Logto is an Auth0 alternative designed for modern apps and SaaS products. It offers both Cloud and Open-source services to help you quickly launch your identity and management (IAM) system. Enjoy authentication, authorization, and multi-tenant management all in one.
We recommend starting with a free development tenant on Logto Cloud. This allows you to explore all the features easily.
In this article, we will go through the steps to quickly build the Okta enterprise SSO sign-in experience (user authentication) with Java Spring Boot and Logto.
Prerequisites
- A running Logto instance. Check out the introduction page to get started.
- Basic knowledge of Java Spring Boot.
- A usable Okta enterprise SSO account.
Create an application in Logto
Logto is based on OpenID Connect (OIDC) authentication and OAuth 2.0 authorization. It supports federated identity management across multiple applications, commonly called Single Sign-On (SSO).
To create your Traditional web application, simply follow these steps:
- Open the Logto Console. In the "Get started" section, click the "View all" link to open the application frameworks list. Alternatively, you can navigate to Logto Console > Applications, and click the "Create application" button.
- In the opening modal, click the "Traditional web" section or filter all the available "Traditional web" frameworks using the quick filter checkboxes on the left. Click the "Java Spring Boot" framework card to start creating your application.
- Enter the application name, e.g., "Bookstore," and click "Create application".
🎉 Ta-da! You just created your first application in Logto. You'll see a congrats page which includes a detailed integration guide. Follow the guide to see what the experience will be in your application.
Integrate Java Spring Boot with Logto
- You may find the sample code for this guide in our spring-boot-sample github repository.
- No official SDK is required to integrate Logto with your Java Spring Boot application. We will use the Spring Security and Spring Security OAuth2 libraries to handle the OIDC authentication flow with Logto.
Configure your Java Spring Boot application
Adding dependencies
For gradle users, add the following dependencies to your build.gradle file:
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-security'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client'
}
For maven users, add the following dependencies to your pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
OAuth2 Client Configuration
Register a new Java Spring Boot application in Logto Console and get the client credential and IdP configurations for your web application.
Add the following configuration to your application.properties file:
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.client-name=logto
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.client-id={{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}}
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.client-secret={{YOUR_CLIENT_ID}}
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.redirect-uri={baseUrl}/login/oauth2/code/{registrationId}
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.authorization-grant-type=authorization_code
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.scope=openid,profile,offline_access
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.provider=logto
spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.logto.issuer-uri={{LOGTO_ENDPOINT}}/oidc
spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.logto.authorization-uri={{LOGTO_ENDPOINT}}/oidc/auth
spring.security.oauth2.client.provider.logto.jwk-set-uri={{LOGTO_ENDPOINT}}/oidc/jwks
Implementation
Before we dive into the details, here's a quick overview of the end-user experience. The sign-in process can be simplified as follows:
- Your app invokes the sign-in method.
- The user is redirected to the Logto sign-in page. For native apps, the system browser is opened.
- The user signs in and is redirected back to your app (configured as the redirect URI).
Regarding redirect-based sign-in
- This authentication process follows the OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol, and Logto enforces strict security measures to protect user sign-in.
- If you have multiple apps, you can use the same identity provider (Logto). Once the user signs in to one app, Logto will automatically complete the sign-in process when the user accesses another app.
To learn more about the rationale and benefits of redirect-based sign-in, see Logto sign-in experience explained.
In order to redirect users back to your application after they sign in, you need to set the redirect URI using the client.registration.logto.redirect-uri property in the previous step.
Configure redirect URIs
Switch to the application details page of Logto Console. Add a redirect URI http://localhost:3000/callback.

Just like signing in, users should be redirected to Logto for signing out of the shared session. Once finished, it would be great to redirect the user back to your website. For example, add http://localhost:3000/ as the post sign-out redirect URI section.
Then click "Save" to save the changes.
Implement the WebSecurityConfig
Create a new class WebSecurityConfig in your project
The WebSecurityConfig class will be used to configure the security settings for your application. It is the key class that will handle the authentication and authorization flow. Please check the Spring Security documentation for more details.
package com.example.securingweb;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig {
// ...
}
Create a idTokenDecoderFactory bean
This is required because Logto uses ES384 as the default algorithm, we need to overwrite the default OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory to use the same algorithm.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.oidc.authentication.OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.registration.ClientRegistration;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jose.jws.SignatureAlgorithm;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.jwt.JwtDecoderFactory;
public class WebSecurityConfig {
// ...
@Bean
public JwtDecoderFactory<ClientRegistration> idTokenDecoderFactory() {
OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory idTokenDecoderFactory = new OidcIdTokenDecoderFactory();
idTokenDecoderFactory.setJwsAlgorithmResolver(clientRegistration -> SignatureAlgorithm.ES384);
return idTokenDecoderFactory;
}
}
Create a LoginSuccessHandler class to handle the login success event
We will redirect the user to the /user page after a successful login.
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.AuthenticationSuccessHandler;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class CustomSuccessHandler implements AuthenticationSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
response.sendRedirect("/user");
}
}
Create a LogoutSuccessHandler class to handle the logout success event
Clear the session and redirect the user to the home page.
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.springframework.security.core.Authentication;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.logout.LogoutSuccessHandler;
import jakarta.servlet.ServletException;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpSession;
public class CustomLogoutHandler implements LogoutSuccessHandler {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Authentication authentication)
throws IOException, ServletException {
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
if (session != null) {
session.invalidate();
}
response.sendRedirect("/home");
}
}
Update the WebSecurityConfig class with a securityFilterChain
securityFilterChain is a chain of filters that are responsible for processing the incoming requests and responses.
We will configure the securityFilterChain to allow access to the home page and require authentication for all other requests. Use the CustomSuccessHandler and CustomLogoutHandler to handle the login and logout events.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultSecurityFilterChain;
public class WebSecurityConfig {
// ...
@Bean
public DefaultSecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests(authorizeRequests ->
authorizeRequests
.antMatchers("/", "/home").permitAll() // Allow access to the home page
.anyRequest().authenticated() // All other requests require authentication
)
.oauth2Login(oauth2Login ->
oauth2Login
.successHandler(new CustomSuccessHandler())
)
.logout(logout ->
logout
.logoutSuccessHandler(new CustomLogoutHandler())
);
return http.build();
}
}
Create a home page
(You may skip this step if you already have a home page in your project)
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.security.Principal;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping({ "/", "/home" })
public String home(Principal principal) {
return principal != null ? "redirect:/user" : "home";
}
}
This controller will redirect the user to the user page if the user is authenticated, otherwise, it will show the home page. Add a sign-in link to the home page.
<body>
<h1>Welcome!</h1>
<p><a th:href="@{/oauth2/authorization/logto}">Login with Logto</a></p>
</body>
Create a user page
Create a new controller to handle the user page:
package com.example.securingweb;
import java.security.Principal;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.authentication.OAuth2AuthenticationToken;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.OAuth2User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public String user(Model model, Principal principal) {
if (principal instanceof OAuth2AuthenticationToken) {
OAuth2AuthenticationToken token = (OAuth2AuthenticationToken) principal;
OAuth2User oauth2User = token.getPrincipal();
Map<String, Object> attributes = oauth2User.getAttributes();
model.addAttribute("username", attributes.get("username"));
model.addAttribute("email", attributes.get("email"));
model.addAttribute("sub", attributes.get("sub"));
}
return "user";
}
}
Once the user is authenticated, we will retrieve the OAuth2User data from the authenticated principal object. Please refer OAuth2AuthenticationToken and OAuth2User for more details.
Read the user data and pass it to the user.html template.
<body>
<h1>User Details</h1>
<div>
<p>
<div><strong>name:</strong> <span th:text="${username}"></span></div>
<div><strong>email:</strong> <span th:text="${email}"></span></div>
<div><strong>id:</strong> <span th:text="${sub}"></span></div>
</p>
</div>
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="Logout" />
</form>
</body>
Request additional claims
You may find some user information are missing in the returned object from principal (OAuth2AuthenticationToken). This is because OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC) are designed to follow the principle of least privilege (PoLP), and Logto is built on top of these standards.
By default, limited claims are returned. If you need more information, you can request additional scopes to access more claims.
A "claim" is an assertion made about a subject; a "scope" is a group of claims. In the current case, a claim is a piece of information about the user.
Here's a non-normative example the scope - claim relationship:
The "sub" claim means "subject", which is the unique identifier of the user (i.e. user ID).
Logto SDK will always request three scopes: openid, profile, and offline_access.
To retrieve additional user information, you can add extra scopes to the application.properties file. For example, to request the email, phone, and urn:logto:scope:organizations scope, add the following line to the application.properties file:
spring.security.oauth2.client.registration.logto.scope=openid,profile,offline_access,email,phone,urn:logto:scope:organizations
Then you can access the additional claims in the OAuth2User object.
Run and test the application
Run the application and navigate to http://localhost:8080.
- You will see the home page with a sign-in link.
- Click on the link to sign in with Logto.
- After successful authentication, you will be redirected to the user page with your user details.
- Click on the logout button to sign out. You will be redirected back to the home page.
Add Okta enterprise SSO connector
To simplify access management and gain enterprise-level safeguards for your big clients, connect with Java Spring Boot as a federated identity provider. The Logto enterprise SSO connector helps you establish this connection in minutes by allowing several parameter inputs.
To add an enterprise SSO connector, simply follow these steps:
- Navigate to Logto console > Enterprise SSO.
- Click "Add enterprise connector" button and choose your SSO provider type. Choose from prebuilt connectors for Microsoft Entra ID (Azure AD), Google Workspace, and Okta, or create a custom SSO connection using the standard OpenID Connect (OIDC) or SAML protocol.
- Provide a unique name (e.g., SSO sign-in for Acme Company).
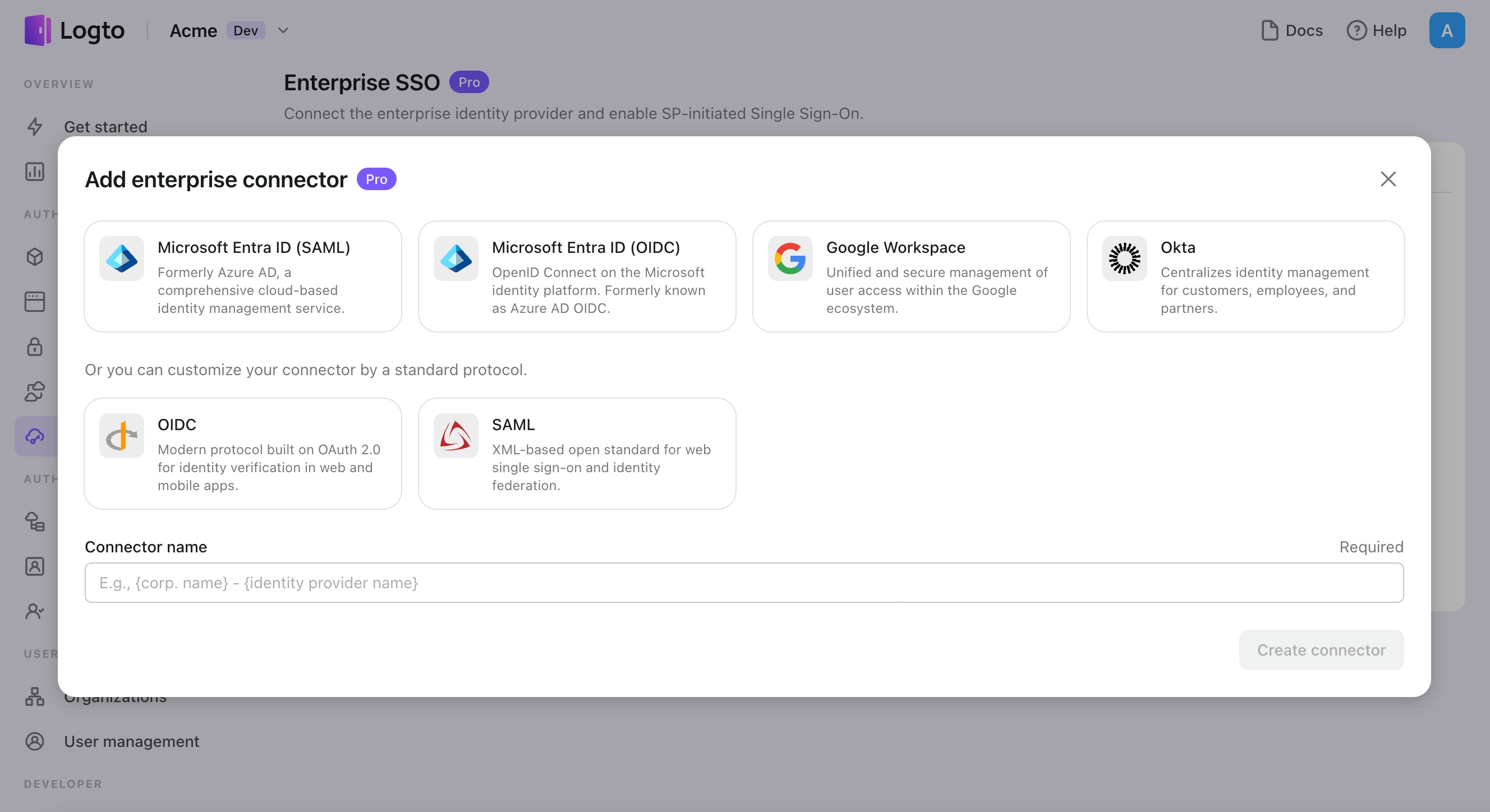
- Configure the connection with your IdP in the "Connection" tab. Check the guides above for each connector types.
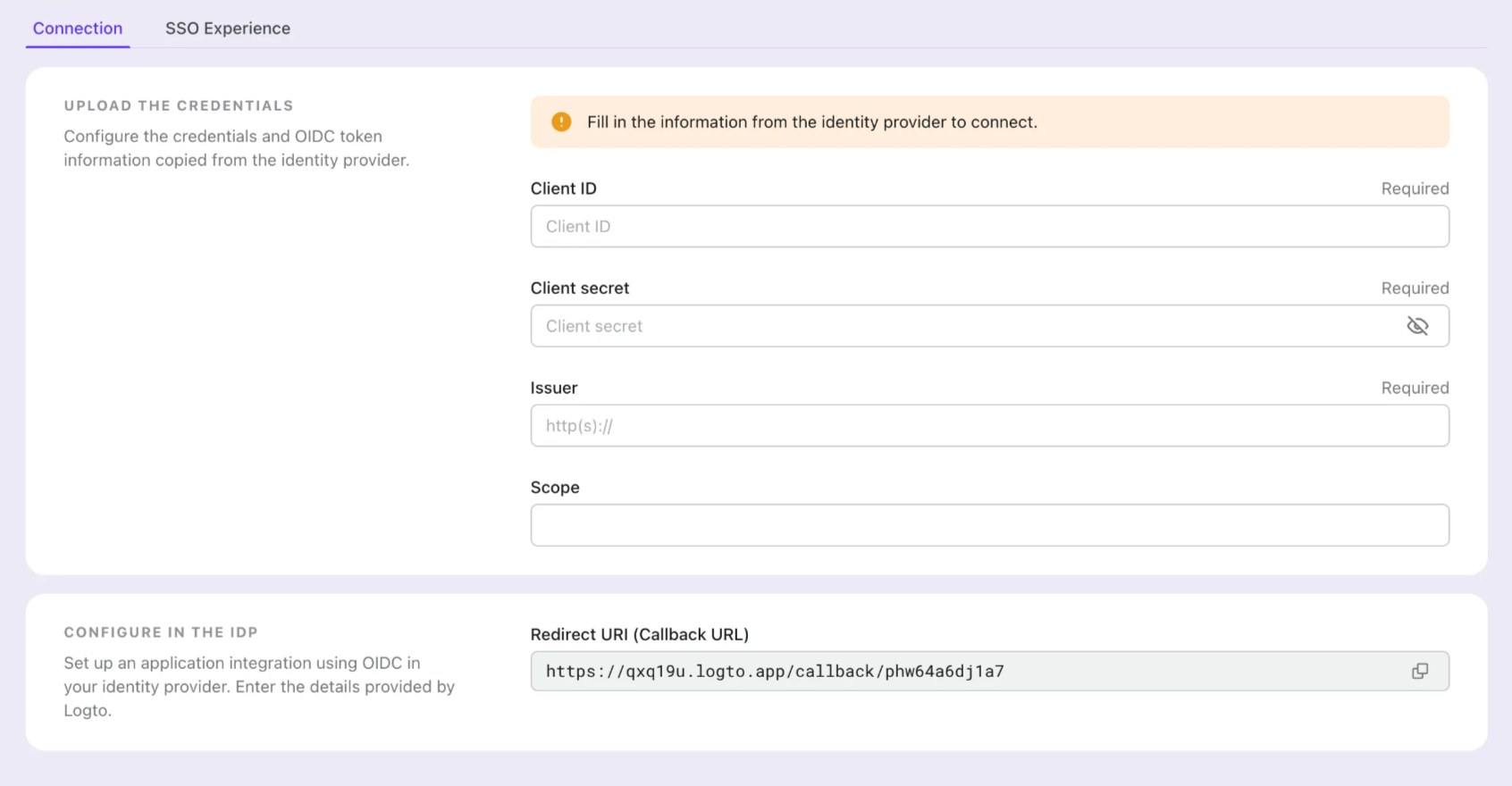
- Customize the SSO experience and enterprise’s email domain in the "Experience" tab. Users sign in with the SSO-enabled email domain will be redirected to SSO authentication.
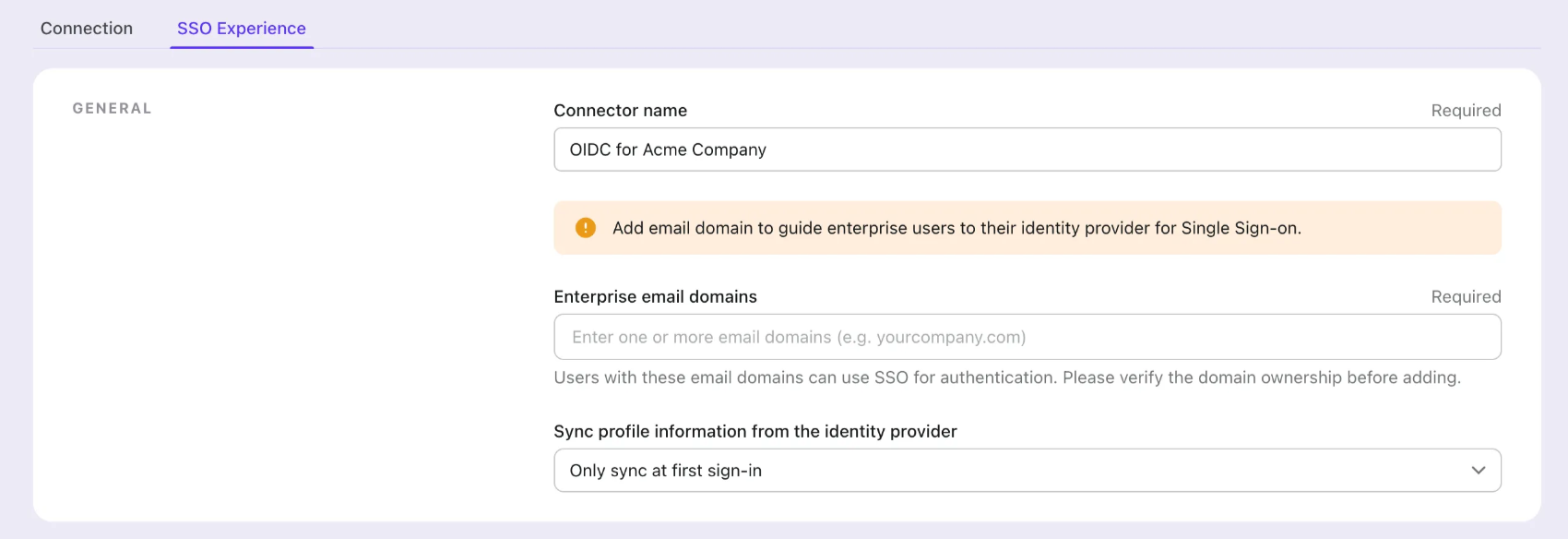
- Save changes.
Set up OIDC application on Okta admin portal
Step 1: Create an OIDC application on Okta admin portal {#step-1-create-an-oidc-application-on-okta-admin-portal}
- Visit the Okta admin portal and sign in as an administrator.
- Navigate to the
Applications/Applicationspage using the side menu. - Click the
Create App Integrationbutton to create a new OIDC application. - Select the
OIDC - OpenID Connectoption as theSign-in method. - Select the
Web Applicationoption as theApplication type.
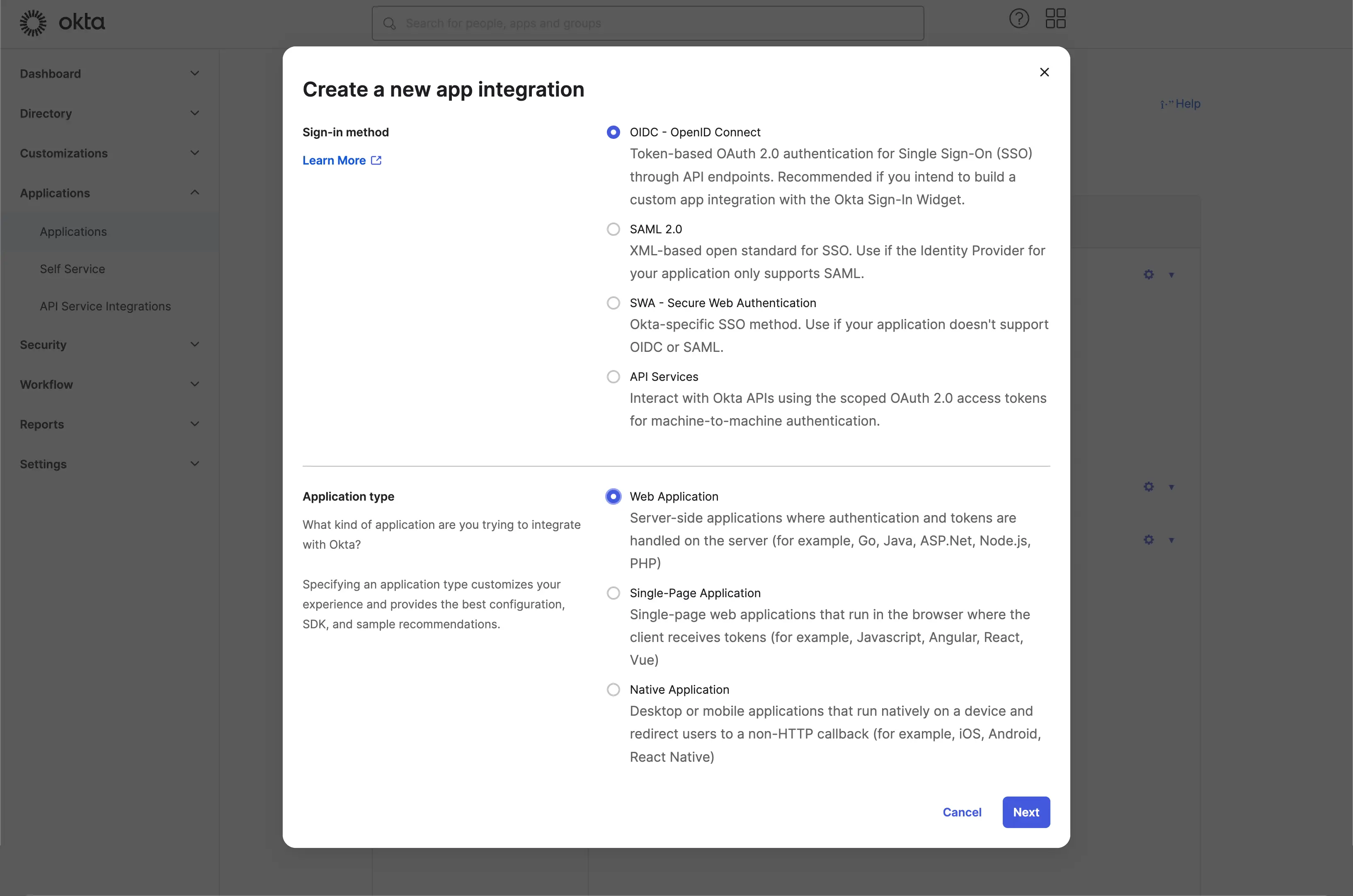
Click the Next button to continue.
Step 2: Configure the application settings
- Provide an
App integration name. It will be used as the identifier of your OIDC application. - Add a new
Sign-in redirect URIsusing the Logto SSO connector's callback URL.
This is the URI that the Okta will redirect the user's browser after successful authentication. After a user successfully authenticates with the IdP, the IdP redirects the user's browser back to this designated URI along with an authorization code. Logto will complete the authentication process based on the authorization code received from this URI.
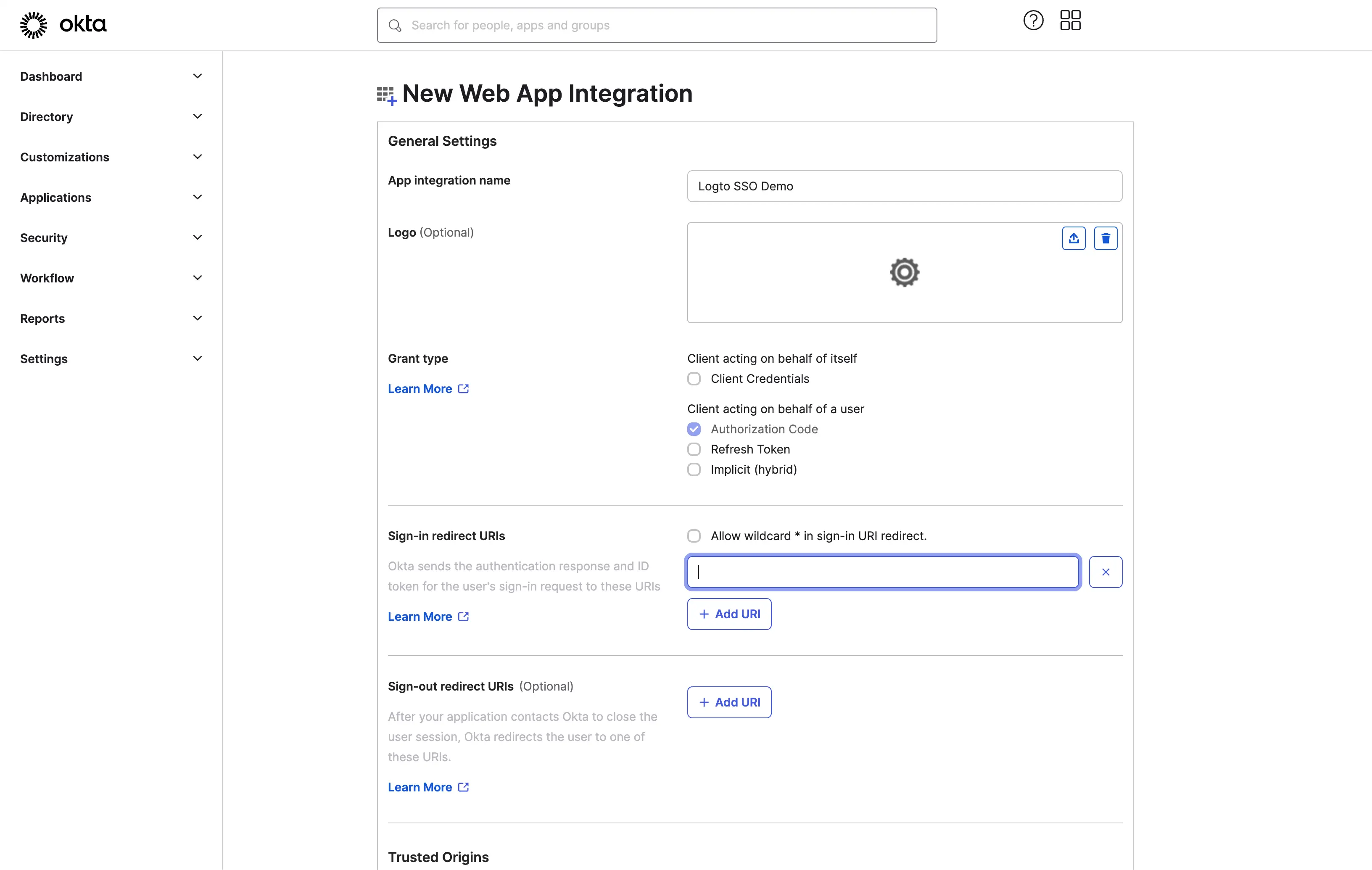
- Assign users to the application.
Based on the Assignments settings, you can choose to assign the application to all users or specific users/groups.
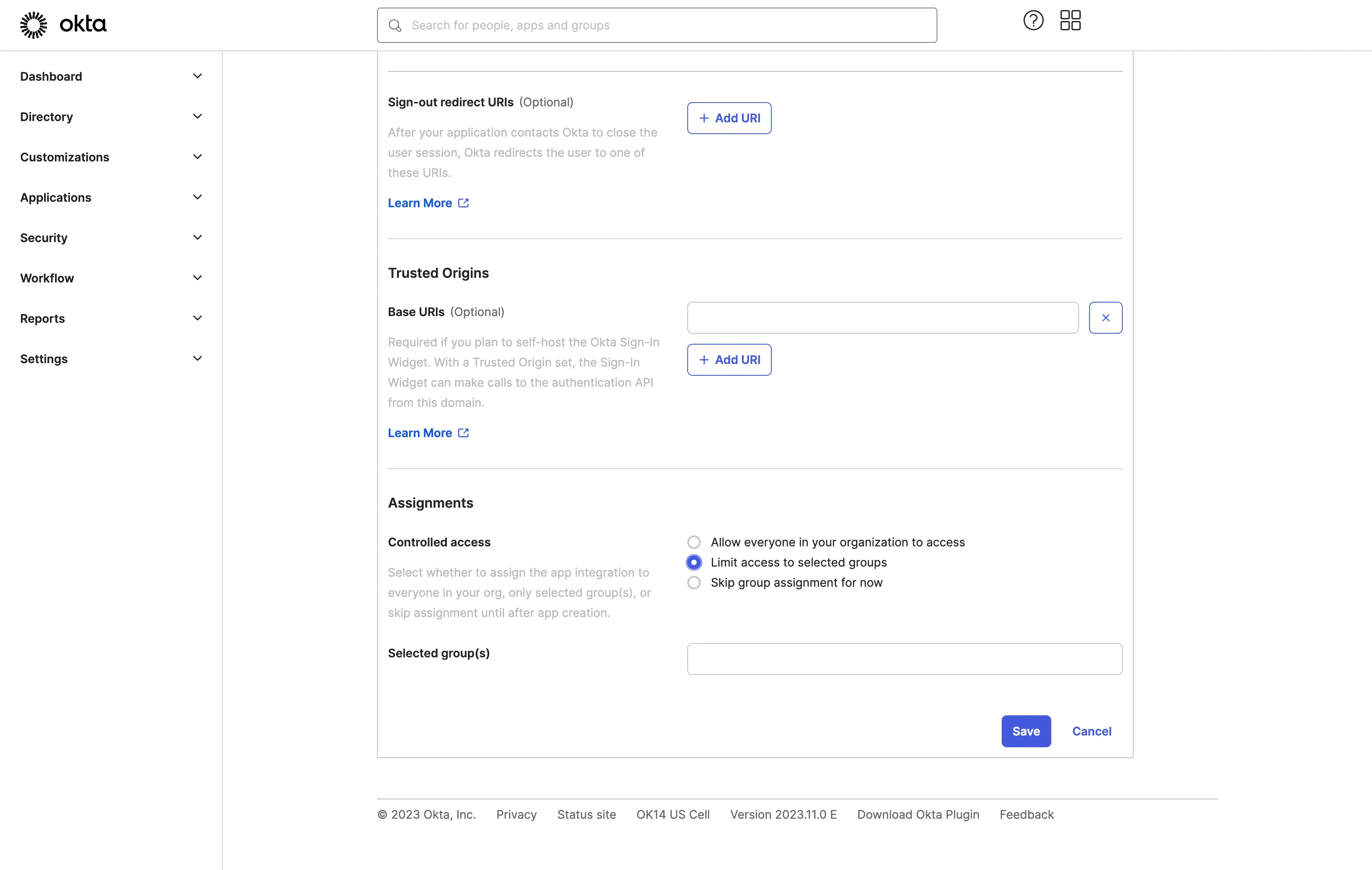
Click the Save button to save the application settings.
Step 3: Set up Logto connector with the client credentials
After successfully creating the OIDC application, you will be redirected to the application details page.
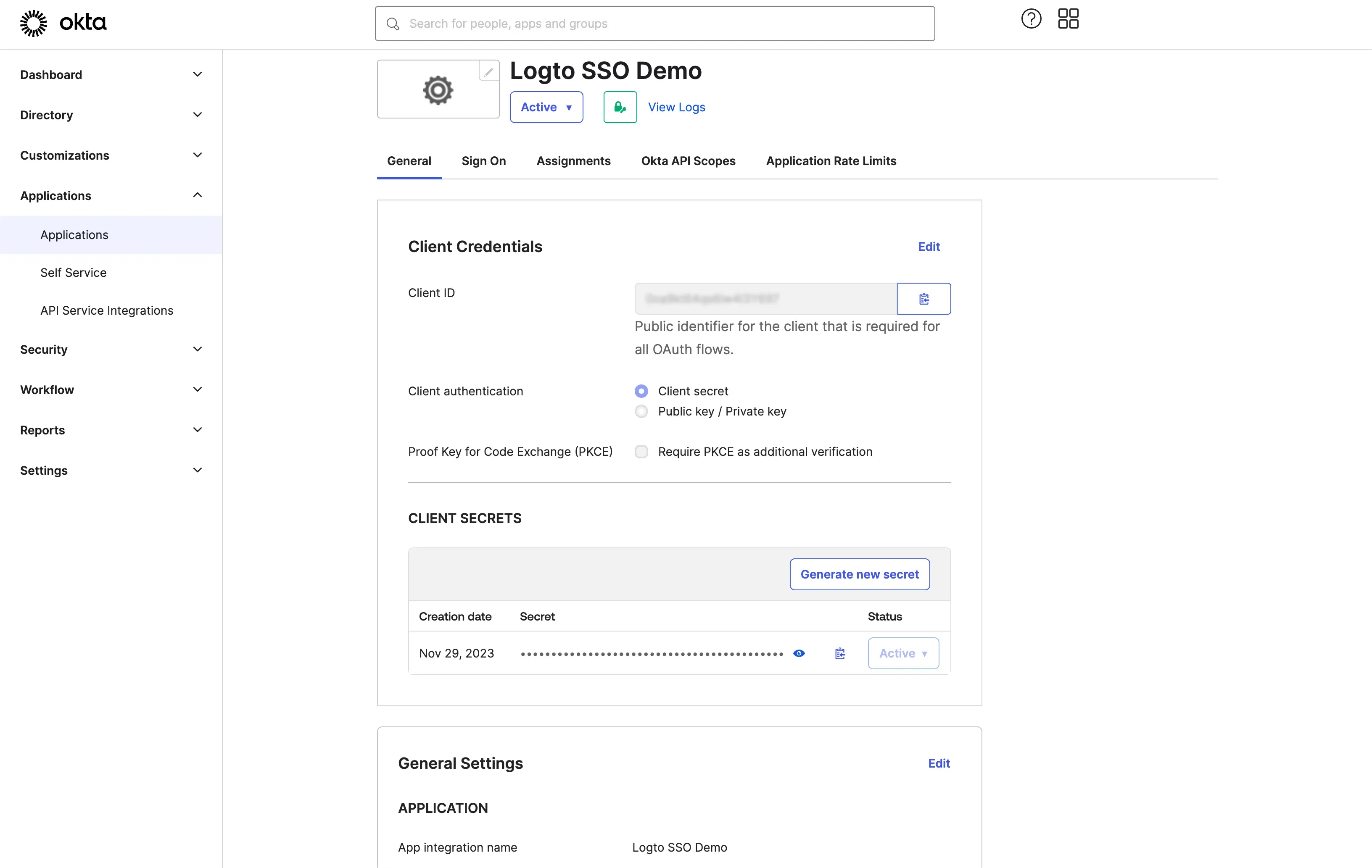
Copy the client ID and client secret and fill in the corresponding fields on the Logto SSO connector Connection tab.
Use your Okta domain as the issuer. Example: https://dev-12345678.okta.com. Once you have filled in all the fields, click the Save button to save the connector settings.
If the issuer link you provided is valid, you will see a parsed full list of Okta IdP configurations shown below the issuer field.
Step 4: Additional Scopes (Optional)
Use the Scope field to add additional scopes to your OAuth request. This will allow you to request more information from the Okta OAuth server. Please refer to the Okta documentation for more details about the available scopes.
Regardless of the custom scope settings, Logto will always send the openid, profile, and email scopes to the IdP. This is to ensure that Logto can retrieve the user's identity information and email address properly.
Step 5: Set email domains and enable the SSO connector
Provide the email domains of your organization on Logto’s connector SSO experience tab. This will enable the SSO connector as an authentication method for those users.
Users with email addresses in the specified domains will be redirected to use your SSO connector as their only authentication method.
For more details about creating OIDC integration with Okta, please check Create OIDC App Integrations.
Save your configuration
Double check you have filled out necessary values in the Logto connector configuration area. Click "Save and Done" (or "Save changes") and the Okta enterprise SSO connector should be available now.
Enable Okta enterprise SSO connector in Sign-in Experience
You don’t need to configure enterprise connectors individually, Logto simplifies SSO integration into your applications with just one click.
- Navigate to: Console > Sign-in experience > Sign-up and sign-in.
- Enable the "Enterprise SSO" toggle.
- Save changes.
Once enabled, a "Single Sign-On" button will appear on your sign-in page. Enterprise users with SSO-enabled email domains can access your services using their enterprise identity providers (IdPs).
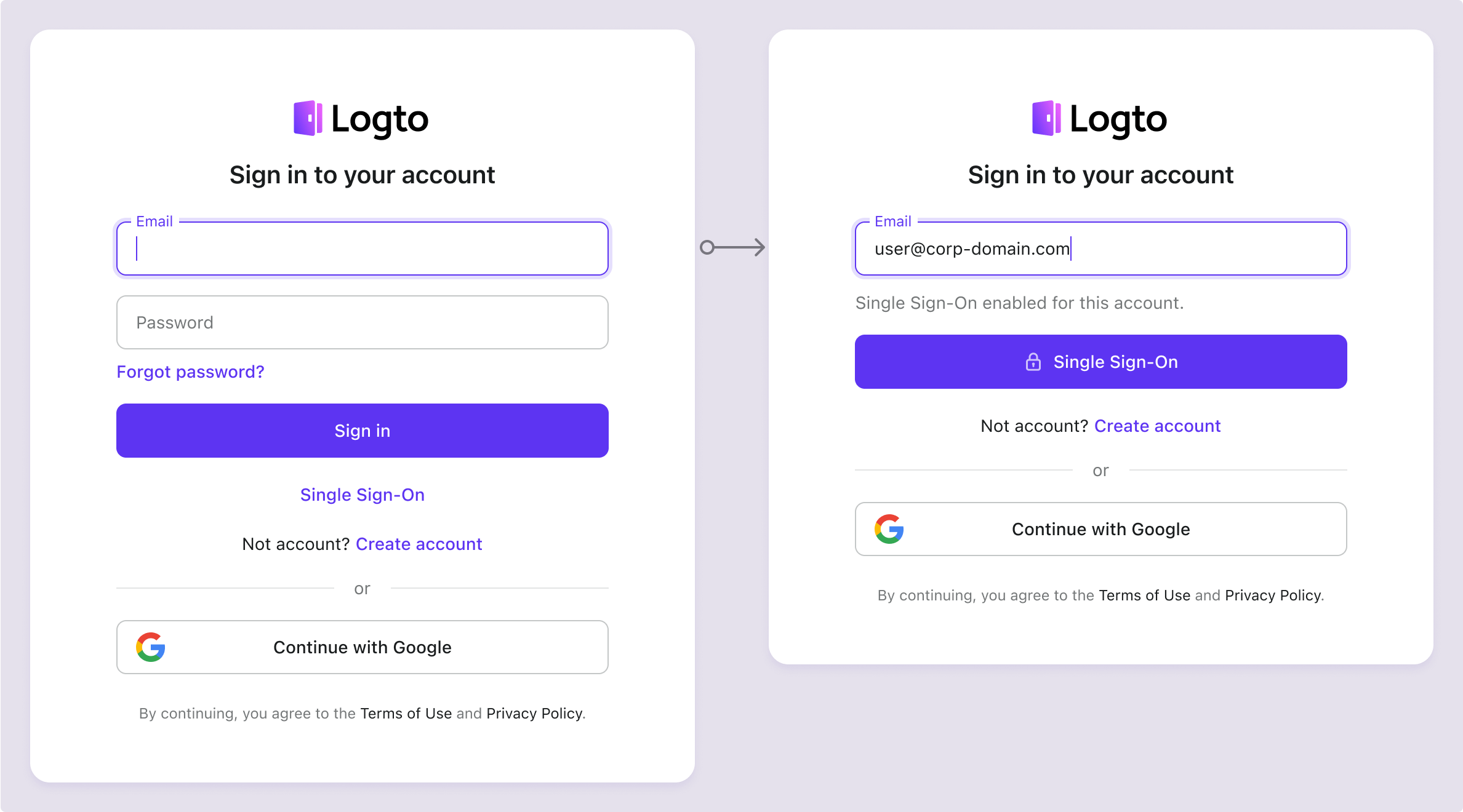
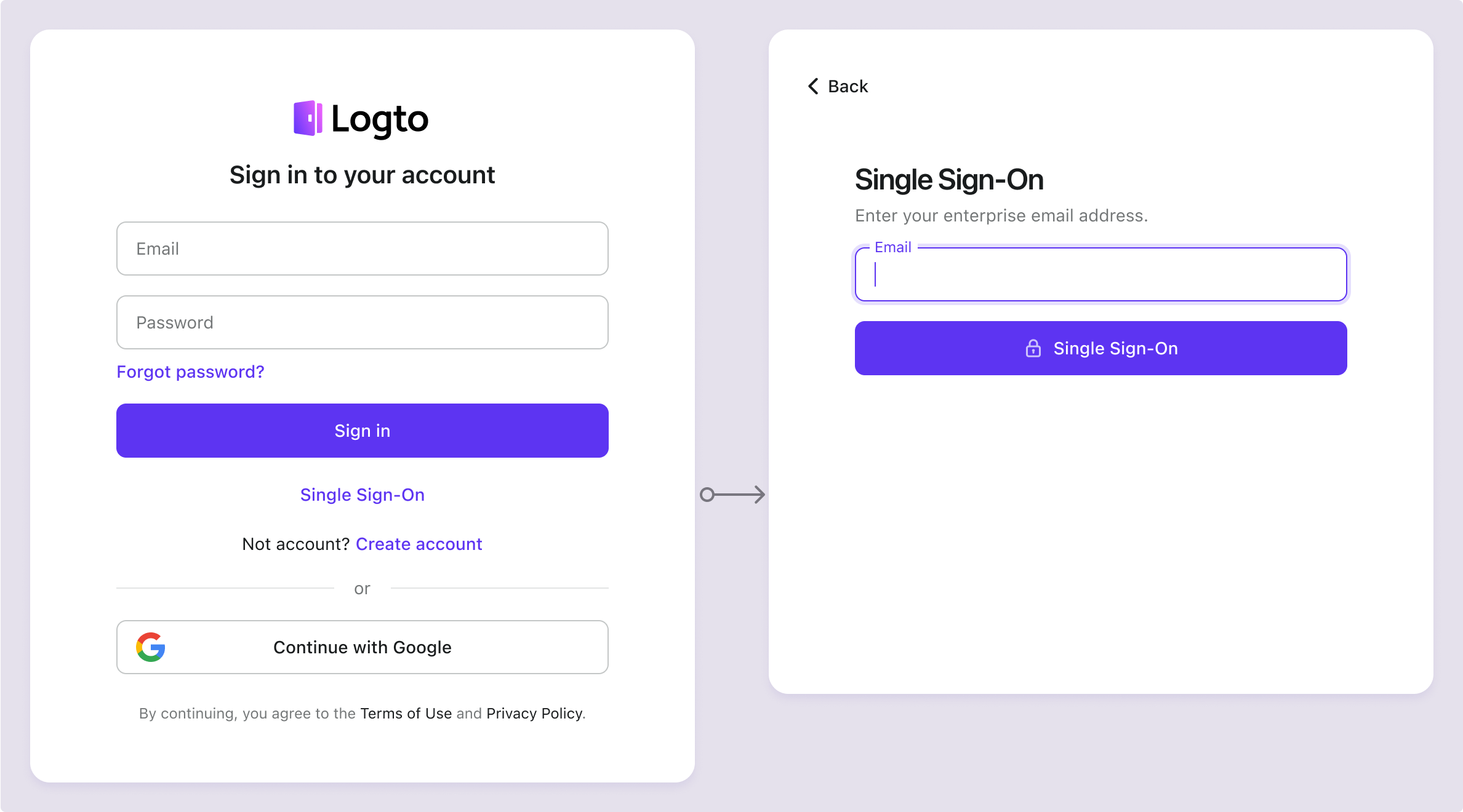
To learn more about the SSO user experience, including SP-initiated SSO and IdP-initiated SSO, refer to User flows: Enterprise SSO.
Testing and Validation
Return to your Java Spring Boot app. You should now be able to sign in with Okta enterprise SSO. Enjoy!
Further readings
End-user flows: Logto provides a out-of-the-box authentication flows including MFA and enterprise SSO, along with powerful APIs for flexible implementation of account settings, security verification, and multi-tenant experience.
Authorization: Authorization defines the actions a user can do or resources they can access after being authenticated. Explore how to protect your API for native and single-page applications and implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC).
Organizations: Particularly effective in multi-tenant SaaS and B2B apps, the organization feature enable tenant creation, member management, organization-level RBAC, and just-in-time-provisioning.
Customer IAM series Our serial blog posts about Customer (or Consumer) Identity and Access Management, from 101 to advanced topics and beyond.