Logto is an Auth0 alternative designed for modern apps and SaaS products. It offers both Cloud and Open-source services to help you quickly launch your identity and management (IAM) system. Enjoy authentication, authorization, and multi-tenant management all in one.
We recommend starting with a free development tenant on Logto Cloud. This allows you to explore all the features easily.
In this article, we will go through the steps to quickly build the SAML sign-in experience (user authentication) with Java Spring Boot and Logto.
Prerequisites
- A running Logto instance. Check out the introduction page to get started.
- Basic knowledge of Java Spring Boot.
- A usable SAML account.
Create an application in Logto
Logto is based on OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication and OAuth 2.0 authorization. It supports federated identity management across multiple applications, commonly called Single Sign-On (SSO).
To create your Traditional web application, simply follow these steps:
- Open the Logto Console. In the "Get started" section, click the "View all" link to open the application frameworks list. Alternatively, you can navigate to Logto Console > Applications, and click the "Create application" button.
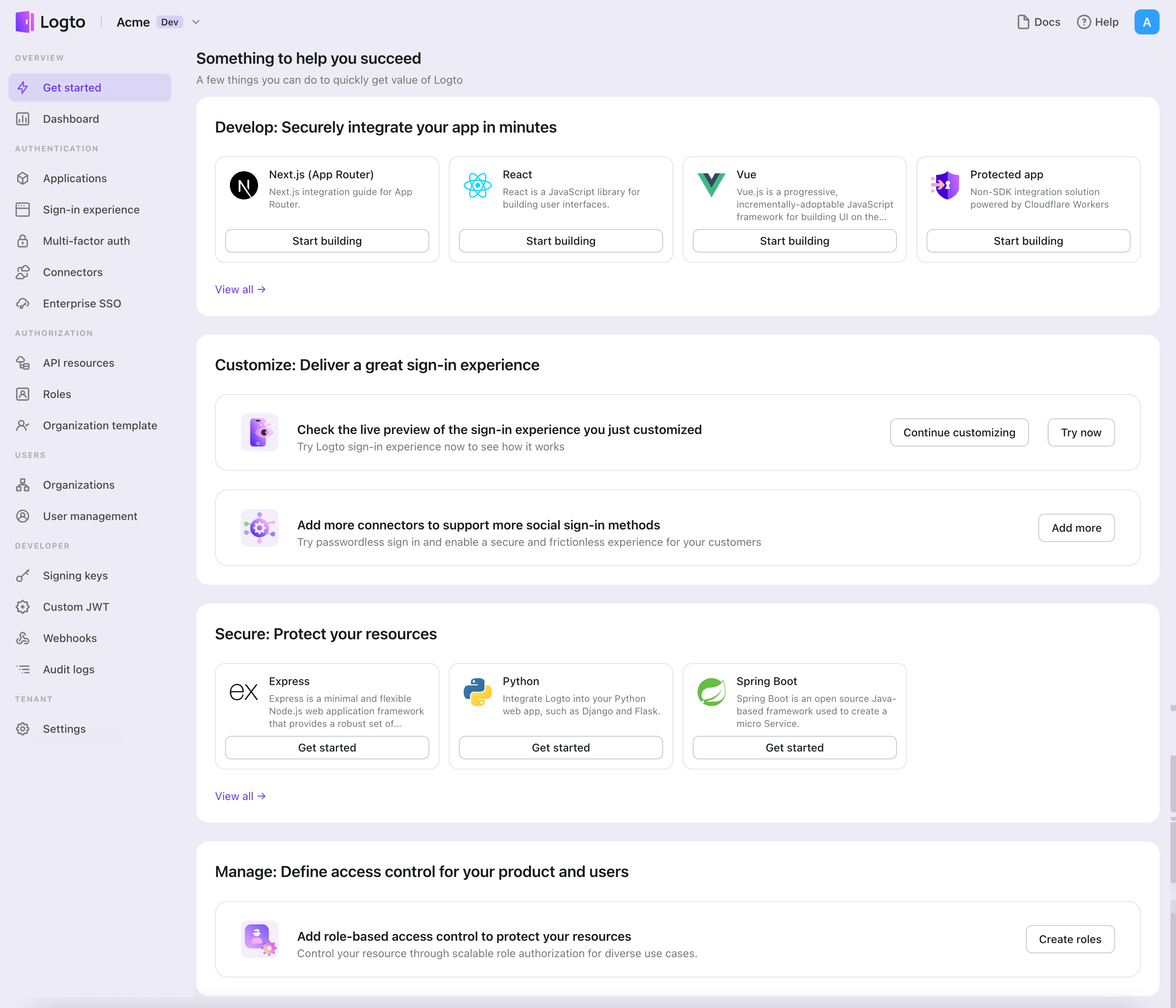
- In the opening modal, click the "Traditional web" section or filter all the available "Traditional web" frameworks using the quick filter checkboxes on the left. Click the "Java Spring Boot" framework card to start creating your application.
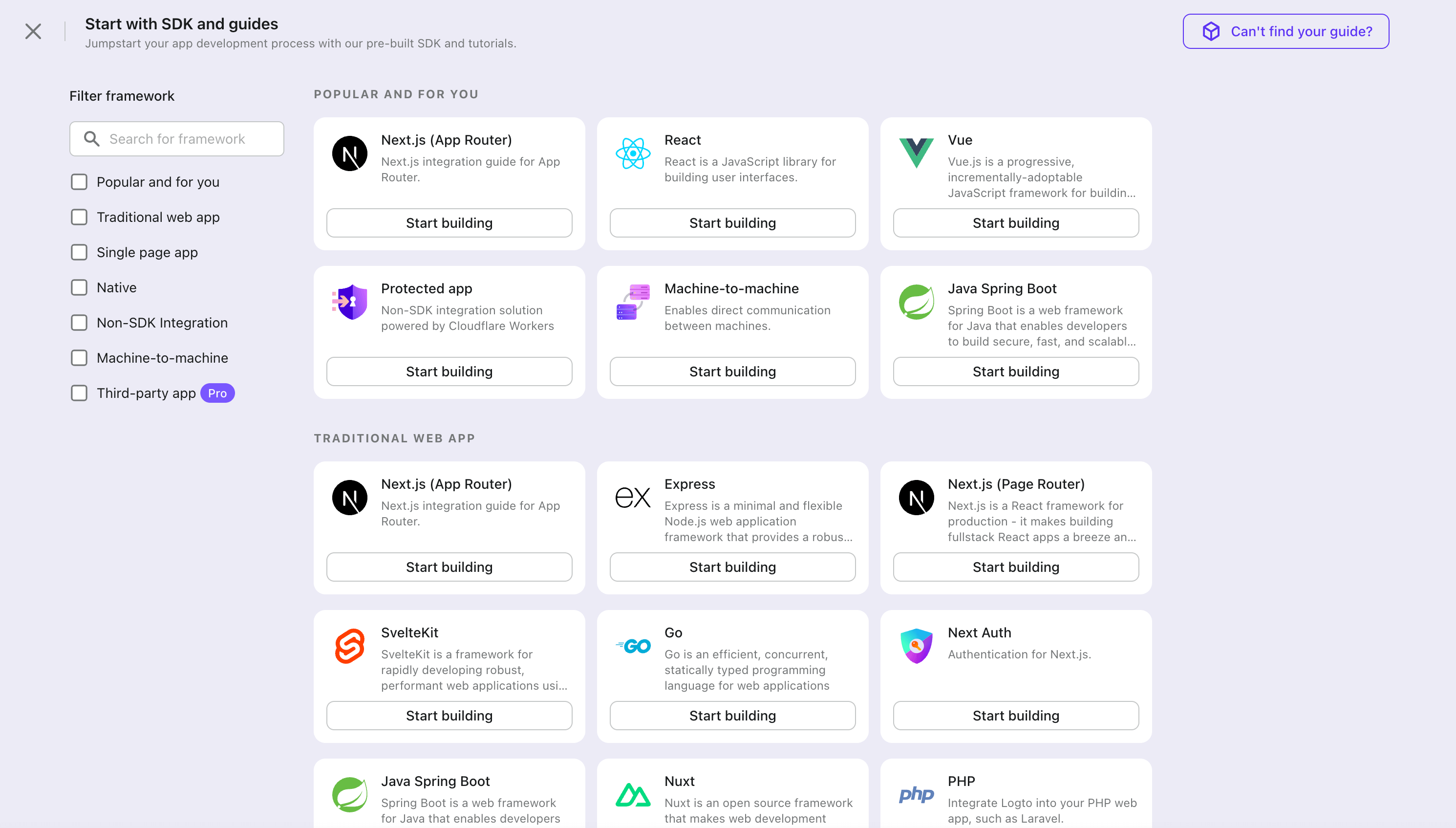
- Enter the application name, e.g., "Bookstore," and click "Create application".
🎉 Ta-da! You just created your first application in Logto. You'll see a congrats page which includes a detailed integration guide. Follow the guide to see what the experience will be in your application.
Integrate Java Spring Boot with Logto
- You may find the sample code for this guide in our spring-boot-sample github repository.
- No official SDK is required to integrate Logto with your Java Spring Boot application. We will use the Spring Security and Spring Security OAuth2 libraries to handle the OIDC authentication flow with Logto.
Configure your Java Spring Boot application
Adding dependencies
For gradle users, add the following dependencies to your build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client'
}
For maven users, add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
OAuth2 Client Configuration
Register a new Java Spring Boot application in Logto Console and get the client credential and IdP configurations for your web application.
Add the following configuration to your application.properties file:
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.client-name=logto
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.client-id={{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}}
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.client-secret={{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}}
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.redirect-uri={baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/{registrationId}
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.authorization-grant-type=authorization_code
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.scope=openid,profile,offline_access
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.provider=logto
spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.logto.issuer-uri={{LOGTO_ENDPOINT}}/oidc
spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.logto.authorization-uri={{LOGTO_ENDPOINT}}/oidc/auth
spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.logto.jwk-set-uri={{LOGTO_ENDPOINT}}/oidc/jwks
Implementation
Before we dive into the details, here's a quick overview of the end-user experience. The sign-in process can be simplified as follows:
- Your app invokes the sign-in method.
- The user is redirected to the Logto sign-in page. For native apps, the system browser is opened.
- The user signs in and is redirected back to your app (configured as the redirect URI).
Regarding redirect-based sign-in
- This authentication process follows the OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol, and Logto enforces strict security measures to protect user sign-in.
- If you have multiple apps, you can use the same identity provider (Logto). Once the user signs in to one app, Logto will automatically complete the sign-in process when the user accesses another app.
To learn more about the rationale and benefits of redirect-based sign-in, see Logto sign-in experience explained.
In order to redirect users back to your application after they sign in, you need to set the redirect URI using the client.registration.logto.redirect-uri property in the previous step.
Configure redirect URIs
Switch to the application details page of Logto Console. Add a redirect URI http://localhost:3000/callback.

Just like signing in, users should be redirected to Logto for signing out of the shared session. Once finished, it would be great to redirect the user back to your website. For example, add http://localhost:3000/ as the post sign-out redirect URI section.
Then click "Save" to save the changes.
Implement the WebSecurityConfig
Create a new class WebSecurityConfig in your project
The WebSecurityConfig class will be used to configure the security settings for your application. It is the key class that will handle the authentication and authorization flow. Please check the Spring Security documentation for more details.
package com.example.securingweb;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
// ...
}
Create a idTokenDecoderFactory bean
This is required because Logto uses ES384 as the default algorithm, we need to overwrite the default OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory to use the same algorithm.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.oidc.authentication.OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.registration.ClientRegistration;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jose.jws.SignatureAlgorithm;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.JwtDecoderFactory;
public class WebSecurityConfig {
// ...
@Bean
public JwtDecoderFactory<ClientRegistration> idTokenDecoderFactory() {
OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory idTokenDecoderFactory = new OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory();
idTokenDecoderFactory.setJwsAlgorithmResolver(clientRegistration -> SignatureAlgorithm.ES384);
return idTokenDecoderFactory;
}
}
Create a LoginSuccessHandler class to handle the login success event
We will redirect the user to the /user page after a successful login.
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class CustomSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendRedirect("/user");
}
}
Create a LogoutSuccessHandler class to handle the logout success event
Clear the session and redirect the user to the home page.
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutSuccessHandler;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
public class CustomLogoutHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (session != null) {
session.invalidate();
}
response.sendRedirect("/home");
}
}
Update the WebSecurityConfig class with a securityFilterChain
securityFilterChain is a chain of filters that are responsible for processing the incoming requests and responses.
We will configure the securityFilterChain to allow access to the home page and require authentication for all other requests. Use the CustomSuccessHandler and CustomLogoutHandler to handle the login and logout events.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultSecurityFilterChain;
public class WebSecurityConfig {
// ...
@Bean
public DefaultSecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests(authorizeRequests ->
authorizeRequests
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll() // Allow access to the home page
.anyRequest().authenticated() // All other requests require authentication
)
.oauth2Login(oauth2Login ->
oauth2Login
.successHandler(new CustomSuccessHandler())
)
.logout(logout ->
logout
.logoutSuccessHandler(new CustomLogoutHandler())
);
return http.build();
}
}
Create a home page
(You may skip this step if you already have a home page in your project)
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.security.Principal;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping({ "/", "/home" })
public String home(Principal principal) {
return principal != null ? "redirect:/user" : "home";
}
}
This controller will redirect the user to the user page if the user is authenticated, otherwise, it will show the home page. Add a sign-in link to the home page.
<body>
<h1>Welcome!</h1>
<p><a th:href="@{/oauth2/authorization/logto}">Login with Logto</a></p>
</body>
Create a user page
Create a new controller to handle the user page:
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.authentication.OAuth2AuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.OAuth2User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public String user(Model model, Principal principal) {
if (principal instanceof OAuth2AuthenticationToken) {
OAuth2AuthenticationToken token = (OAuth2AuthenticationToken) principal;
OAuth2User oauth2User = token.getPrincipal();
Map<String, Object> attributes = oauth2User.getAttributes();
model.addAttribute("username", attributes.get("username"));
model.addAttribute("email", attributes.get("email"));
model.addAttribute("sub", attributes.get("sub"));
}
return "user";
}
}
Once the user is authenticated, we will retrieve the OAuth2User data from the authenticated principal object. Please refer OAuth2AuthenticationToken and OAuth2User for more details.
Read the user data and pass it to the user.html template.
<body>
<h1>User Details</h1>
<div>
<p>
<div><strong>name:</strong> <span th:text="${username}"></span></div>
<div><strong>email:</strong> <span th:text="${email}"></span></div>
<div><strong>id:</strong> <span th:text="${sub}"></span></div>
</p>
</div>
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="Logout" />
</form>
</body>
Request additional claims
You may find some user information are missing in the returned object from principal (OAuth2AuthenticationToken). This is because OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) are designed to follow the principle of least privilege (PoLP), and Logto is built on top of these standards.
By default, limited claims are returned. If you need more information, you can request additional scopes to access more claims.
A "claim" is an assertion made about a subject; a "scope" is a group of claims. In the current case, a claim is a piece of information about the user.
Here's a non-normative example the scope - claim relationship:
The "sub" claim means "subject", which is the unique identifier of the user (i.e. user ID).
Logto SDK will always request three scopes: openid, profile, and offline_access.
To retrieve additional user information, you can add extra scopes to the application.properties file. For example, to request the email, phone, and urn:logto:scope:organizations scope, add the following line to the application.properties file:
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.scope=openid,profile,offline_access,email,phone,urn:logto:scope:organizations
Then you can access the additional claims in the OAuth2User object.
Run and test the application
Run the application and navigate to http://localhost:8080.
- You will see the home page with a sign-in link.
- Click on the link to sign in with Logto.
- After successful authentication, you will be redirected to the user page with your user details.
- Click on the logout button to sign out. You will be redirected back to the home page.
Add SAML connector
To enable quick sign-in and improve user conversion, connect with Java Spring Boot as an identity provider. The Logto social connector helps you establish this connection in minutes by allowing several parameter inputs.
To add a social connector, simply follow these steps:
- Navigate to Console > Connectors > Social Connectors.
- Click "Add social connector" and select "SAML".
- Follow the README guide and complete required fields and customize settings.
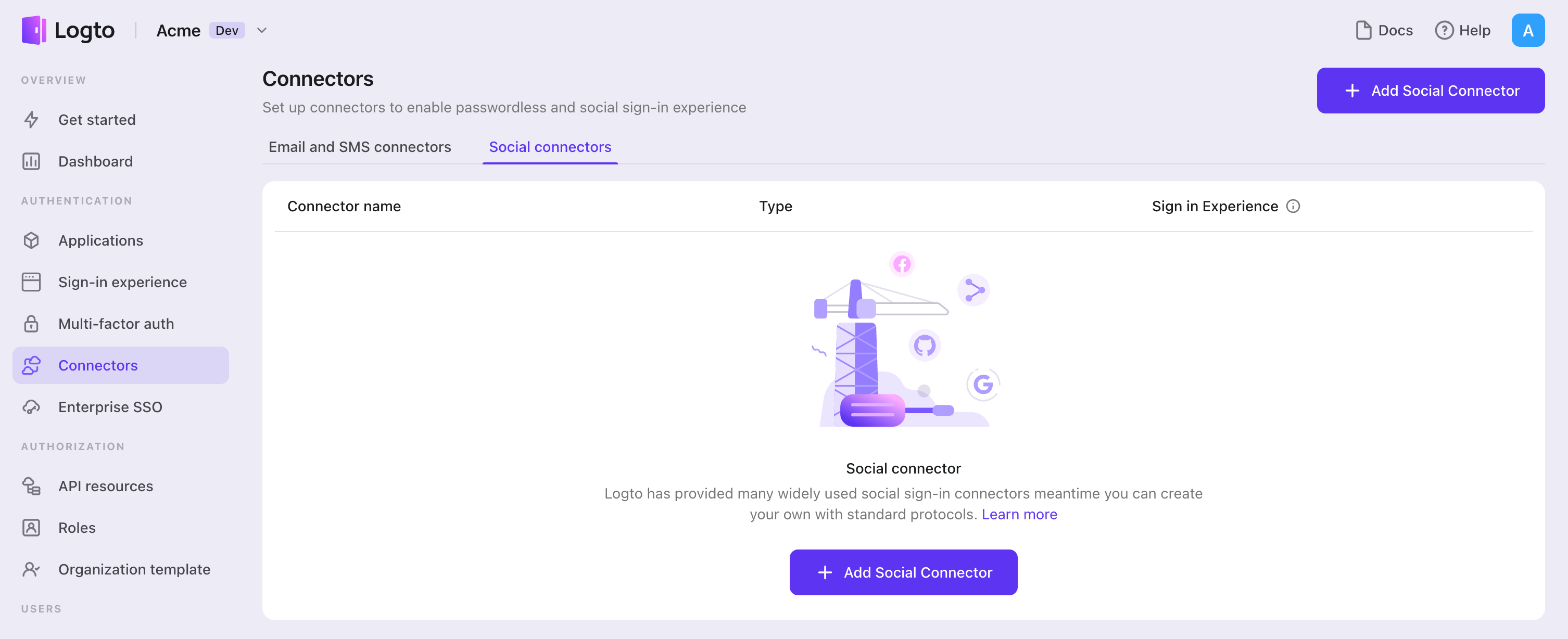
If you are following the in-place Connector guide, you can skip the next section.
Set up Standard SAML app
Create social IdP's account and register SAML application (IdP)
Let's go through configurations of SAML connector.
Before we kicking off, you can go to a social identity provider which supports SAML protocol and create your own account. Okta, OneLogin, Salesforce and some other platforms support authentication based on SAML protocol.
If your IdP mandate the encryption of SAML assertion and receiving of signed authentication requests, you should generate your private key and corresponding certificate using RSA algorithm. Keep the private key for your SP use and upload the certificate to IdP.
You also need to configure the ACS (Assertion Consumer Service) URL as ${your_logto_origin}/api/authn/saml/${connector_id} to handle IdP's SAML assertion. Where you can find your connectorId at SAML connector's details page in Logto's Admin Console.
Per current Logto's design, we only support Redirect-binding for sending authentication request and POST-binding for receiving SAML assertion. Although this sounds not cool, but we believe that the current design can handle most of your use cases. If you have any problems, feel free to reach out!
Configure SAML connector (SP)
In this section, we will introduce each attribute in detail.
entityID Required
entityID (i.e. issuer) is Entity identifier. It is used to identify your entity (SAML SP entity), and match the equivalence in each SAML request/response.
signInEndpoint Required
The IdP's endpoint that you send SAML authentication requests to. Usually, you can find this value in IdP details page (i.e. IdP's SSO URL or Login URL).
x509Certificate Required
The x509 certificate generated from IdPs private key, IdP is expected to have this value available.
The content of the certificate comes with -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- header and -----END CERTIFICATE----- tail.
idpMetadataXml Required
The field is used to place contents from your IdP metadata XML file.
The XML parser we are using does not support customized namespace. If the IdP metadata comes with namespace, you should manually remove them. For namespace of XML file, see reference.
assertionConsumerServiceUrl Required
The assertion consumer service (ACS) URL is the SP's endpoint to receive IdP's SAML Assertion POST requests. As we mentioned in previous part, it is usually configured at IdP settings but some IdP get this value from SAML authentication requests, we hence also add this value as a REQUIRED field. It's value should look like ${your_logto_origin}/api/authn/saml/${connector_id}.
signAuthnRequest
The boolean value that controls whether SAML authentication request should be signed, whose default value is false.
encryptAssertion
encryptAssertion is a boolean value that indicates if IdP will encrypt SAML assertion, with default value false.
The signAuthnRequest and encryptAssertion attributes should align with corresponding parameters of IdP setting, otherwise error will be thrown to show that configuration does not match.
All SAML responses need to be signed.
requestSignatureAlgorithm
This should be aligned with the signature algorithms of IdP so that Logto can verify the signature of the SAML assertion. Its value should be either http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsa-sha1, http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256 or http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha512 and the default value is http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256.
messageSigningOrder
messageSigningOrder indicates the signing and encrypting order of IdP, it's value should be either sign-then-encrypt or encrypt-then-sign and the default value is sign-then-encrypt.
privateKey and privateKeyPass
privateKey is an OPTIONAL value and is required when signAuthnRequest is true.
privateKeyPass is the password you've set when creating privateKey, required when necessary.
If signAuthnRequest is true, the corresponding certificate generated from privateKey is required by IdP for checking the signature.
encPrivateKey and encPrivateKeyPass
encPrivateKey is an OPTIONAL value and is required when encryptAssertion is true.
encPrivateKeyPass is the password you've set when creating encPrivateKey, required when necessary.
If encryptAssertion is true, the corresponding certificate generated from encPrivateKey is required by IdP for encrypting SAML assertion.
For keys and certificates generation, openssl is a wonderful tool. Here is sample command line that might be helpful:
openssl genrsa -passout pass:${privateKeyPassword} -out ${encryptPrivateKeyFilename}.pem 4096
openssl req -new -x509 -key ${encryptPrivateKeyFilename}.pem -out ${encryptionCertificateFilename}.cer -days 3650
privateKey and encPrivateKey files are enforced to be encoded in pkcs1 scheme as pem string, which means the private key files should start with -----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY----- and end with -----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----.
nameIDFormat
nameIDFormat is an OPTIONAL attribute that declares the name id format that would respond. The value can be among urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified, urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress, urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:X509SubjectName, urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent and urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient, and the default value is urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:unspecified.
timeout
timeout is the time tolerance for time validation, since the time between your SP entity and IdP entity could be different and network connection may also bring some delay. The unit is in millisecond, and the default value is 5000 (i.e. 5s).
profileMap
Logto also provide a profileMap field that users can customize the mapping from the social vendors' profiles which are usually not standard. Each profileMap keys is Logto's standard user profile field name and corresponding value should be social profiles field name. In current stage, Logto only concern 'id', 'name', 'avatar', 'email' and 'phone' from social profile, only 'id' is REQUIRED and others are optional fields.
Config types
| Name | Type | Required | Default Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| signInEndpoint | string | true | |
| x509certificate | string | true | |
| idpMetadataXml | string | true | |
| entityID | string | true | |
| assertionConsumerServiceUrl | string | true | |
| messageSigningOrder | encrypt-then-sign | sign-then-encrypt | false | sign-then-encrypt |
| requestSignatureAlgorithm | http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#rsa-sha1 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256 | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha512 | false | http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#rsa-sha256 |
| signAuthnRequest | boolean | false | false |
| encryptAssertion | boolean | false | false |
| privateKey | string | false | |
| privateKeyPass | string | false | |
| nameIDFormat | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:X509SubjectName | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:transient | false | urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:unspecified |
| timeout | number | false | 5000 |
| profileMap | ProfileMap | false |
| ProfileMap fields | Type | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | string | false | id |
| name | string | false | name |
| avatar | string | false | avatar |
| string | false | ||
| phone | string | false | phone |
Reference
- Profiles for the OASIS Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) V2.0
- samlify - Highly configuarable Node.js SAML 2.0 library for Single Sign On
Save your configuration
Double check you have filled out necessary values in the Logto connector configuration area. Click "Save and Done" (or "Save changes") and the SAML connector should be available now.
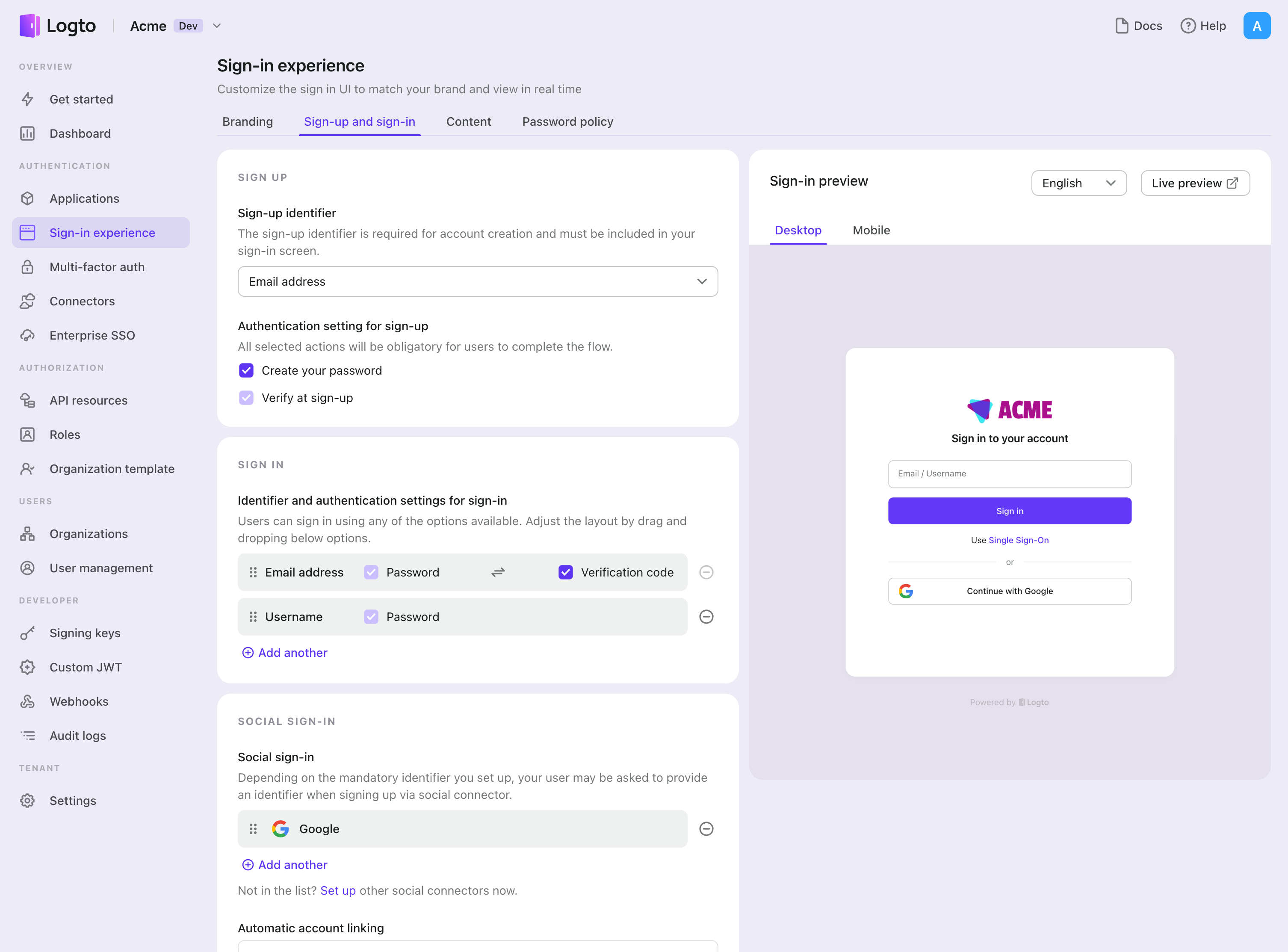
Enable SAML connector in Sign-in Experience
Once you create a social connector successfully, you can enable it as a "Continue with SAML" button in Sign-in Experience.
- Navigate to Console > Sign-in experience > Sign-up and sign-in.
- (Optional) Choose "Not applicable" for sign-up identifier if you need social login only.
- Add configured SAML connector to the "Social sign-in" section.
Testing and Validation
Return to your Java Spring Boot app. You should now be able to sign in with SAML. Enjoy!
Further readings
End-user flows: Logto provides a out-of-the-box authentication flows including MFA and enterprise SSO, along with powerful APIs for flexible implementation of account settings, security verification, and multi-tenant experience.
Authorization: Authorization defines the actions a user can do or resources they can access after being authenticated. Explore how to protect your API for native and single-page applications and implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC).
Organizations: Particularly effective in multi-tenant SaaS and B2B apps, the organization feature enable tenant creation, member management, organization-level RBAC, and just-in-time-provisioning.
Customer IAM series Our serial blog posts about Customer (or Consumer) Identity and Access Management, from 101 to advanced topics and beyond.