Logto is an Auth0 alternative designed for modern apps and SaaS products. It offers both Cloud and Open-source services to help you quickly launch your identity and management (IAM) system. Enjoy authentication, authorization, and multi-tenant management all in one.
We recommend starting with a free development tenant on Logto Cloud. This allows you to explore all the features easily.
In this article, we will go through the steps to quickly build the Facebook sign-in experience (user authentication) with .NET Core (Blazor Server) and Logto.
Prerequisites
- A running Logto instance. Check out the introduction page to get started.
- Basic knowledge of .NET Core (Blazor Server).
- A usable Facebook account.
Create an application in Logto
Logto is based on OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication and OAuth 2.0 authorization. It supports federated identity management across multiple applications, commonly called Single Sign-On (SSO).
To create your Traditional web application, simply follow these steps:
- Open the Logto Console. In the "Get started" section, click the "View all" link to open the application frameworks list. Alternatively, you can navigate to Logto Console > Applications, and click the "Create application" button.
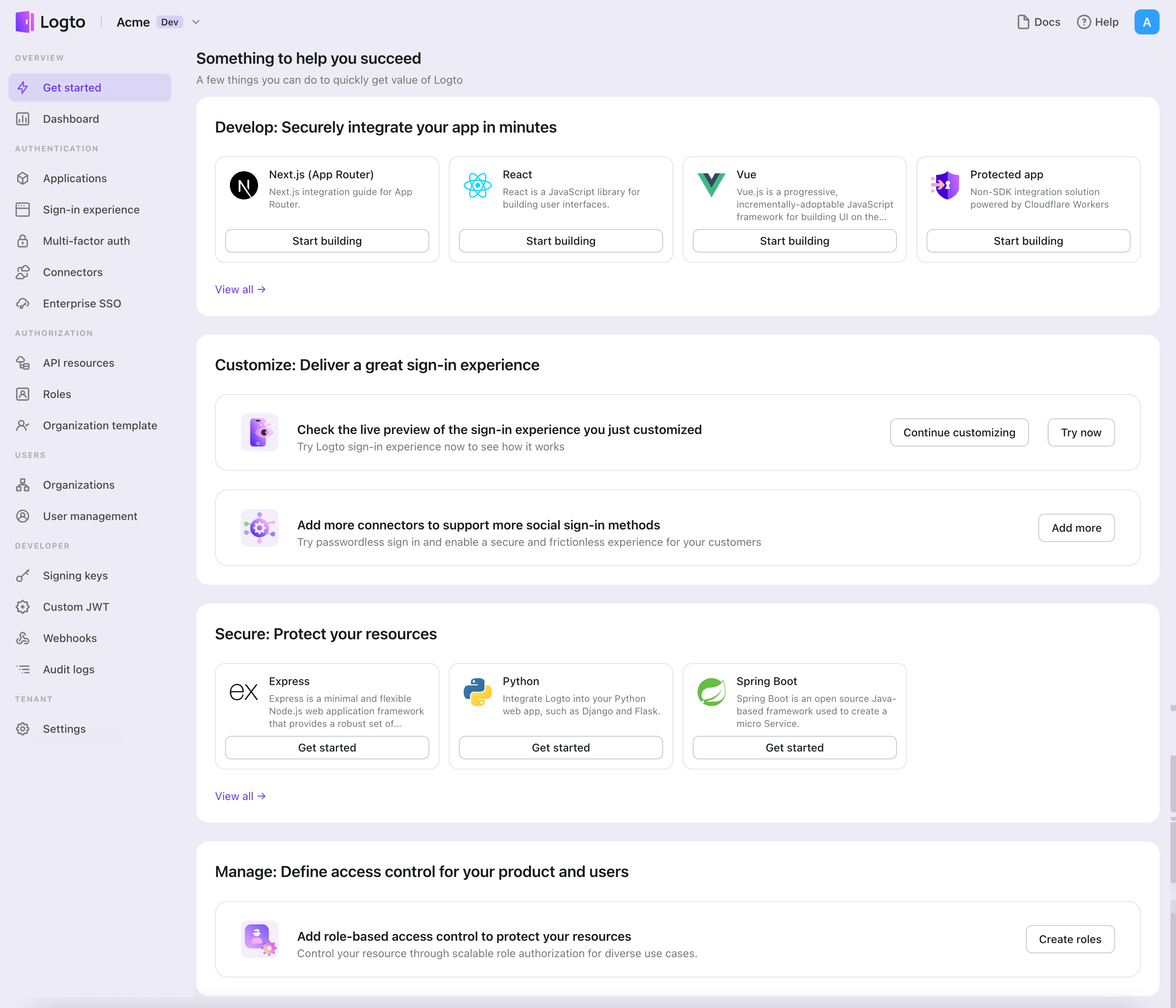
- In the opening modal, click the "Traditional web" section or filter all the available "Traditional web" frameworks using the quick filter checkboxes on the left. Click the ".Net Core (Blazor Server)" framework card to start creating your application.
- Enter the application name, e.g., "Bookstore," and click "Create application".
🎉 Ta-da! You just created your first application in Logto. You'll see a congrats page which includes a detailed integration guide. Follow the guide to see what the experience will be in your application.
Integrate .Net Core (Blazor Server) with Logto
- The following demonstration is built on .NET Core 8.0. The SDK is compatible with .NET 6.0 or higher.
- The .NET Core sample projects are available in the GitHub repository.
Installation
Add the NuGet package to your project:
dotnet add package Logto.AspNetCore.Authentication
Add Logto authentication
Open Startup.cs (or Program.cs) and add the following code to register Logto authentication services:
using Logto.AspNetCore.Authentication;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
builder.Services.AddLogtoAuthentication(options =>
{
options.Endpoint = builder.Configuration["Logto:Endpoint"]!;
options.AppId = builder.Configuration["Logto:AppId"]!;
options.AppSecret = builder.Configuration["Logto:AppSecret"];
});
The AddLogtoAuthentication method will do the following things:
- Set the default authentication scheme to
LogtoDefaults.CookieScheme. - Set the default challenge scheme to
LogtoDefaults.AuthenticationScheme. - Set the default sign-out scheme to
LogtoDefaults.AuthenticationScheme. - Add cookie and OpenID Connect authentication handlers to the authentication scheme.
Sign-in and sign-out flows
Before we proceed, there are two confusing terms in the .NET Core authentication middleware that we need to clarify:
- CallbackPath: The URI that Logto will redirect the user back to after the user has signed in (the "redirect URI" in Logto)
- RedirectUri: The URI that will be redirected to after necessary actions have been taken in the Logto authentication middleware.
The sign-in process can be illustrated as follows:
Similarly, .NET Core also has SignedOutCallbackPath and RedirectUri for the sign-out flow.
For the sake of clarity, we'll refer them as follows:
| Term we use | .NET Core term |
|---|---|
| Logto redirect URI | CallbackPath |
| Logto post sign-out redirect URI | SignedOutCallbackPath |
| Application redirect URI | RedirectUri |
Regarding redirect-based sign-in
- This authentication process follows the OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol, and Logto enforces strict security measures to protect user sign-in.
- If you have multiple apps, you can use the same identity provider (Logto). Once the user signs in to one app, Logto will automatically complete the sign-in process when the user accesses another app.
To learn more about the rationale and benefits of redirect-based sign-in, see Logto sign-in experience explained.
Configure redirect URIs
In the following code snippets, we assume your app is running on http://localhost:3000/.
First, let's configure the Logto redirect URI. Add the following URI to the "Redirect URIs" list in the Logto application details page:
http://localhost:3000/Callback
To configure the Logto post sign-out redirect URI, add the following URI to the "Post sign-out redirect URIs" list in the Logto application details page:
http://localhost:3000/SignedOutCallback
Change the default paths
The Logto redirect URI has a default path of /Callback, and the Logto post sign-out redirect URI has a default path of /SignedOutCallback.
You can leave them as are if there's no special requirement. If you want to change it, you can set the CallbackPath and SignedOutCallbackPath property for LogtoOptions:
builder.Services.AddLogtoAuthentication(options =>
{
// Other configurations...
options.CallbackPath = "/Foo";
options.SignedOutCallbackPath = "/Bar";
});
Remember to update the value in the Logto application details page accordingly.
Add routes
Since Blazor Server uses SignalR to communicate between the server and the client, this means methods that directly manipulate the HTTP context (like issuing challenges or redirects) don't work as expected when called from a Blazor component.
To make it right, we need to explicitly add two endpoints for sign-in and sign-out redirects:
app.MapGet("/SignIn", async context =>
{
if (!(context.User?.Identity?.IsAuthenticated ?? false))
{
await context.ChallengeAsync(new AuthenticationProperties { RedirectUri = "/" });
} else {
context.Response.Redirect("/");
}
});
app.MapGet("/SignOut", async context =>
{
if (context.User?.Identity?.IsAuthenticated ?? false)
{
await context.SignOutAsync(new AuthenticationProperties { RedirectUri = "/" });
} else {
context.Response.Redirect("/");
}
});
Now we can redirect to these endpoints to trigger sign-in and sign-out.
Implement sign-in/sign-out buttons
In the Razor component, add the following code:
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization
@using System.Security.Claims
@inject AuthenticationStateProvider AuthenticationStateProvider
@inject NavigationManager NavigationManager
@* ... *@
<p>Is authenticated: @User.Identity?.IsAuthenticated</p>
@if (User.Identity?.IsAuthenticated == true)
{
<button @onclick="SignOut">Sign out</button>
}
else
{
<button @onclick="SignIn">Sign in</button>
}
@* ... *@
@code {
private ClaimsPrincipal? User { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
var authState = await AuthenticationStateProvider.GetAuthenticationStateAsync();
User = authState.User;
}
private void SignIn()
{
NavigationManager.NavigateTo("/SignIn", forceLoad: true);
}
private void SignOut()
{
NavigationManager.NavigateTo("/SignOut", forceLoad: true);
}
}
Explanation:
- The injected
AuthenticationStateProvideris used to get the current user's authentication state, and populate theUserproperty. - The
SignInandSignOutmethods are used to redirect the user to the sign-in and sign-out endpoints respectively. Since the nature of Blazor Server, we need to useNavigationManagerwith force load to trigger the redirection.
The page will show the "Sign in" button if the user is not authenticated, and show the "Sign out" button if the user is authenticated.
The <AuthorizeView /> component
Alternatively, you can use the AuthorizeView component to conditionally render content based on the user's authentication state. This component is useful when you want to show different content to authenticated and unauthenticated users.
In your Razor component, add the following code:
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Components.Authorization
@* ... *@
<AuthorizeView>
<Authorized>
<p>Name: @User?.Identity?.Name</p>
@* Content for authenticated users *@
</Authorized>
<NotAuthorized>
@* Content for unauthenticated users *@
</NotAuthorized>
</AuthorizeView>
@* ... *@
The AuthorizeView component requires a cascading parameter of type Task<AuthenticationState>. A direct way to get this parameter is to add the <CascadingAuthenticationState> component. However, due to the nature of Blazor Server, we cannot simply add the component to the layout or the root component (it may not work as expected). Instead, we can add the following code to the builder (Program.cs or Startup.cs) to provide the cascading parameter:
builder.Services.AddCascadingAuthenticationState();
Then you can use the AuthorizeView component in every component that needs it.
Checkpoint: Test your application
Now, you can test your application:
- Run your application, you will see the sign-in button.
- Click the sign-in button, the SDK will init the sign-in process and redirect you to the Logto sign-in page.
- After you signed in, you will be redirected back to your application and see the sign-out button.
- Click the sign-out button to clear token storage and sign out.
Add Facebook connector
To enable quick sign-in and improve user conversion, connect with .Net Core (Blazor Server) as an identity provider. The Logto social connector helps you establish this connection in minutes by allowing several parameter inputs.
To add a social connector, simply follow these steps:
- Navigate to Console > Connectors > Social Connectors.
- Click "Add social connector" and select "Facebook".
- Follow the README guide and complete required fields and customize settings.
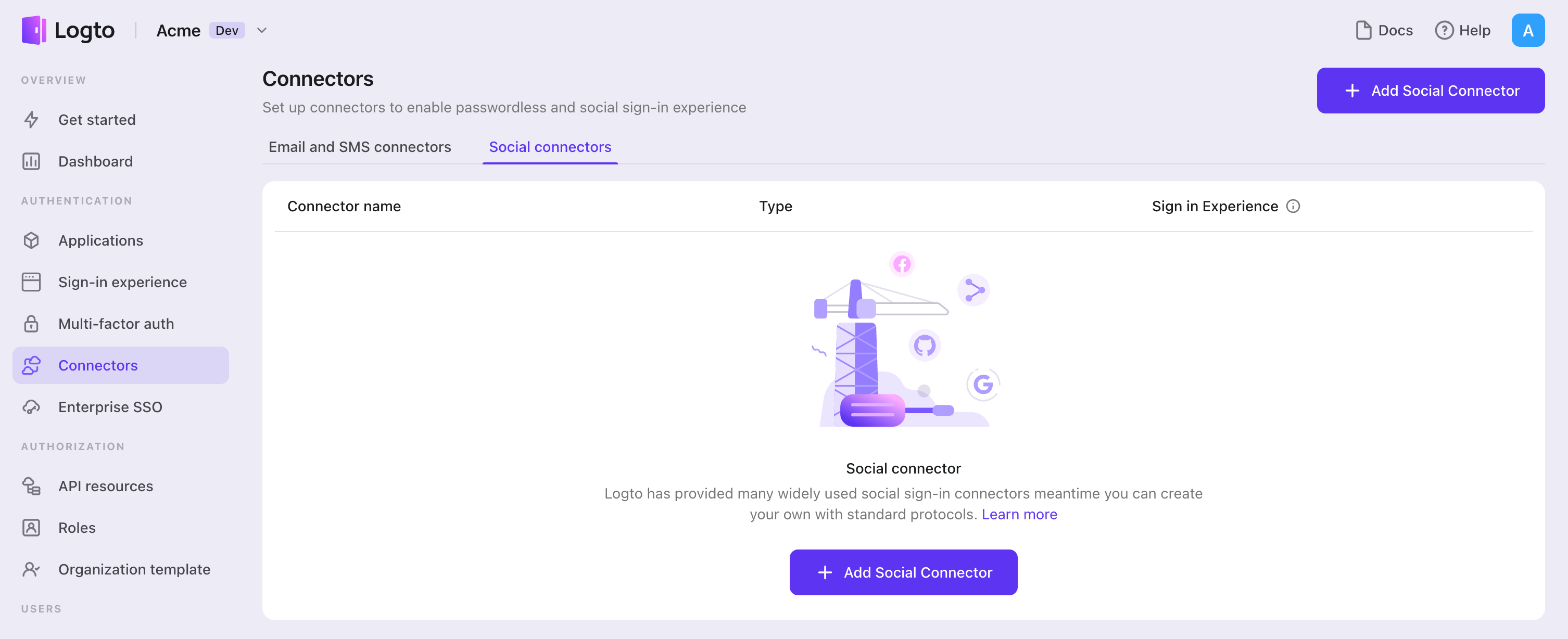
If you are following the in-place Connector guide, you can skip the next section.
Set up Facebook login
Register a Facebook developer account
Register as a Facebook Developer if you don't already have one
Set up a Facebook app
- Visit the Apps page.
- Click your existing app or create a new one if needed.
- The selected app type is up to you, but it should have the product Facebook Login.
- On the app dashboard page, scroll to the "Add a product" section and click the "Set up" button on the "Facebook Login" card.
- Skip the Facebook Login Quickstart page, and click the sidebar -> "Products" -> "Facebook Login" -> "Settings".
- In the Facebook Login Settings page, fill
${your_logto_origin}/callback/${connector_id}in the "Valid OAuth Redirect URIs" field. Theconnector_idcan be found on the top bar of the Logto Admin Console connector details page. E.g.:https://logto.dev/callback/${connector_id}for productionhttps://localhost:3001/callback/${connector_id}for testing in the local environment
- Click the "Save changes" button at the bottom right corner.
Compose the connector JSON
- In the Facebook app dashboard page, click the sidebar -> "Settings" -> "Basic".
- You will see the "App ID" and "App secret" on the panel.
- Click the "Show" button following the App secret input box to copy its content.
- Fill out the Logto connector settings:
- Fill out the
clientIdfield with the string from App ID. - Fill out the
clientSecretfield with the string from App secret. - Fill out the
scopefield with a comma or space separated list of permissions in string. If you do not specify a scope, the default scope isemail,public_profile.
- Fill out the
Test sign-in with Facebook's test users
You can use the accounts of the test, developer, and admin users to test sign-in with the related app under both development and live app modes.
You can also take the app live directly so that any Facebook user can sign in with the app.
- In the app dashboard page, click the sidebar -> "Roles" -> "Test Users".
- Click the "Create test users" button to create a testing user.
- Click the "Options" button of the existing test user, and you will see more operations, e.g., "Change name and password".
Publish Facebook sign-in settings
Usually, only the test, admin, and developer users can sign in with the related app under development mode.
To enable normal Facebook users sign-in with the app in the production environment, you maybe need to switch your Facebook app to live mode, depending on the app type. E.g., the pure business type app doesn't have the "live" switch button, but it won't block your use.
- In the Facebook app dashboard page, click the sidebar -> "Settings" -> "Basic".
- Fill out the "Privacy Policy URL" and "User data deletion" fields on the panel if required.
- Click the "Save changes" button at the bottom right corner.
- Click the "Live" switch button on the app top bar.
Config types
| Name | Type |
|---|---|
| clientId | string |
| clientSecret | string |
| scope | string |
Save your configuration
Double check you have filled out necessary values in the Logto connector configuration area. Click "Save and Done" (or "Save changes") and the Facebook connector should be available now.
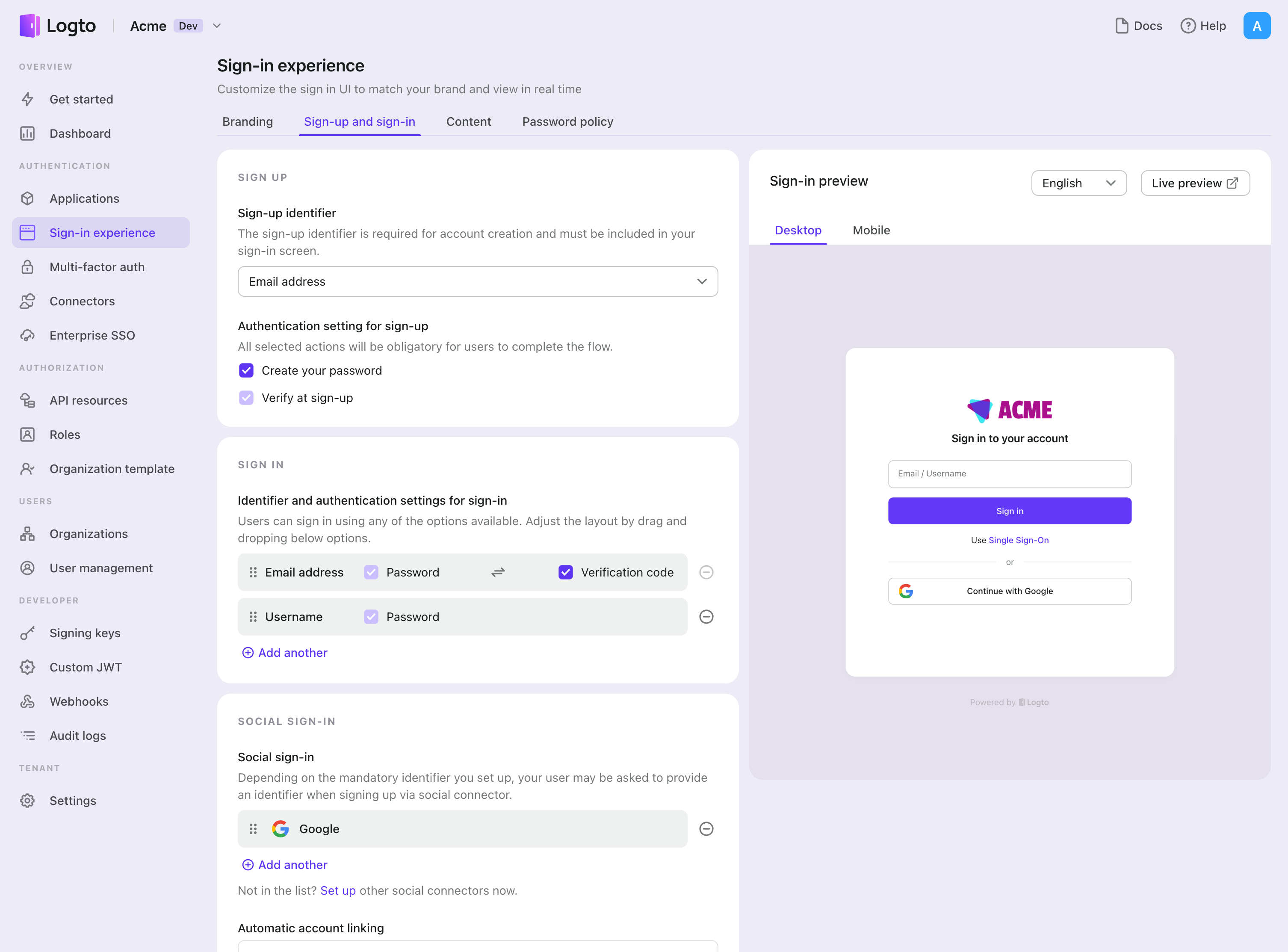
Enable Facebook connector in Sign-in Experience
Once you create a social connector successfully, you can enable it as a "Continue with Facebook" button in Sign-in Experience.
- Navigate to Console > Sign-in experience > Sign-up and sign-in.
- (Optional) Choose "Not applicable" for sign-up identifier if you need social login only.
- Add configured Facebook connector to the "Social sign-in" section.
Testing and Validation
Return to your .NET Core (Blazor Server) app. You should now be able to sign in with Facebook. Enjoy!
Further readings
End-user flows: Logto provides a out-of-the-box authentication flows including MFA and enterprise SSO, along with powerful APIs for flexible implementation of account settings, security verification, and multi-tenant experience.
Authorization: Authorization defines the actions a user can do or resources they can access after being authenticated. Explore how to protect your API for native and single-page applications and implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC).
Organizations: Particularly effective in multi-tenant SaaS and B2B apps, the organization feature enable tenant creation, member management, organization-level RBAC, and just-in-time-provisioning.
Customer IAM series Our serial blog posts about Customer (or Consumer) Identity and Access Management, from 101 to advanced topics and beyond.