Logto is an Auth0 alternative designed for modern apps and SaaS products. It offers both Cloud and Open-source services to help you quickly launch your identity and management (IAM) system. Enjoy authentication, authorization, and multi-tenant management all in one.
We recommend starting with a free development tenant on Logto Cloud. This allows you to explore all the features easily.
In this article, we will go through the steps to quickly build the Apple sign-in experience (user authentication) with Vanilla JS and Logto.
Prerequisites
- A running Logto instance. Check out the introduction page to get started.
- Basic knowledge of Vanilla JS.
- A usable Apple account.
Create an application in Logto
Logto is based on OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication and OAuth 2.0 authorization. It supports federated identity management across multiple applications, commonly called Single Sign-On (SSO).
To create your Single page app application, simply follow these steps:
- Open the Logto Console. In the "Get started" section, click the "View all" link to open the application frameworks list. Alternatively, you can navigate to Logto Console > Applications, and click the "Create application" button.
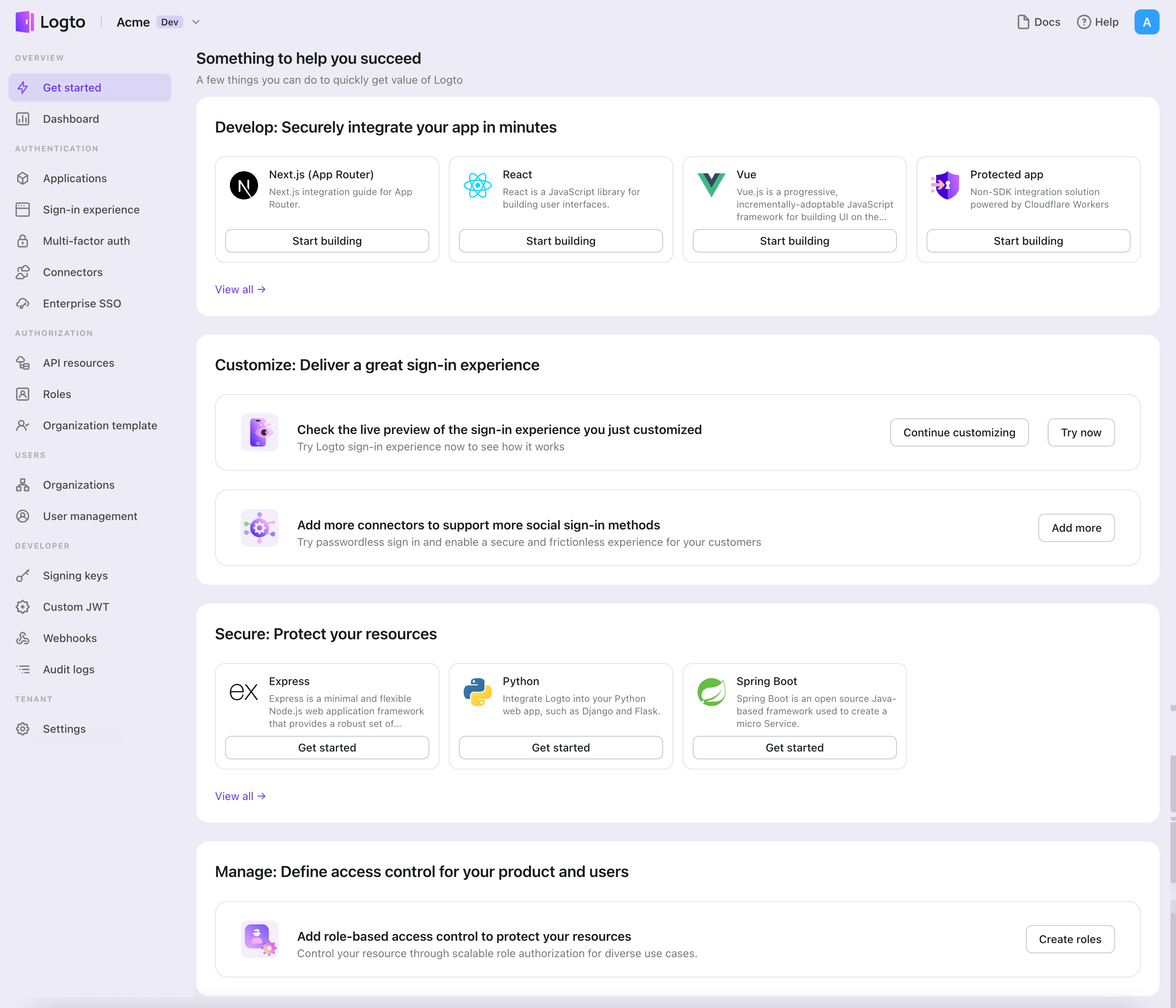
- In the opening modal, click the "Single page app" section or filter all the available "Single page app" frameworks using the quick filter checkboxes on the left. Click the "Vanilla JS" framework card to start creating your application.
- Enter the application name, e.g., "Bookstore," and click "Create application".
🎉 Ta-da! You just created your first application in Logto. You'll see a congrats page which includes a detailed integration guide. Follow the guide to see what the experience will be in your application.
Integrate Vanilla JS with Logto
- The vanilla-js SDK is framework-agnostic, you can use it in any frontend framework by writing a wrapper to fit it.
- The sample project is available on our SDK repository.
Installation
Choose your favorite package manager or use the CDN to install the Logto Browser SDK.
- npm
- pnpm
- yarn
- CDN
npm i @logto/browser
pnpm add @logto/browser
yarn add @logto/browser
<!-- Special thanks to jsdelivr -->
<script type="module">
import LogtoClient from 'https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@logto/[email protected]/+esm';
</script>
Init LogtoClient
Import and init a LogtoClient instance by passing config:
import LogtoClient from '@logto/browser';
const logtoClient = new LogtoClient({
endpoint: '<your-logto-endpoint>',
appId: '<your-application-id>',
});
The endpoint and appId can be found in the application details page in Logto Console.
Implement a sign-in and sign-out
Configure redirect URIs
Before we dive into the details, here's a quick overview of the end-user experience. The sign-in process can be simplified as follows:
- Your app invokes the sign-in method.
- The user is redirected to the Logto sign-in page. For native apps, the system browser is opened.
- The user signs in and is redirected back to your app (configured as the redirect URI).
Regarding redirect-based sign-in
- This authentication process follows the OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol, and Logto enforces strict security measures to protect user sign-in.
- If you have multiple apps, you can use the same identity provider (Logto). Once the user signs in to one app, Logto will automatically complete the sign-in process when the user accesses another app.
To learn more about the rationale and benefits of redirect-based sign-in, see Logto sign-in experience explained.
In the following code snippets, we assume your app is running on http://localhost:3000/.
Configure redirect URIs
Switch to the application details page of Logto Console. Add a redirect URI http://localhost:3000/callback.

Just like signing in, users should be redirected to Logto for signing out of the shared session. Once finished, it would be great to redirect the user back to your website. For example, add http://localhost:3000/ as the post sign-out redirect URI section.
Then click "Save" to save the changes.
Handle redirect
There are still things to do after the user is redirected back to your application from Logto. Let's handle it properly.
const callbackHandler = async (logtoClient) => {
await logtoClient.handleSignInCallback(window.location.href);
if (!logtoClient.isAuthenticated) {
// Handle failed sign-in
alert('Failed to sign in');
return;
}
// Handle successful sign-in
window.location.assign('/');
};
Implement sign-in and sign-out
logtoClient provides signIn and signOut methods to help you easily manage the authentication flow.
Before calling .signIn(), make sure you have correctly configured Redirect URI
in Admin Console.
const isAuthenticated = await logtoClient.isAuthenticated();
const onClickSignIn = () => {
logtoClient.signIn('http://localhost:3000/callback');
};
const onClickSignOut = () => {
logtoClient.signOut('http://localhost:3000');
};
const button = document.createElement('button');
button.innerHTML = isAuthenticated ? 'Sign Out' : 'Sign In';
button.addEventListener('click', isAuthenticated ? onClickSignOut : onClickSignIn);
document.body.appendChild(button);
Calling .signOut() will clear all the Logto data in memory and localStorage if they exist.
Handle authentication status
In Logto SDK, generally we can use logtoClient.isAuthenticated to check the authentication status, if the user is signed in, the value will be true, otherwise, the value will be false.
In your vanilla JS app, you can use the isAuthenticated status to programmatically show and hide the sign-in and sign-out buttons. Let's see how to do it.
const redirectUrl = 'http://localhost:3000/callback';
const baseUrl = 'http://localhost:3000';
// Conditional rendering of sign-in and sign-out buttons
const render = async (logtoClient) => {
const isAuthenticated = await logtoClient.isAuthenticated();
const container = document.querySelector('#container');
const onClickSignIn = () => logtoClient.signIn(redirectUrl);
const onClickSignOut = () => logtoClient.signOut(baseUrl);
const button = document.createElement('button');
button.innerHTML = isAuthenticated ? 'Sign Out' : 'Sign In';
button.addEventListener('click', isAuthenticated ? onClickSignOut : onClickSignIn);
container.append(button);
};
Checkpoint: Test your application
Now, you can test your application:
- Run your application, you will see the sign-in button.
- Click the sign-in button, the SDK will init the sign-in process and redirect you to the Logto sign-in page.
- After you signed in, you will be redirected back to your application and see the sign-out button.
- Click the sign-out button to clear token storage and sign out.
Add Apple connector
To enable quick sign-in and improve user conversion, connect with Vanilla JS as an identity provider. The Logto social connector helps you establish this connection in minutes by allowing several parameter inputs.
To add a social connector, simply follow these steps:
- Navigate to Console > Connectors > Social Connectors.
- Click "Add social connector" and select "Apple".
- Follow the README guide and complete required fields and customize settings.
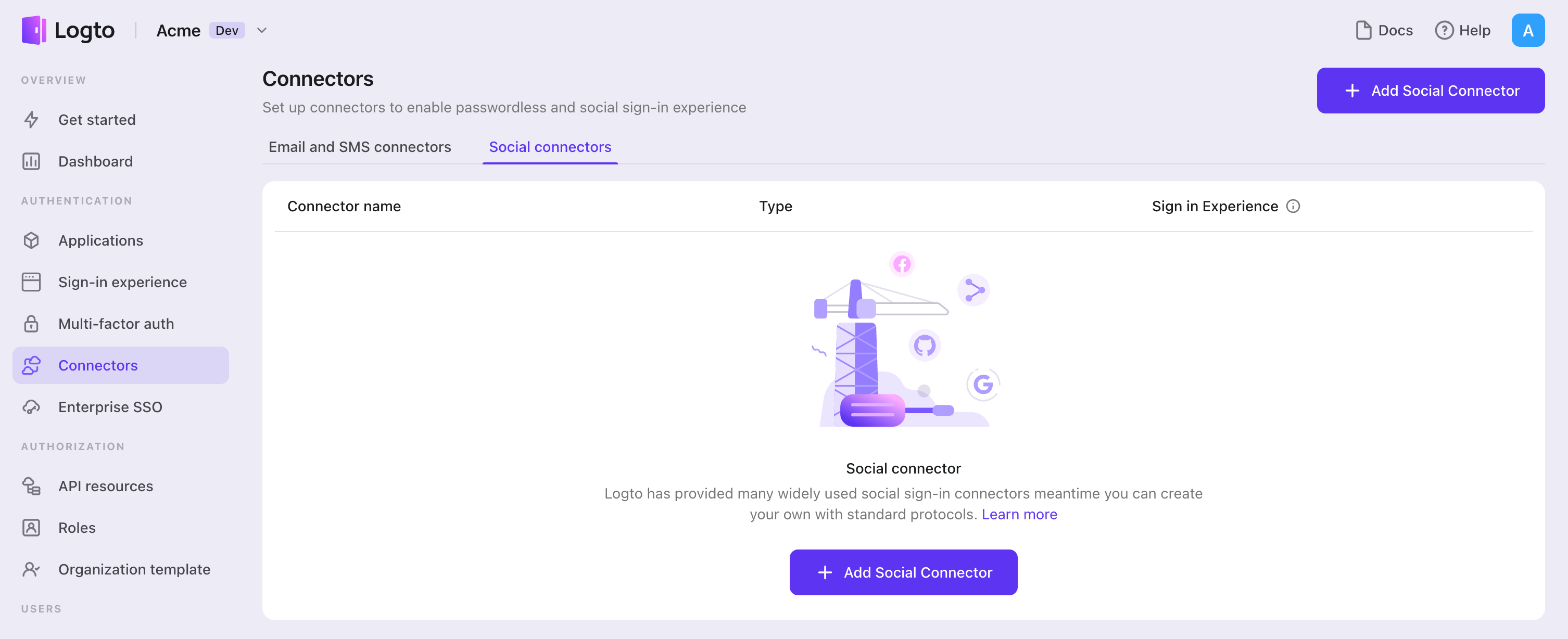
If you are following the in-place Connector guide, you can skip the next section.
Set up Apple Sign-in
Apple sign-in is required for AppStore if you have other social sign-in methods in your app. Having Apple sign-in on Android devices is great if you also provide an Android app.
You need to enroll Apple Developer Program before continuing.
Enable Sign in with Apple for your app
Even if you want to implement Sign in with Apple on a web app only, you still need to have an existing app that embraces the AppStore ecosystem (i.e., have a valid App ID).
You can do it via Xcode -> Project settings -> Signing & Capabilities, or visit Certificates, Identifiers & Profiles.
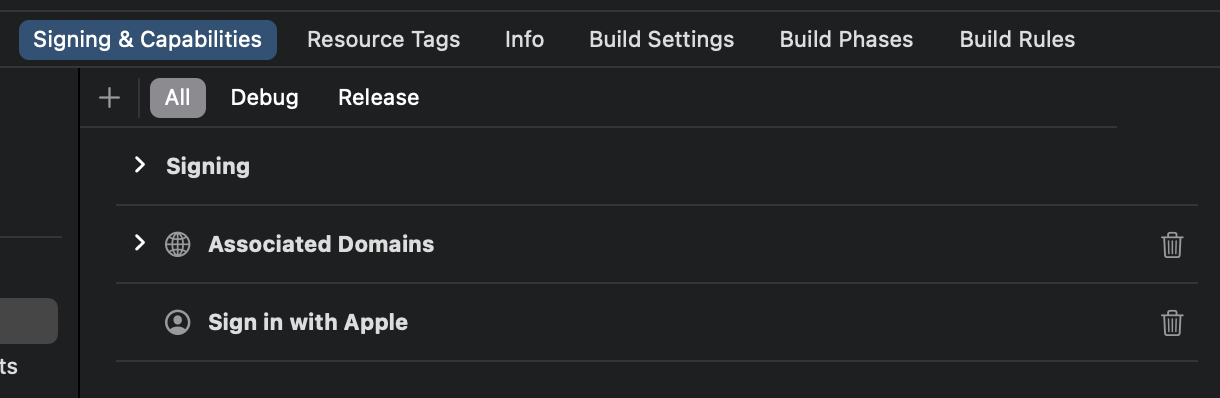
See the "Enable an App ID" section in Apple official docs for more info.
Create an identifier
- Visit Certificates, Identifiers & Profiles, then click the "+" button next to "Identifier".
- In the "Register a new identifier" page, choose "Services IDs" and click "Continue".
- Fill out "Description" and "Identifier" (E.g.,
Logto Testandio.logto.test), then click "Continue". - Double-check the info and click "Register".
Enable Sign in with Apple for your identifier
Click the identifier you just created. Check "Sign in with Apple" on the details page and click "Configure".

In the opening modal, select the App ID you just enabled Sign in with Apple.
Enter the domain of your Logto instance without protocol and port, e.g., your.logto.domain; then enter the "Return URL" (i.e., Redirect URI), which is the Logto URL with /callback/${connector_id}, e.g., https://your.logto.domain/callback/apple-universal. You can get the randomly generated connector_id after creating Apple connector in Admin Console.
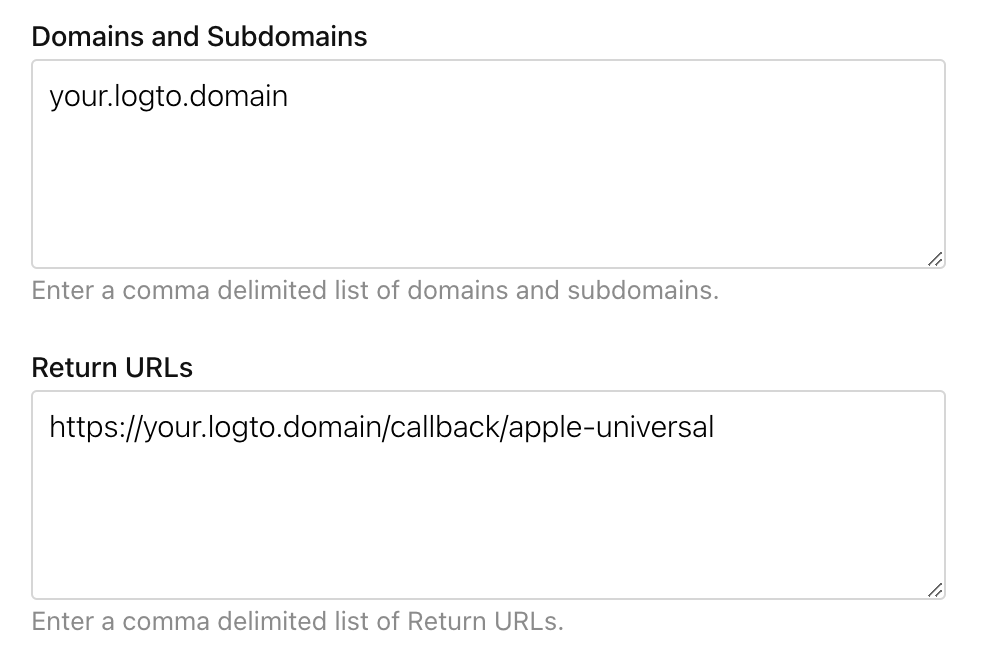
Click "Next" then "Done" to close the modal. Click "Continue" on the top-right corner, then click "Save" to save your configuration.
Apple does NOT allow Return URLs with HTTP protocol and localhost domain.
If you want to test locally, you need to edit /etc/hosts file to map localhost to a custom domain and set up a local HTTPS environment. mkcert can help you for setting up local HTTPS.
Configure scope
To get user's email from Apple, you need to configure the scope to include email. For both email and name, you can use name email as the scope. See Apple official docs for more info.
The user may choose to hide their email address from your app. In this case, you will not be able to retrieve the real email address. An email address like [email protected] will be returned instead.
Save your configuration
Double check you have filled out necessary values in the Logto connector configuration area. Click "Save and Done" (or "Save changes") and the Apple connector should be available now.
Enable Apple connector in Sign-in Experience
Once you create a social connector successfully, you can enable it as a "Continue with Apple" button in Sign-in Experience.
- Navigate to Console > Sign-in experience > Sign-up and sign-in.
- (Optional) Choose "Not applicable" for sign-up identifier if you need social login only.
- Add configured Apple connector to the "Social sign-in" section.
Testing and Validation
Return to your Vanilla JS app. You should now be able to sign in with Apple. Enjoy!
Further readings
End-user flows: Logto provides a out-of-the-box authentication flows including MFA and enterprise SSO, along with powerful APIs for flexible implementation of account settings, security verification, and multi-tenant experience.
Authorization: Authorization defines the actions a user can do or resources they can access after being authenticated. Explore how to protect your API for native and single-page applications and implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC).
Organizations: Particularly effective in multi-tenant SaaS and B2B apps, the organization feature enable tenant creation, member management, organization-level RBAC, and just-in-time-provisioning.
Customer IAM series Our serial blog posts about Customer (or Consumer) Identity and Access Management, from 101 to advanced topics and beyond.