:在组织模板中创建如
invite:member、manage:billing等非 API 组织权限 - 设置组织角色:在组织模板中配置组织专属角色,并为其分配权限
- 分配组织角色:在每个组织上下文中将用户分配到组织角色
- 创建 API 资源:如上注册你的 API 资源,但它将在组织上下文中使用
- 定义权限:添加如
read:data、write:settings等限定于组织上下文的权限(Scopes) - 配置组织模板:设置包含你的 API 资源权限的组织角色
- 分配组织角色:将用户或 M2M 应用程序分配到包含 API 权限的组织角色
- 多租户设置:确保你的 API 能处理组织范围的数据和校验
从我们的 基于角色的访问控制 (RBAC) 指南 开始,获取分步设置说明。
更新你的客户端应用
在客户端请求合适的权限(Scopes):
- 用户认证 (Authentication):更新你的应用 → 以请求你的 API 权限和 / 或组织上下文
- 机器对机器:为服务器间访问 配置 M2M 权限(Scopes)→
通常需要在客户端配置中更新以下一项或多项:
- OAuth 流程中的
scope参数 - 用于 API 资源访问的
resource参数 - 用于组织上下文的
organization_id
请确保你测试的用户或 M2M 应用已被分配包含所需 API 权限的合适角色或组织角色。
初始化你的 API 项目
要初始化一个新的 Rocket 项目,创建一个目录并设置基本结构:
cargo new your-api-name
cd your-api-name
在你的 Cargo.toml 中添加 Rocket 依赖:
[dependencies]
rocket = { version = "0.5", features = ["json"] }
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
serde_json = "1.0"
创建一个基础的 Rocket 应用程序:
use rocket::{get, launch, routes, serde::json::Json};
use serde_json::{json, Value};
#[get("/")]
fn hello_handler() -> Json<Value> {
Json(json!({ "message": "Hello from Rocket" }))
}
#[launch]
fn rocket() -> _ {
rocket::build()
.mount("/", routes![hello_handler])
}
启动开发服务器:
cargo run
更多关于如何设置路由、请求守卫以及其他功能的详细信息,请参考 Rocket 文档。
初始化常量和工具方法
在你的代码中定义必要的常量和工具函数,用于处理令牌的提取和校验。一个有效的请求必须包含 Authorization 请求头,格式为 Bearer <访问令牌 (Access token)>。
use serde::{Deserialize, Serialize};
use std::fmt;
pub const JWKS_URI: &str = "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/jwks";
pub const ISSUER: &str = "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc";
#[derive(Debug, Clone, Serialize, Deserialize)]
pub struct AuthInfo {
pub sub: String,
pub client_id: Option<String>,
pub organization_id: Option<String>,
pub scopes: Vec<String>,
pub audience: Vec<String>,
}
impl AuthInfo {
pub fn new(
sub: String,
client_id: Option<String>,
organization_id: Option<String>,
scopes: Vec<String>,
audience: Vec<String>,
) -> Self {
Self {
sub,
client_id,
organization_id,
scopes,
audience,
}
}
}
#[derive(Debug)]
pub struct AuthorizationError {
pub message: String,
pub status_code: u16,
}
impl AuthorizationError {
pub fn new(message: impl Into<String>) -> Self {
Self {
message: message.into(),
status_code: 403,
}
}
pub fn with_status(message: impl Into<String>, status_code: u16) -> Self {
Self {
message: message.into(),
status_code,
}
}
}
impl fmt::Display for AuthorizationError {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter<'_>) -> fmt::Result {
write!(f, "{}", self.message)
}
}
impl std::error::Error for AuthorizationError {}
pub fn extract_bearer_token(authorization: Option<&str>) -> Result<&str, AuthorizationError> {
let auth_header = authorization.ok_or_else(|| {
AuthorizationError::with_status("Authorization header is missing", 401)
})?;
if !auth_header.starts_with("Bearer ") {
return Err(AuthorizationError::with_status(
"Authorization header must start with \"Bearer \"",
401,
));
}
Ok(&auth_header[7..]) // 移除 'Bearer ' 前缀
}
获取你的 Logto 租户信息
你需要以下数值来验证 Logto 签发的令牌:
- JSON Web Key Set (JWKS) URI:Logto 公钥的 URL,用于验证 JWT 签名。
- 发行者 (Issuer):期望的发行者 (Issuer) 值(Logto 的 OIDC URL)。
首先,找到你的 Logto 租户的端点。你可以在多个地方找到它:
- 在 Logto 控制台的 设置 → 域名 下。
- 在你在 Logto 配置的任何应用程序设置中,设置 → 端点与凭证。
从 OpenID Connect 发现端点获取
这些数值可以从 Logto 的 OpenID Connect 发现端点获取:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/.well-known/openid-configuration
以下是一个示例响应(为简洁省略了其他字段):
{
"jwks_uri": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/jwks",
"issuer": "https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc"
}
在代码中硬编码(不推荐)
由于 Logto 不允许自定义 JWKS URI 或发行者 (Issuer),你可以在代码中硬编码这些数值。但对于生产环境的应用程序,这并不推荐,因为如果将来某些配置发生变化,可能会增加维护成本。
- JWKS URI:
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc/jwks - 发行者 (Issuer):
https://<your-logto-endpoint>/oidc
校验令牌和权限
在提取令牌并获取 OIDC 配置后,请验证以下内容:
- 签名: JWT 必须有效且由 Logto(通过 JWKS)签名。
- 发行者 (Issuer): 必须与你的 Logto 租户的发行者 (Issuer) 匹配。
- 受众 (Audience): 必须与你在 Logto 中注册的 API 的资源指示器 (resource indicator) 匹配,或在适用时匹配组织 (organization) 上下文。
- 过期时间: 令牌必须未过期。
- 权限 (Scopes): 令牌必须包含你的 API / 操作所需的权限 (scopes)。权限 (scopes) 是
scope声明中的以空格分隔的字符串。 - 组织 (Organization) 上下文: 如果保护的是组织级 API 资源,请验证
organization_id声明。
参见 JSON Web Token 以了解更多关于 JWT 结构和声明 (Claims) 的信息。
针对每种权限 (Permission) 模型需要检查什么
不同的权限 (Permission) 模型,其声明 (Claims) 和验证规则也不同:
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (非 API) 权限
- 组织级 API 资源
- 受众 (Audience) 声明 (
aud): API 资源指示器 (resource indicator) - 组织 (Organization) 声明 (
organization_id): 不存在 - 需要检查的权限 (Scopes) (
scope): API 资源权限 (permissions)
- 受众 (Audience) 声明 (
aud):urn:logto:organization:<id>(组织上下文在aud声明中) - 组织 (Organization) 声明 (
organization_id): 不存在 - 需要检查的权限 (Scopes) (
scope): 组织权限 (permissions)
- 受众 (Audience) 声明 (
aud): API 资源指示器 (resource indicator) - 组织 (Organization) 声明 (
organization_id): 组织 ID(必须与请求匹配) - 需要检查的权限 (Scopes) (
scope): API 资源权限 (permissions)
对于非 API 的组织 (Organization) 权限 (Permissions),组织上下文由 aud 声明表示
(例如,urn:logto:organization:abc123)。organization_id 声明仅在组织级 API 资源令牌中存在。
对于安全的多租户 API,请始终同时验证权限 (scopes) 和上下文(受众 (audience)、组织 (organization))。
添加校验逻辑
我们使用 jsonwebtoken 来验证 JWT。请在你的 Cargo.toml 中添加所需依赖:
[dependencies]
jsonwebtoken = "9.0"
serde = { version = "1.0", features = ["derive"] }
serde_json = "1.0"
reqwest = { version = "0.11", features = ["json"] }
tokio = { version = "1.0", features = ["full"] }
首先,添加这些用于处理 JWT 验证的通用工具:
use crate::{AuthInfo, AuthorizationError, ISSUER, JWKS_URI};
use jsonwebtoken::{decode, decode_header, Algorithm, DecodingKey, Validation};
use serde_json::Value;
use std::collections::HashMap;
pub struct JwtValidator {
jwks: HashMap<String, DecodingKey>,
}
impl JwtValidator {
pub async fn new() -> Result<Self, AuthorizationError> {
let jwks = Self::fetch_jwks().await?;
Ok(Self { jwks })
}
async fn fetch_jwks() -> Result<HashMap<String, DecodingKey>, AuthorizationError> {
let response = reqwest::get(JWKS_URI).await.map_err(|e| {
AuthorizationError::with_status(format!("Failed to fetch JWKS: {}", e), 401)
})?;
let jwks: Value = response.json().await.map_err(|e| {
AuthorizationError::with_status(format!("Failed to parse JWKS: {}", e), 401)
})?;
let mut keys = HashMap::new();
if let Some(keys_array) = jwks["keys"].as_array() {
for key in keys_array {
if let (Some(kid), Some(kty), Some(n), Some(e)) = (
key["kid"].as_str(),
key["kty"].as_str(),
key["n"].as_str(),
key["e"].as_str(),
) {
if kty == "RSA" {
if let Ok(decoding_key) = DecodingKey::from_rsa_components(n, e) {
keys.insert(kid.to_string(), decoding_key);
}
}
}
}
}
if keys.is_empty() {
return Err(AuthorizationError::with_status("No valid keys found in JWKS", 401));
}
Ok(keys)
}
pub fn validate_jwt(&self, token: &str) -> Result<AuthInfo, AuthorizationError> {
let header = decode_header(token).map_err(|e| {
AuthorizationError::with_status(format!("Invalid token header: {}", e), 401)
})?;
let kid = header.kid.ok_or_else(|| {
AuthorizationError::with_status("Token missing kid claim", 401)
})?;
let key = self.jwks.get(&kid).ok_or_else(|| {
AuthorizationError::with_status("Unknown key ID", 401)
})?;
let mut validation = Validation::new(Algorithm::RS256);
validation.set_issuer(&[ISSUER]);
validation.validate_aud = false; // 我们会手动验证受众 (Audience)
let token_data = decode::<Value>(token, key, &validation).map_err(|e| {
AuthorizationError::with_status(format!("Invalid token: {}", e), 401)
})?;
let claims = token_data.claims;
self.verify_payload(&claims)?;
Ok(self.create_auth_info(claims))
}
fn verify_payload(&self, claims: &Value) -> Result<(), AuthorizationError> {
// 在这里根据权限模型实现你的验证逻辑
// 具体内容将在下方权限模型部分展示
Ok(())
}
fn create_auth_info(&self, claims: Value) -> AuthInfo {
let scopes = claims["scope"]
.as_str()
.map(|s| s.split(' ').map(|s| s.to_string()).collect())
.unwrap_or_default();
let audience = match &claims["aud"] {
Value::Array(arr) => arr.iter().filter_map(|v| v.as_str().map(|s| s.to_string())).collect(),
Value::String(s) => vec![s.clone()],
_ => vec![],
};
AuthInfo::new(
claims["sub"].as_str().unwrap_or_default().to_string(),
claims["client_id"].as_str().map(|s| s.to_string()),
claims["organization_id"].as_str().map(|s| s.to_string()),
scopes,
audience,
)
}
}
然后,实现中间件以验证访问令牌 (Access token):
use crate::{AuthInfo, AuthorizationError, extract_bearer_token};
use crate::jwt_validator::JwtValidator;
use rocket::{
http::Status,
outcome::Outcome,
request::{self, FromRequest, Request},
State,
};
#[rocket::async_trait]
impl<'r> FromRequest<'r> for AuthInfo {
type Error = AuthorizationError;
async fn from_request(req: &'r Request<'_>) -> request::Outcome<Self, Self::Error> {
let validator = match req.guard::<&State<JwtValidator>>().await {
Outcome::Success(validator) => validator,
Outcome::Failure((status, _)) => {
return Outcome::Failure((
status,
AuthorizationError::with_status("未找到 JWT 校验器 (JWT validator not found)", 500),
))
}
Outcome::Forward(()) => {
return Outcome::Forward(())
}
};
let authorization = req.headers().get_one("authorization");
match extract_bearer_token(authorization)
.and_then(|token| validator.validate_jwt(token))
{
Ok(auth_info) => Outcome::Success(auth_info),
Err(e) => {
let status = Status::from_code(e.status_code).unwrap_or(Status::Forbidden);
Outcome::Failure((status, e))
}
}
}
}
根据你的权限模型,在 JwtValidator 中实现相应的验证逻辑:
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (非 API) 权限
- 组织级 API 资源
fn verify_payload(&self, claims: &Value) -> Result<(), AuthorizationError> {
// 检查受众 (Audience) 声明是否匹配你的 API 资源指示器
let audiences = match &claims["aud"] {
Value::Array(arr) => arr.iter().filter_map(|v| v.as_str()).collect::<Vec<_>>(),
Value::String(s) => vec![s.as_str()],
_ => vec![],
};
if !audiences.contains(&"https://your-api-resource-indicator") {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Invalid audience"));
}
// 检查全局 API 资源所需的权限 (Scopes)
let required_scopes = vec!["api:read", "api:write"]; // 替换为你实际需要的权限
let scopes = claims["scope"]
.as_str()
.map(|s| s.split(' ').collect::<Vec<_>>())
.unwrap_or_default();
for required_scope in &required_scopes {
if !scopes.contains(required_scope) {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Insufficient scope"));
}
}
Ok(())
}
fn verify_payload(&self, claims: &Value) -> Result<(), AuthorizationError> {
// 检查受众 (Audience) 声明是否符合组织格式
let audiences = match &claims["aud"] {
Value::Array(arr) => arr.iter().filter_map(|v| v.as_str()).collect::<Vec<_>>(),
Value::String(s) => vec![s.as_str()],
_ => vec![],
};
let has_org_audience = audiences.iter().any(|aud| aud.starts_with("urn:logto:organization:"));
if !has_org_audience {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Invalid audience for organization permissions"));
}
// 检查组织 ID 是否与上下文匹配(你可能需要从请求上下文中提取)
let expected_org_id = "your-organization-id"; // 从请求上下文中提取
let expected_aud = format!("urn:logto:organization:{}", expected_org_id);
if !audiences.contains(&expected_aud.as_str()) {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Organization ID mismatch"));
}
// 检查所需的组织权限 (Scopes)
let required_scopes = vec!["invite:users", "manage:settings"]; // 替换为你实际需要的权限
let scopes = claims["scope"]
.as_str()
.map(|s| s.split(' ').collect::<Vec<_>>())
.unwrap_or_default();
for required_scope in &required_scopes {
if !scopes.contains(required_scope) {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Insufficient organization scope"));
}
}
Ok(())
}
fn verify_payload(&self, claims: &Value) -> Result<(), AuthorizationError> {
// 检查受众 (Audience) 声明是否匹配你的 API 资源指示器
let audiences = match &claims["aud"] {
Value::Array(arr) => arr.iter().filter_map(|v| v.as_str()).collect::<Vec<_>>(),
Value::String(s) => vec![s.as_str()],
_ => vec![],
};
if !audiences.contains(&"https://your-api-resource-indicator") {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Invalid audience for organization-level API resources"));
}
// 检查组织 ID 是否与上下文匹配(你可能需要从请求上下文中提取)
let expected_org_id = "your-organization-id"; // 从请求上下文中提取
let org_id = claims["organization_id"].as_str().unwrap_or_default();
if expected_org_id != org_id {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Organization ID mismatch"));
}
// 检查组织级 API 资源所需的权限 (Scopes)
let required_scopes = vec!["api:read", "api:write"]; // 替换为你实际需要的权限
let scopes = claims["scope"]
.as_str()
.map(|s| s.split(' ').collect::<Vec<_>>())
.unwrap_or_default();
for required_scope in &required_scopes {
if !scopes.contains(required_scope) {
return Err(AuthorizationError::new("Insufficient organization-level API scopes"));
}
}
Ok(())
}
将中间件应用到你的 API
现在,将中间件应用到你的受保护 API 路由。
use rocket::{get, launch, routes, serde::json::Json};
use serde_json::{json, Value};
mod lib;
mod jwt_validator;
mod guards;
use lib::AuthInfo;
use jwt_validator::JwtValidator;
#[get("/api/protected")]
fn protected_handler(auth: AuthInfo) -> Json<Value> {
// 直接从请求守卫中访问认证 (Authentication) 信息
Json(json!({ "auth": auth }))
}
#[launch]
async fn rocket() -> _ {
let validator = JwtValidator::new().await.expect("初始化 JWT 验证器失败");
rocket::build()
.manage(validator)
.mount("/", routes![protected_handler])
}
测试你的受保护 API
获取访问令牌 (Access tokens)
从你的客户端应用程序获取: 如果你已经完成了客户端集成,你的应用可以自动获取令牌。提取访问令牌 (Access token),并在 API 请求中使用它。
使用 curl / Postman 进行测试:
-
用户令牌: 使用你的客户端应用的开发者工具,从 localStorage 或网络面板复制访问令牌 (Access token)
-
机器对机器令牌: 使用客户端凭证流。以下是一个使用 curl 的非规范示例:
curl -X POST https://your-tenant.logto.app/oidc/token \
-H "Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" \
-d "grant_type=client_credentials" \
-d "client_id=your-m2m-client-id" \
-d "client_secret=your-m2m-client-secret" \
-d "resource=https://your-api-resource-indicator" \
-d "scope=api:read api:write"你可能需要根据你的 API 资源和权限调整
resource和scope参数;如果你的 API 是组织范围的,还可能需要organization_id参数。
需要查看令牌内容?使用我们的 JWT 解码器 来解码和验证你的 JWT。
测试受保护的端点
有效令牌请求
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
预期响应:
{
"auth": {
"sub": "user123",
"clientId": "app456",
"organizationId": "org789",
"scopes": ["api:read", "api:write"],
"audience": ["https://your-api-resource-indicator"]
}
}
缺少令牌
curl http://localhost:3000/api/protected
预期响应 (401):
{
"error": "Authorization header is missing"
}
无效令牌
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer invalid-token" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
预期响应 (401):
{
"error": "Invalid token"
}
权限模型相关测试
- 全局 API 资源
- 组织 (非 API) 权限
- 组织级 API 资源
针对受全局权限保护的 API 的测试场景:
- 有效权限 (Scopes): 使用包含所需 API 权限(如
api:read、api:write)的令牌进行测试 - 缺少权限 (Scopes): 当令牌缺少所需权限时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 受众 (Audience) 错误: 当受众与 API 资源不匹配时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
# 缺少权限的令牌 - 预期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-without-required-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
针对组织特定访问控制的测试场景:
- 有效组织令牌 (Organization token): 使用包含正确组织上下文(组织 ID 和权限)的令牌进行测试
- 缺少权限 (Scopes): 当用户没有请求操作的权限时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 组织错误: 当受众与组织上下文(
urn:logto:organization:<organization_id>)不匹配时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
# 错误组织的令牌 - 预期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer token-for-different-organization" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
结合 API 资源验证与组织上下文的测试场景:
- 有效组织 + API 权限: 使用同时包含组织上下文和所需 API 权限的令牌进行测试
- 缺少 API 权限: 当组织令牌缺少所需 API 权限时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 组织错误: 使用来自不同组织的令牌访问 API 时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
- 受众 (Audience) 错误: 当受众与组织级 API 资源不匹配时,预期返回 403 Forbidden
# 组织令牌缺少 API 权限 - 预期 403
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer organization-token-without-api-scopes" \
http://localhost:3000/api/protected
延伸阅读
RBAC 实践:为你的应用实现安全授权 (Authorization)
构建多租户 SaaS 应用:从设计到实现的完整指南